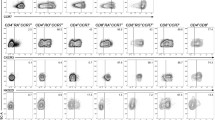
In this investigation, we have examined the relative sensitivity of human naïve, central memory (TCM), and two types of effector memory CD8+ T cells (TEM and TEMRA) to TNF-α-induced apoptosis. Our data show that naïve and TCM CD8+ T cells were sensitive, whereas TEM and TEMRA CD8+ T cells were relatively resistant to TNF-a-induced apoptosis. The apoptosis profile correlated with the activation of caspase-8 and caspase-3. However, no correlation was observed between relative sensitivity of four CD8 + T cell subsets to apoptosis and the expression of TNFR-I or TNFR-II. TEM and TEMRA CD8+ T cells displayed increased phosphorylation of IKKα/β and IκB and increased NF-κB activity as compared to naïve and TCM CD8+ T cells. Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and FLIPL expression was higher and Bax expression was lower in TEM and TEMRA CD8+ T cells as compared to naïve and TCM CD8+ T cells. These data suggest that signaling molecules downstream of TNFRs may be responsible for differential sensitivity among subsets of CD8+ T cells to TNF-α-induced apoptosis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IAPs:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis proteins
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
- TNFR-I and TNFR-II:
-
tumor necrosis factor I and II
- TCM :
-
central memory T cells
- TEM :
-
effector memory T cells
- TEMRA :
-
effector memory CD45RA+ T cells
- TRAF2:
-
TNFR-associated factor 2
REFERENCES
Sallusto F, Geginat J, Lanzavecchia A: Central memory and effector memory T cell subsets: Function, generation, and maintenance. Ann Rev Immunol 22:745–763, 2004
Moser B, Loetscher P: Lymphocyte traffic control by chemokines. Nature Immunol 2:123–128, 2001
Schluns KS, Lefrancois L: Cytokine control of memory T-cell development and survival. Nature Rev Immunol 3:269–279, 2003
Arbones SL, Ord DC, Ley K, Ratech H, Maynard-Curry C, Otten G, Capon DJ, Tedder TF: Lymphocyte homing and leukocyte rolling and migration are impaired in L-selectin-deficienct mice. Immunity 1:247–260, 1994
Campbell JJ, Bowman EP, Murphy K, Youngman KR, Siani MA, Thompson DA, Wu L, Zlotnik A, Butcher EC: 6-C-kine (SLC), a lymphocyte adhesion-triggering chemokine expressed by high endothelium, is an agonist for MIP-13β receptor (CCR7). J Biol Chem 414:1053–1059, 1998
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Forster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A: Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature 401:708–712, 1999
Kataoka T, Budd RC, Holler N, Thome M, Martinon F, Irmler M, Burns K, Masopust D, Vezys V, Marzo AL, Lanzavecchia A: Preferential localization of effector memory cells in nonlymphoid tissue. Science 291:2413–2417, 2001
Weninger W, Crowley MA, Manjunath N, von Andriane UH: Migratory properties of naïve, effector, and memory CD8 (+) T cells. J Exp Med 194:953–966, 2001
Tomiyama H, Matsuda T, Takiguchi M: Differentiation of CD8+ T cells from a memory to memory/effector phenotype. J Immunol 168:5538–5550, 2002
Waring P, Kos FJ, Mullbacher A: Apoptosis or programmed cell death. Med Res Rev 11:219–236, 1991
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776, 2000
Krammer PH: CD95's deadly mission in the immune system. Nature 407:789–795, 2000
Green DR, Evan GI: A matter of life and death. Cancer Cell 1:19–30, 2002
Gupta S: Molecular steps of TNF receptor-mediated apoptosis. Curr Mol Med 1:299–306, 2002
Gupta S: A decision between life and death during TNF-α-induced signaling. J Clin Immunol 22:270–278, 2002
Rath PC, Aggarwal BB: TNF-induced signaling in apoptosis. J Clin Immunol 19:350–364, 1999
Wajant H, Pfizenmaieer K, Scheurich P: Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ 10:45–65, 2003
Ghosh S, Karin M: Missing pieces in the NF-kB puzzle. Cell 109:S81–S96, 2002
Karin M, Lin A: NF-κB at the crossroads of life and death. Nature Immunol 3:221–227, 2002
Beg AA, Baltimore D: An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF-α-induced cell death. Science 274:782–784, 1996
Li Q, Verma IM: NF-kB regulation in the immune system. Nature Rev Immunol 2:725–734, 2002
Gupta S, Bi R, Su K, Yel L, Chiplunkar S, Gollapudi S: Characterization of naïve, memory, and effector CD8+ T cells: Effect of age. Exp Gerontol 39:545–550, 2004
Mora A, Corn RA, Stanik AK, Goenka S, Aronika M, Stanley S, Ballard DW, Joyce S, Boothby M: Antiapoptotic function of NF-κB in T lymphocytes is influenced by their differentiation status: Roles of Fas, c-FLIP, and Bcl-xL. Cell Death Diff 10:1032–1044, 2003
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS, Jr: NF-κB anti-apoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and cIAP1 and cIAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 281:1680–1683, 1998
Tamatan M, Che WH, Matsuzaki H, Ogawa S, Okado H, Miyake S, Mizuno T, Tohyama M: Tumor necrosis factor-induces Bcl-2 and Bcl-x expression through NF-κB activation in primary hippocampus neurons. J Biol Chem 274:8531–8538, 1999
Bentires-Alj M, Dejardin E, Viatour P, Van Lint C, Froesch B, Reed JC, Merville MP, Bours V: Inhibition of the NF-kappa B transcription factor increases Bax expression in cancer cell lines. Oncogene 20:2805–2813, 2001
Thome M, Tschopp J: Regulation of lymphocyte proliferation and death by FLIP. Nature Rev Immunol 1:50–58, 2001
Muppidi JR, Tschopp J, Siegel RM: Life and death decisions: Secondary complexes and lipid rafts in TNF receptor family signal transduction. Immunity 21:461–465, 2004
Pimental-Muinos FX, Seed B: Regulated commitment of TNF receptor signaling: A molecular switch for death or activation. Immunity 18:3034–3043, 1999
Declercz W, Denecker G, Fiers W, Vandenabeele P: Cooperation of both TNF receptors in inducing apoptosis: Involvement of the TNF receptor-associated factor binding domain of the TNF receptor 75. J Immunol 161:390–399, 1998
Haridas V, Darnay BG, Natrajan K, Helle R, Aggarwal BB: Overexpression of the p80 TNFR leads to TNF-dependent apoptosis, nuclear factor-kappa B activation. J Immunol 160:3152–3162, 1998
Weiss T, Grell M, Siekienski K, Muhlenbeck F, Durkop H, Pfizenmaier K, Scheurich P, Wajant H: TNFR80-dependent enhancement of TNFR60-induced cell death is mediated by TNFR-associated factor 2 and is specific for TNFR60. J Immunol 161:3136–3142, 1998
Chen FK, Lenardo MJ: A crucial role for p80 TNF-R2 in amplifying p60 TNF-R1 apoptosis signals in T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 30:652–660, 2002
Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Vanhaesebroeck B, Grooten J, Fiers W: Both TNF receptors are required for TNF-mediated induction of apoptosis in PC60 cells. J Immunol 154:2904–2913, 1995
Tartaglia L, Pennica D, Godde DVL: Ligand passing: The 75-kDa tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor recruits TNF for signaling by the p55-kDa TNF receptor. J Biol Chem 268:18542–18548, 1993
Devin A, Cook A, Lin Y, Rodriguez Y, Kelliher M, Liu Z-G: The distinct role of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK activation by TNFR1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP mediates IKK activation. Immunity 12:419–429, 2000
Kelliher MA, Grimm S, Ishida Y, Kuo F, Stanger BZ, Leader P: The death domain kinase RIP mediates the TNF-induced NF-κB signal. Immunity 8:297–303, 1998
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopolous K, Tschopp J: NF-κB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol Cell Biol 21:5299–5305, 2001
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schnieder P, Hoffmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer J-L, Schroter M, Burns K, Mattmann C, Rimoldi D, French LE, Tschopp J: Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 388:190–195, 1997
MIcheau O, Tschopp J: Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114:181–190, 2003
Kataoka T, Budd RC, Holler N, Thome M, Martinon F, Irmler M, Burns K, Hahne M, Kennedy N, Koacsovics M, Tschopp J: The caspase inhibitor FLIP promotes activation of NF-κB and ERK signaling pathways. Curr Biol 10:640–648, 2000
Dohrman A, Kataoka T, Cuenin S, Russell RQ, Tschopp J, Budd RC: Cellular FLIP (long form) regulates CD8+ T cells activation through caspase-8-dependent NF-κB activation. J Immunol 174:5270–5278, 2005
Li H, Zhu H, Xu C, Yuan J: Cleavage of Bid by caspase-8 mediates mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94:491–501, 1998
Zhang N, He Y-W: The anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL is dispensable for the development of effector and memory T lymphocytes. J Immunol 174:6967–6973, 2005
Sprent J: Turnovere of memory phenotype CD8+ T cells. Microbes Infect 5:227–231, 2003
Wherry EJ, Teichgraber V, Becker TC, Masopust D, Kaech SM, Antia R, von Andrian UH, Ahmed R: Lineage relationship and protective immunity of memory CD8+ T cell subsets. Nature Immunol 4:225–234, 2003
Monteiro J, Baltiwala F, Ostere H, Gregersen PK: Shortened telomere in clonally expanded CD28−CD8+ T cells imply a replicative history that is distinct from there CD28+CD8+ counterparts. J Immunol 156:3587–3590, 1996
Alpdogan O, van den Brink MRM: IL-7 and IL-15: Therapeutic cytokines for immunodeficiency. Trends Immunol 26:56–64, 2005
Berard M, Brandt K, Bulfone-Paus S,Tough DF: IL-15 promotes the survival of naive and memory phenotype CD8+ T cells. J Immunol 171:5018–5026, 2003
Petrovas C, Mueller YM, Dimitriou ID, Bojczuk PM, Mounzer KC, Witek J, Altman JD, Katsikis PD: HIV-specific CD8+ T cells exhibit markedly reduced levels of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. J Immunol 172:4444–4453, 2004
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported in part by USPHS grant AG18313.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Su, H., Bi, R. et al. Differential Sensitivity of Naïve and Memory Subsets of Human CD8+ T Cells to TNF-α-Induced Apoptosis. J Clin Immunol 26, 193–203 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9019-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9019-1