Abstract
Rationale
Studies with mite allergens demonstrated that proteolytic activity augments allergic airway inflammation. This knowledge is limited to few enzyme allergens.
Objective
The objective of this study is to investigate the effect of serine protease Cur l 1 from Curvularia lunata in airway inflammation/hyper-responsiveness.
Methods
Cur l 1 was purified and inactivated using a serine protease inhibitor. Balb/c mice were sensitized with enzymatically active Cur l 1 or C. lunata extract. Sensitized mice were given booster dose on day 14 with active or inactivated Cur l 1. Intranasal challenge was given on day 28, 29, and 30. Airway hyper-responsiveness was measured by plethysmography. Blood, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), spleen, and lungs from mice were analyzed for cellular infiltration, immunoglobulins, and cytokine levels.
Results
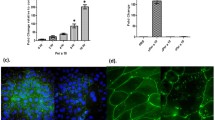
Mice challenged with enzymatically active Cur l 1 demonstrated significantly higher airway inflammation than inactive Cur l 1 group mice (p < 0.01). There was a significant difference in serum IgE and IgG1 levels among mice immunized with active Cur l 1 and inactive Cur l 1 (p < 0.01). IL-4 and IL-5 were higher in BALF and splenocyte culture supernatant of active Cur l 1 than inactive Cur l 1 mice. Lung histology revealed increased eosinophil infiltration, goblet cell hyperplasia and mucus secretion in active group.
Conclusion
Proteolytic activity of Cur l 1 plays an important role in airway inflammation and the inactivated Cur l 1 has potential to be explored for immunotherapy.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAEE:
-
α-benzoyl-l-arginine-ethyl ester hydrochloride
- BALF:
-
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- CBB:
-
Coomassie brilliant blue
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- EPO:
-
eosinophil peroxidase
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- HE:
-
hematoxylin–eosin
- HTAB:
-
hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
- MTT:
-
3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- OD:
-
optical density
- OPD:
-
o-phenylenediamine
- OVA:
-
ovalbumin
- PAR:
-
protease activated receptors
- PAS:
-
periodic acid-Schiff
- PHA:
-
phytohemagglutinin
- PMSF:
-
phenyl methyl sulphonyl fluoride
- RPMI:
-
Roswell Park Memorial Institute
References
Van Weel C, Bateman ED, Bousquet J, Reid J, Grouse L, Schermer T, et al. Asthma management pocket reference. Allergy 2008;63:997–1004. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01643.x.
Holgate ST. Pathogenesis of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 2008;38:872–97. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.02971.x.
Davies DE, Wicks J, Powell RM, Puddicombe SM, Holgate ST. Airway remodeling in asthma: new insights. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003;111:215–25. doi:10.1067/mai.2003.128.
Aalberse RC. Structural biology of allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000;106:228–38. doi:10.1067/mai.2000.108434.
Thomas WR, Smith WA, Hales BJ, Mills KL, O’Brien RM. Characterization and immunobiology of house dust mite allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2002;129:1–18. doi:10.1159/000065179.
Kurup VP, Shen HD, Vijay H. Immunobiology of fungal allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2002;129:181–8. doi:10.1159/000066780.
Shakib F, Schulz O, Sewell HF. A mite subversive: cleavage of CD23 and CD25 by Der p 1 enhances allergenicity. Immunol Today 1998;19:313–6. doi:10.1016/S0167-5699(98)01284-5.
Ghaemmaghami AM, Gough L, Sewell HF, Shakib F. The proteolytic activity of the major dust mite allergen Der p 1 conditions dendritic cells to produce less interleukin-12: allergen-induced Th2 bias determined at the dendritic cell level. Clin Exp Allergy 2002;32:1468–75. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2745.2002.01504.x.
Sehgal N, Custovic A, Woodcock A. Potential roles in rhinitis for protease and other enzymatic activities of allergens. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2005;5:221–6. doi:10.1007/s11882-005-0041-9.
Gough L, Schulz O, Sewell HF, Shakib F. The cysteine protease activity of the major dust mite allergen Der p 1 selectively enhances the immunoglobulin E antibody response. J Exp Med 1999;190:1897–902. doi:10.1084/jem.190.12.1897.
Gough L, Campbell E, Bayley D, Van Heeke G, Shakib F. Proteolytic activity of the house dust mite allergen Der p 1 enhances allergenicity in a mouse inhalation model. Clin Exp Allergy 2003;33:1159–63. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2222.2003.01716.x.
Tai HY, Tam MF, Chou H, Peng HJ, Su SN, Perng DW, et al. Pen ch 13 allergen induces secretion of mediators and degradation of occludin protein of human lung epithelial cells. Allergy 2006;61:382–8. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2005.00958.x.
Kurup VP, Xia JQ, Shen HD, Rickaby DA, Henderson JD Jr, Fink JN, et al. Alkaline serine proteinase from Aspergillus fumigatus has synergistic effects on Asp-f-2-induced immune response in mice. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2002;129:129–37. doi:10.1159/000065882.
Sun G, Stacey MA, Schmidt M, Mori L, Mattoli S. Interaction of mite allergens Der p 3 and Der p 9 with protease-activated receptor-2 expressed by lung epithelial cells. J Immunol 2001;167:1014–21.
Su NY, Yu CJ, Shen HD, Pan FM, Chow LP. Pen c 1, a novel enzymic allergen protein from Penicillium citrinum. Purification, characterization, cloning and expression. Eur J Biochem 1999;261:115–23. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00242.x.
Shen HD, Wang CW, Lin WL, Lai HY, Tam MF, Chou H, et al. cDNA cloning and immunologic characterization of Pen o 18, the vacuolar serine protease major allergen of Penicillium oxalicum. J Lab Clin Med 2001;137:115–24. doi:10.1067/mlc.2001.112096.
Bisht V, Arora N, Singh BP, Pasha S, Gaur SN, Sridhara S. Epi p 1, an allergenic glycoprotein of Epicoccum purpurascens is a serine protease. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2004;42:205–11. doi:10.1016/j.femsim.2004.05.003.
Sudha VT, Arora N, Gaur SN, Pasha S, Singh BP. Identification of a serine protease as a major allergen (Per a 10) of Periplaneta americana. Allergy 2008;63:768–76. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01602.x.
Gupta R, Singh BP, Sridhara S, Gaur SN, Chaudhary VK, Arora N. Allergens of Curvularia lunata during cultivation in different media. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1999;104:857–62. doi:10.1016/S0091-6749(99)70299-X.
Gupta R, Singh BP, Sridhara S, Gaur SN, Kumar R, Chaudhary VK, et al. Identification of cross-reactive proteins amongst different Curvularia species. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2002;127:38–46. doi:10.1159/000048167.
Gupta R, Sharma V, Sridhara S, Singh BP, Arora N. Identification of serine protease as a major allergen of Curvularia lunata. Allergy 2004;59:421–7. doi:10.1046/j.1398-9995.2003.00378.x.
Heussen C, Dowdle EB. Electrophoretic analysis of plasminogen activators in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and copolymerized substrates. Anal Biochem 1980;102:196–202. doi:10.1016/0003–2697(80)90338–3.
Hamelmann E, Schwarze J, Takeda K, Oshiba A, Larsen GL, Irvin CG, et al. Noninvasive measurement of airway responsiveness in allergic mice using barometric plethysmography. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997;156:766–75.
Schneider T, van Velzen D, Moqbel R, Issekutz AC. Kinetics and quantitation of eosinophil and neutrophil recruitment to allergic lung inflammation in a brown Norway rat model. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1997;17:702–12.
Cui T, Kusunose M, Hamada A, Ono M, Miyamura M, Yoshioka S, et al. Relationship between the eosinophilia of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and the severity of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 2003;26:959–63. doi:10.1248/bpb.26.959.
Inoue K, Takano H, Hiyoshi K, Ichinose T, Sadakane K, Yanagisawa R, et al. Naphthoquinone enhances antigen related airway inflammation in mice. Eur Respir J 2007;29:259–67. doi:10.1183/09031936.00033106.
Mehta AK, Gaur SN, Arora N, Singh BP. Effect of choline chloride in allergen-induced mouse model of airway inflammation. Eur Respir J 2007;30:662–71. doi:10.1183/09031936.00019307.
Smith PK, Harper JI. Serine proteases, their inhibitors and allergy. Allergy 2006;61:1441–7. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01233.x.
Schulz O, Laing P, Sewell HF, Shakib F. Der p I, a major allergen of the house dust mite, proteolytically cleaves the low-affinity receptor for human IgE (CD23). Eur J Immunol 1995;25:3191–4. doi:10.1002/eji.1830251131.
Ghaemmaghami AM, Robins A, Gough L, Sewell HF, Shakib F. Human T cell subset commitment determined by the intrinsic property of antigen: the proteolytic activity of the major mite allergen Der p 1 conditions T cells to produce more IL-4 and less IFN-gamma. Eur J Immunol 2001;31:1211–6. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200104)31:4<1211::AID-IMMU1211>3.0.CO;2-R.
Kauffman HF. Interaction of environmental allergens with airway epithelium as a key component of asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2003;3:101–8. doi:10.1007/s11882-003-0021-x.
Ebeling C, Forsythe P, Ng J, Gordon JR, Hollenberg M, Vliagoftis H. Proteinase-activated receptor 2 activation in the airways enhances antigen-mediated airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness through different pathways. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;115:623–30. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2004.11.042.
Herbert CA, King CM, Ring PC, Holgate ST, Stewart GA, Thompson PJ, et al. Augmentation of permeability in the bronchial epithelium by the house dust mite allergen Der p1. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1995;12:369–78.
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (Prabhanshu Tripathi) is a ‘Senior Research Fellow’ from Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Delhi. The authors are thankful to CSIR task force project for financial support to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, P., Kukreja, N., Singh, B.P. et al. Serine Protease Activity of Cur l 1 from Curvularia lunata Augments Th2 Response in Mice. J Clin Immunol 29, 292–302 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-008-9261-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-008-9261-9