Abstract
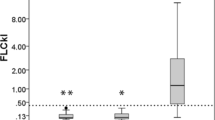
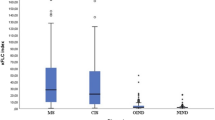
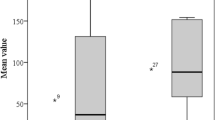
Oligoclonal free light chains (FLC) banding has been described in multiple sclerosis (MS) and should be correlated with disease activity. However, discrepancies between studies have been reported because of differences in methods. A new quantitative, rapid, and automated method using nephelometry is now available. Our objective was to investigate the interest of this method for the diagnosis and prognosis of MS. For this purpose, FLC index was determined in paired samples of CSF and serum from consecutive and unselected patients from the same department of neurology. We enrolled 89 patients (33 MS, 15 “possible MS”, and 41 controls) and correlated with IgG index, IgG oligoclonal banding, and clinical MS progression criteria. The main results were (1) FLC kappa index was more sensitive but less specific than IgG index for the diagnosis of MS, (2) two MS patients were negative for oligoclonal banding but exhibited a positive kappa index, (3) no relation between FLC kappa indices, MS clinical criteria, and disease progression was found. In conclusion, FLC kappa index should be considered as a useful complementary test for MS diagnosis. Its pronostic interest remains to be determined on a larger cohort of possible MS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FLC:
-
free light chains; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; MS, multiple sclerosis; EDSS, expanded disability status scale; Ig, immunoglobulin; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CISSMS, clinical isolated syndrome suggestive of MS; IEF, isoelectric focusing; CNS, central nervous system.
References
Tibbling GLH, Ohman S: Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37:385–390, 1977
Andersson M, Alvarez-Cermeno J, Bernardi G, Cogato I, Fredman P, Frederiksen J, Fredrikson S, Gallo P, Grimaldi LM, Gronning M: Cerebrospinal fluid in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: A consensus report. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:897–902, 1994
Laman JD, Thompson EJ, Kappos L: Body fluid markers to monitor multiple sclerosis: The assays and the challenges. Mult Scler 4:266–269, 1998
Chofflon M, Juillard C, Juillard P, Gauthier G, Grau GE: Tumor necrosis factor alpha production as a possible predictor of relapse in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur Cytokine Netw 3:523–531, 1992
Flachenecker P, Jung S, Rieckmann P, Toyka KV: sICAM-1 is not a marker for disease activity in the relapse-free interval of multiple sclerosis–-A cross-sectional pilot study. J Neurol 249:1001–1003, 2002
Ohta M, Ohta K, Ma J, Takeuchi J, Saida T, Nishimura M, Itoh N: Clinical and analytical evaluation of an enzyme immunoassay for myelin basic protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem 46:1326–1330, 2000
Giovannoni G, Lai M, Kidd D, Thorpe JW, Miller DH, Thompson AJ, Keir G, Feldmann M, Thompson EJ: Daily urinary neopterin excretion as an immunological marker of disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Brain 120:1–13, 1997
Goffette S, Schluep M, Henry H, Duprez T, Sindic CJ: Detection of oligoclonal free kappa chains in the absence of oligoclonal IgG in the CSF of patients with suspected multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:308–310, 2004
Contini C, Fainardi E, Cultrera R, Seraceni S, Castellazzi M, Peyron F, Granieri E: Evidence of cerebrospinal fluid free kappa light chains in AIDS patients with Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis. J Neuroimmunol 108:221–226, 2000
Krakauer M, Schaldemose Nielsen H, Jensen J, Sellebjerg F: Intrathecal synthesis of free immunoglobulin light chains in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 98:161–165, 1998
Bracco F, Gallo P, Menna R: Routine detection of IgG oligoclonal bands and free light chains patterns by means of agarose isoelectric focusing and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex staining in multiple sclerosis unconcentrated cerebrospinal fluid. Ital J Neurol Sci 6:81–84, 1987
Sindic CJ, Laterre EC: Oligoclonal free kappa and lambda bands in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. An immunoaffinity-mediated capillary blot study. J Neuroimmunol 33:63–72, 1991
Lamers KJ, de Jong JG, Jongen PJ, Kock-Jansen MJ, Teunesen MA, Prudon-Rosmulder EM: Cerebrospinal fluid free kappa light chains versus IgG findings in neurological disorders: Qualitative and quantitative measurements. J Neuroimmunol 62:19–25, 1995
Lolli F, Amaducci L: Measurement of free kappa immunoglobulin light chains in the cerebrospinal fluid by a competitive avidin-biotin ELISA. Clin Chim Acta 182:229–234, 1989
Fagnart OC, Sindic CJ, Laterre C: Free kappa and lambda light chain levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. J Neuroimmunol 19:119–132, 1988
Rudick RA, Medendorp SV, Namey M, Boyle S, Fischer J: Multiple sclerosis progression in a natural history study: Predictive value of cerebrospinal fluid free kappa light chains. Mult Scler 1:150–155, 1995
Bracco F, Gallo P, Menna R, Battistin L, Tavolato B: Free light chains in the CSF in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 234:303–307, 1987
Vakaet A, Thompson EJ: Free light chains in the cerebrospinal fluid: An indicator of recent immunological stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:995–998, 1985
Bradwell AR, Carr-Smith HD, Mead GP, Tang LX, Showell PJ, Drayson MT, Drew R: Highly sensitive, automated immunoassay for immunoglobulin free light chains in serum and urine. Clin Chem 47:673–680, 2001
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sibley W, Thompson A, van den Noort S, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS: Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: Guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50:121–127, 2001
Barkhof F, Filippi M, Miller DH, Scheltens P, Campi A, Polman CH, Comi G, Ader HJ, Losseff N, Valk J: Comparison of MRI criteria at first presentation to predict conversion to clinically definite multiple sclerosis. Brain 120:2059–2069, 1997
Barkhof F, Rocca M, Francis G, Van Waesberghe JH, Uitdehaag BM, Hommes OR, Hartung HP, Durelli L, Edan G, Fernandez O, Seeldrayers P, Sorensen P, Margrie S, Rovaris M, Comi G, Filippi M: Validation of diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging criteria for multiple sclerosis and response to interferon beta1a. Ann Neurol 53:718–724, 2003
Kurtzke JF: Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452, 1983
Stendahl-Brodin L, Link H: Relation between benign course of multiple sclerosis and low-grade humoral immune response in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:102–105, 1980
Reiber H, Felgenhauer K: Protein transfer at the blood cerebrospinal fluid barrier and the quantitation of the humoral immune response within the central nervous system. Clin Chim Acta 163:319–328, 1987
Desplat S, Pelletier J, Pouget J, Bellon F, Bernard D, Boucraut J: Sensitized immunofixation: a new technique for analyzing the oligoclonal pattern of CSF immunoglobulins. Rev Neurol 156:885–889, 2000
Caudie C, Allausen O, Bancel J: Detection of oligoclonal IgG bands in cerebrospinal fluid by immunofixation after electrophoretic migration in the automated Hydrasys sebia system. Ann Biol Clin 58:376–379, 2000
Richard S, Miossec V, Moreau JF, Taupin JL: Detection of oligoclonal immunoglobulins in cerebrospinal fluid by an immunofixation-peroxidase method. Clin Chem 48:167–173, 2002
Katzmann JA, Clark RJ, Abraham RS, Bryant S, Lymp JF, Bradwell AR, Kyle RA: Serum reference intervals and diagnostic ranges for free kappa and free lambda immunoglobulin light chains: Relative sensitivity for detection of monoclonal light chains. Clin Chem 48:1437–1444, 2002
Jenkins MA, Cheng L, Ratnaike S: Multiple sclerosis: Use of light-chain typing to assist diagnosis. Ann Clin Biochem 38:235–241, 2001
Rudick RA, Pallant A, Bidlack JM, Herndon RM: Free kappa light chains in multiple sclerosis spinal fluid. Ann Neurol 20:63–69,1986
Wakasugi K, Suzuki H, Imai A, Konishi S, Kishioka H: Immunoglobulin free light chain assay using latex agglutination. Int J Clin Lab Res 25:211–215, 1995
Lolli F, Siracusa G, Amato MP, Fratiglioni L, Dal Pozzo G, Galli E, Amaducci L: Intrathecal synthesis of free immunoglobulin light chains and IgM in initial multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 83:239–243, 1991
Khoury SJ, Weiner HL: Kappa light chains in spinal fluid for diagnosing multiple sclerosis. JAMA 272:242–243, 1994
DeCarli C, Menegus MA, Rudick RA: Free light chains in multiple sclerosis and infections of the CNS. Neurology 37:1334–1338,1987
Fischer C, Arneth B, Koehler J, Lotz J, Lackner KJ: Kappa free light chains in cerebrospinal fluid as markers of intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis. Clin Chem 50:1809–1813, 2004
Leary SM, McLean BN, Thompson EJ: Local synthesis of IgA in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurological diseases. J Neurol 247:609–615, 2000
Rudick RA, Cookfair DL, Simonian NA, Ransohoff RM, Richert JR, Jacobs LD, Herndon RM, Salazar AM, Fischer JS, Granger CV, Goodkin DE, Simon JH, Bartoszak DM, Bourdette DN, Braiman J, Brownscheidle CM, Coats ME, Cohan SL, Dougherty DS, Kinkel RP, Mass MK, Munchsauer FE, O’Reilly K, Priore RL, Whitham RH: Cerebrospinal fluid abnormalities in a phase III trial of Avonex (IFNbeta-1a) for relapsing multiple sclerosis. The Multiple Sclerosis Collaborative Research Group. J Neuroimmunol 93:8–14,1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desplat-jégo, S., Feuillet, L., Pelletier, J. et al. Quantification of Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in CerebroSpinal Fluid by Nephelometry. J Clin Immunol 25, 338–345 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-5371-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-5371-9