Abstract
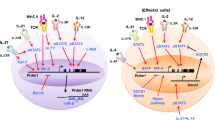
The body tends to maintain a relatively constant number of peripheral T cells, a phenomenon termed T cell homeostasis. Homeostasis is controlled by the coordinated activity of extrinsic regulation, most notably through cytokines of the common gamma chain (cγC) family and intrinsic regulation by transcription factors. Whereas the former mechanism has been extensively studied and is relatively well characterized, the transcription factors that govern the homeostasis of late-stage effector and memory T cells have been less well defined but include regulators such as T-bet, Eomes, Bcl6, and Id2. The transcriptional repressor, Blimp-1 is well known as a master regulator of the terminal differentiation of B cells into antibody secreting plasma cells. Recent experiments have now revealed that Blimp-1 is also a key regulator of T cell differentiation. Blimp-1 is expressed in differentiated effector T cells and controls their homeostasis. Interestingly, Blimp-1 expression is controlled by the same cγC cytokines that regulate T cell homeostasis suggesting a direct link between the extrinsic and intrinsic arms of the process.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams MA, Bevan MJ. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol 2007;25:171–92.
Sprent J, Surh CD. T cell memory. Annu Rev Immunol 2002;20:551–79.
Seder RA, Ahmed R. Similarities and differences in CD4+ and CD8+ effector and memory T cell generation. Nat Immunol 2003;4:835–42.
Sprent J, Surh CD. Cytokines and T cell homeostasis. Immunol Lett 2003;85:145–49.
Jameson SC. Maintaining the norm: T-cell homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol 2002;2:547–56.
Chambers CA, Sullivan TJ, Allison JP. Lymphoproliferation in CTLA-4-deficient mice is mediated by costimulation-dependent activation of CD4+ T cells. Immunity 1997;7:885–95.
Gorelik L, Flavell RA. Transforming growth factor-beta in T-cell biology. Nat Rev Immunol 2002;2:46–53.
Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang DC, Tarlinton DM, Kay TW, Kontgen F, et al. Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 1999;286:1735–738.
Nagata S. Fas ligand-induced apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet 1999;33:29–55.
Lohr J, Knoechel B, Nagabhushanam V, Abbas AK. T-cell tolerance and autoimmunity to systemic and tissue-restricted self-antigens. Immunol Rev 2005;204:116–27.
Sakaguchi S, Powrie F. Emerging challenges in regulatory T cell function and biology. Science 2007;317:627–29.
Boyman O, Purton JF, Surh CD, Sprent J. Cytokines and T-cell homeostasis. Curr Opin Immunol 2007;19:320–26.
Glimcher LH, Townsend MJ, Sullivan BM, Lord GM. Recent developments in the transcriptional regulation of cytolytic effector cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2004;4:900–11.
Pearce EL, Mullen AC, Martins GA, Krawczyk CM, Hutchins AS, Zediak VP, et al. Control of effector CD8+ T cell function by the transcription factor Eomesodermin. Science 2003;302:1041–3.
Cannarile MA, Lind NA, Rivera R, Sheridan AD, Camfield KA, Wu BB, et al. Transcriptional regulator Id2 mediates CD8+ T cell immunity. Nat Immunol 2006;7:1317–325.
Ichii H, Sakamoto A, Hatano M, Okada S, Toyama H, Taki S, et al. Role for Bcl-6 in the generation and maintenance of memory CD8+ T cells. Nat Immunol 2002;3:558–63.
Kallies A, Hawkins ED, Belz GT, Metcalf D, Hommel M, Corcoran LM, et al. Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 is essential for T cell homeostasis and self-tolerance. Nat Immunol 2006;7:466–74.
Martins GA, Cimmino L, Shapiro-Shelef M, Szabolcs M, Herron A, Magnusdottir E, et al. Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 regulates T cell homeostasis and function. Nat Immunol 2006;7:457–65.
Kallies A, Nutt SL. Terminal differentiation of lymphocytes depends on Blimp-1. Curr Opin Immunol 2007;19:156–62.
Angelin-Duclos C, Cattoretti G, Lin KI, Calame K. Commitment of B lymphocytes to a plasma cell fate is associated with Blimp-1 expression in vivo. J Immunol 2000;165:5462–71.
Kallies A, Hasbold J, Tarlinton DM, Dietrich W, Corcoran LM, Hodgkin PD, et al. Plasma cell ontogeny defined by quantitative changes in blimp-1 expression. J exp med 2004;200:967–77.
Turner CA Jr., Mack DH, Davis MM. Blimp-1, a novel zinc finger-containing protein that can drive the maturation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Cell 1994;77:297–306.
Shapiro-Shelef M, Lin KI, McHeyzer-Williams LJ, Liao J, McHeyzer-Williams MG, Calame K. Blimp-1 is required for the formation of immunoglobulin secreting plasma cells and pre-plasma memory B cells. Immunity 2003;19:607–20.
Ohinata Y, Payer B, O’Carroll D, Ancelin K, Ono Y, Sano M, et al. Blimp1 is a critical determinant of the germ cell lineage in mice. Nature 2005;436:207–13.
Magnusdottir E, Kalachikov S, Mizukoshi K, Savitsky D, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Panteleyev AA, Calame K. Epidermal terminal differentiation depends on B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:14988–93.
Horsley V, O’Carroll D, Tooze R, Ohinata Y, Saitou M, Obukhanych T, et al. Blimp1 defines a progenitor population that governs cellular input to the sebaceous gland. Cell 2006;126:597–609.
Baxendale S, Davison C, Muxworthy C, Wolff C, Ingham PW, Roy S. The B-cell maturation factor Blimp-1 specifies vertebrate slow-twitch muscle fiber identity in response to Hedgehog signaling. Nat Genet 2004;36:88–93.
Lee BC, Roy S. Blimp-1 is an essential component of the genetic program controlling development of the pectoral limb bud. Dev Biol 2006;300:623–34.
Yu J, Angelin-Duclos C, Greenwood J, Liao J, Calame K. Transcriptional repression by blimp-1 (PRDI-BF1) involves recruitment of histone deacetylase. Mol Cell Biol 2000;20:2592–603.
Ancelin K, Lange UC, Hajkova P, Schneider R, Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T, et al. Blimp1 associates with Prmt5 and directs histone arginine methylation in mouse germ cells. Nat Cell Biol 2006;8:623–30.
Gyory I, Wu J, Fejer G, Seto E, Wright KL. PRDI-BF1 recruits the histone H3 methyltransferase G9a in transcriptional silencing. Nat Immunol 2004;5:299–308.
Ren B, Chee KJ, Kim TH, Maniatis T. PRDI-BF1/Blimp-1 repression is mediated by corepressors of the Groucho family of proteins. Genes Dev 1999;13:125–37.
Savitsky D, Calame K. B-1 B lymphocytes require Blimp-1 for immunoglobulin secretion. J exp med 2006;203:2305–14.
Kallies A, Hasbold J, Fairfax K, Pridans C, Emslie D, McKenzie BS, et al. Initiation of plasma-cell differentiation is independent of the transcription factor Blimp-1. Immunity 2007;26:555–66.
Shapiro-Shelef M, Lin KI, Savitsky D, Liao J, Calame K. Blimp-1 is required for maintenance of long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow. J Exp Med 2005;202:1471–6.
Gong D, Malek TR. Cytokine-dependent Blimp-1 expression in activated T cells inhibits IL-2 production. J Immunol 2007;178:242–52.
Santer-Nanan B, Berberich-Siebelt F, Xiao Z, Poser N, Sennefelder H, Rauthe S, et al. Blimp-1 is expressed in human and mouse T cell subsets and leads to loss of IL-2 production and to defective proliferation. Signal Transduction 2006;6:268–79.
Lin KI, Lin Y, Calame K. Repression of c-myc is necessary but not sufficient for terminal differentiation of B lymphocytes in vitro. Mol Cell Biol 2000;20:8684–95.
Keller AD, Maniatis T. Identification and characterization of a novel repressor of beta-interferon gene expression. Genes Dev 1991;5:868–79.
Zeng R, Spolski R, Finkelstein SE, Oh S, Kovanen PE, Hinrichs CS, et al. Synergy of IL-21 and IL-15 in regulating CD8+ T cell expansion and function. J exp med 2005;201:139–48.
Kieper WC, Prlic M, Schmidt CS, Mescher MF, Jameson SC. Il-12 enhances CD8 T cell homeostatic expansion. J Immunol 2001;166:5515–21.
Chang J, Cho JH, Lee SW, Choi SY, Ha SJ, Sung YC. IL-12 priming during in vitro antigenic stimulation changes properties of CD8 T cells and increases generation of effector and memory cells. J Immunol 2004;172:2818–26.
Whitmire JK, Benning N, Whitton JL. Cutting edge: early IFN-gamma signaling directly enhances primary antiviral CD4+ T cell responses. J Immunol 2005;175:5624–28.
Kolumam GA, Thomas S, Thompson LJ, Sprent J, Murali-Krishna K. Type I interferons act directly on CD8 T cells to allow clonal expansion and memory formation in response to viral infection. J exp med 2005;202:637–50.
Surh CD, Boyman O, Purton JF, Sprent J. Homeostasis of memory T cells. Immunol Rev 2006;211:154–63.
Joshi NS, Cui W, Chandele A, Lee HK, Urso DR, Hagman J, et al. Inflammation directs memory precursor and short-lived effector CD8(+) T cell fates via the graded expression of T-bet transcription factor. Immunity 2007;27:281–95.
Intlekofer AM, Takemoto N, Kao C, Banerjee A, Schambach F, Northrop JK, et al. Requirement for T-bet in the aberrant differentiation of unhelped memory CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med 2007;204:2015–21.
Intlekofer AM, Takemoto N, Wherry EJ, Longworth SA, Northrup JT, Palanivel VR, et al. Effector and memory CD8+ T cell fate coupled by T-bet and eomesodermin. Nat Immunol 2005;6:1236–44.
Min B, Yamane H, Hu-Li J, Paul WE. Spontaneous and homeostatic proliferation of CD4 T cells are regulated by different mechanisms. J Immunol 2005;174:6039–44.
Lenz DC, Kurz SK, Lemmens E, Schoenberger SP, Sprent J, Oldstone MB, et al. IL-7 regulates basal homeostatic proliferation of antiviral CD4+ T cell memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004;101:9357–62.
Zheng Y, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 in control of the regulatory T cell lineage. Nat Immunol 2007;8:457–62.
Williams MA, Tyznik AJ, Bevan MJ. Interleukin-2 signals during priming are required for secondary expansion of CD8+ memory T cells. Nature 2006;441:890–3.
Boyman O, Kovar M, Rubinstein MP, Surh CD, Sprent J. Selective stimulation of T cell subsets with antibody-cytokine immune complexes. Science 2006;311:1924–7.
Cho JH, Boyman O, Kim HO, Hahm B, Rubinstein MP, Ramsey C, et al. An intense form of homeostatic proliferation of naive CD8+ cells driven by IL-2. J exp med 2007;204:1787–801.
Kamimura D, Bevan MJ. Naive CD8+ T cells differentiate into protective memory-like cells after IL-2 anti IL-2 complex treatment in vivo. J exp med 2007;204:1803–12.
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 2006;126:1121–33.
Lohoff M, Mittrucker HW, Prechtl S, Bischof S, Sommer F, Kock S, et al. Dysregulated T helper cell differentiation in the absence of interferon regulatory factor 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99:11808–12.
Brustle A, Heink S, Huber M, Rosenplanter C, Stadelmann C, Yu P, et al. The development of inflammatory T(H)-17 cells requires interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nat Immunol 2007;8:958–66.
Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG, Glimcher LH. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell 2000;100:655–69.
Szabo SJ, Sullivan BM, Peng SL, Glimcher LH. Molecular mechanisms regulating Th1 immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 2003;21:713–58.
Sullivan BM, Juedes A, Szabo SJ, von Herrath M, Glimcher LH. Antigen-driven effector CD8 T cell function regulated by T-bet. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:15818–23.
Juedes AE, Rodrigo E, Togher L, Glimcher LH, von Herrath MG. T-bet controls autoaggressive CD8 lymphocyte responses in type 1 diabetes. J Exp Med 2004;199:1153–62.
Way SS, Wilson CB. Cutting edge: immunity and IFN-gamma production during Listeria monocytogenes infection in the absence of T-bet. J Immunol 2004;173:5918–22.
Tamura T, Tailor P, Yamaoka K, Kong HJ, Tsujimura H, O'Shea JJ, et al. IFN regulatory factor-4 and -8 govern dendritic cell subset development and their functional diversity. J Immunol 2005;174:2573–81.
Suto A, Wurster AL, Reiner SL, Grusby MJ. IL-21 inhibits IFN-gamma production in developing Th1 cells through the repression of Eomesodermin expression. J Immunol 2006;177:3721–7.
Quong MW, Romanow WJ, Murre C. E protein function in lymphocyte development. Annu Rev Immunol 2002;20:301–22.
Yokota Y, Mansouri A, Mori S, Sugawara S, Adachi S, Nishikawa S, et al. Development of peripheral lymphoid organs and natural killer cells depends on the helix-loop-helix inhibitor Id2. Nature 1999;397:702–6.
Hacker C, Kirsch RD, Ju XS, Hieronymus T, Gust TC, Kuhl C, et al. Transcriptional profiling identifies Id2 function in dendritic cell development. Nat Immunol 2003;4:380–6.
Boos MD, Yokota Y, Eberl G, Kee BL. Mature natural killer cell and lymphoid tissue-inducing cell development requires Id2-mediated suppression of E protein activity. J exp med 2007;204:1119–30.
Ouyang W, Lohning M, Gao Z, Assenmacher M, Ranganath S, Radbruch A, et al. Stat6-independent GATA-3 autoactivation directs IL-4-independent Th2 development and commitment. Immunity 2000;12:27–37.
Ouyang W, Ranganath SH, Weindel K, Bhattacharya D, Murphy TL, Sha WC, et al. Inhibition of Th1 development mediated by GATA-3 through an IL-4-independent mechanism. Immunity 1998;9:745–55.
Zhu J, Min B, Hu-Li J, Watson CJ, Grinberg A, Wang Q, et al. Conditional deletion of Gata3 shows its essential function in T(H)1-T(H)2 responses. Nat Immunol 2004;5:1157–65.
Yamashita M, Ukai-Tadenuma M, Miyamoto T, Sugaya K, Hosokawa H, Hasegawa A, et al. Essential role of GATA3 for the maintenance of type 2 helper T (Th2) cytokine production and chromatin remodeling at the Th2 cytokine gene loci. J Biol Chem 2004;279:26983–90.
Yamashita M, Hirahara K, Shinnakasu R, Hosokawa H, Norikane S, Kimura MY, et al. Crucial role of MLL for the maintenance of memory T helper type 2 cell responses. Immunity 2006;24:611–22.
Ono R, Nosaka T, Hayashi Y. Roles of a trithorax group gene, MLL, in hematopoiesis. Int J Hematol 2005;81:288–93.
Shapiro-Shelef M, Calame K. Regulation of plasma-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol 2005;5:230–42.
Ichii H, Sakamoto A, Kuroda Y, Tokuhisa T. Bcl6 acts as an amplifier for the generation and proliferative capacity of central memory CD8+ T cells. J Immunol 2004;173:883–91.
Manders PM, Hunter PJ, Telaranta AI, Carr JM, Marshall JL, Carrasco M, et al. BCL6b mediates the enhanced magnitude of the secondary response of memory CD8+ T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:7418–25.
Ichii H, Sakamoto A, Arima M, Hatano M, Kuroda Y, Tokuhisa T. Bcl6 is essential for the generation of long-term memory CD4+ T cells. Int Immunol 2007;19:427–33.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Pfizer Australia Research Fellowship (S.L.N.), the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (A.K.), The Wellcome Trust (G.T.B), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (G.T.B), and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nutt, S.L., Kallies, A. & Belz, G.T. Blimp-1 Connects the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Regulation of T Cell Homeostasis. J Clin Immunol 28, 97–106 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9151-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9151-6