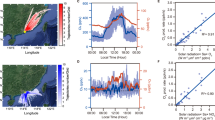
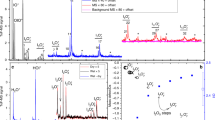
Abstract
The photochemical activation of chlorine by dissolved iron in artificial sea-salt aerosol droplets and by highly dispersed iron oxide (Fe2O3) aerosol particles (mainly hematite, specific surface ~150 m2 g−1) exposed to gaseous HCl, was investigated in humidified air in a Teflon simulation chamber. Employing the radical-clock technique, we quantified the production of gaseous atomic chlorine (Cl) from the irradiated aerosol. When the salt aerosol contained Fe2O3 at pH 6, no significant Cl production was observed, even if the dissolution of iron was forced by “weathering” (repeatedly freezing and thawing for five times). Adjusting the pH in the stock suspension to 2.6, 2.2, and 1.9 and equilibrating for one week resulted in a quantifiable amount of dissolved iron (0.03, 0.2, and 0.6 mmol L−1, respectively) and in gaseous Cl production rates of ~1.6, 6, and 8 × 1021 atoms cm−2 h−1, respectively. In a further series of experiments, the pure Fe2O3 aerosol was exposed to various levels of gaseous hydrogen chloride (HCl). The resulting Cl production rates ranged from 8 × 1020 Cl atoms cm−2 h−1 (at ~4 ppb HCl) to 5 × 1022 Cl atoms cm−2 h−1 (at ~350 ppb HCl) and confirmed the uptake and conversion of HCl to atomic Cl (at HCl to Cl conversion yields of 2–5 %, depending on the relative humidity). The Fe2O3 experiments indicate that iron-induced Cl formation may be important for highly soluble combustion-aerosol particles in marine environments in the presence of gaseous HCl.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Abadleh, H.A.: Review of the bulk and surface chemistry of iron in atmospherically relevant systems containing humic-like substances. RSC Adv. (2015). doi:10.1039/C5RA03132J
Atkinson, R., Baulch, D.L., Cox, R.A., Crowley, J.N., Hampson, R.F., Hynes, R.G., Jenkin, M.E., Rossi, M.J., Troe, J.: Evaluated kinetic and photochemical data for atmospheric chemistry: volume III – Gas phase reactions of inorganic halogens. Atmos. Chem. Phys. (2007). doi:10.5194/acp-7-981-2007
Baker, A.R., Croot, P.L.: Atmospheric and marine controls on aerosol iron solubility in seawater. Mar. Chem. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2008.09.003
Baker, A.R., Jickells, T.D., Witt, M., Linge, K.L.: Trends in the solubility of iron, aluminium, manganese and phosphorus in aerosol collected over the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Chem. (2006). doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2005.06.004
Balzer, N.: Kinetische Untersuchungen der Halogen-Aktivierung einer simulierten Salzpfanne in einer Smogkammer, PhD thesis. University of Bayreuth, Germany (2012). https://epub.uni-bayreuth.de/162/
Bartolomei, V., Gomez Alvarez, E., Wittmer, J., Tlili, S., Strekowski, R., Temime-Roussel, B., Quivet, E., Wortham, H., Zetzsch, C., Kleffmann, J., Gligorovski, S.: Combustion processes as a source of high levels of indoor hydroxyl radicals through the photolysis of nitrous acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2015). doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b01905
Behnke, W., Zetzsch, C.: The generation of radicals on aerosol surfaces. Air Poll. Res. Rep. 17, 119–124 (1988)
Behnke, W., Zetzsch, C.: Heterogeneous production of Cl atoms under simulated tropospheric conditions in a smog chamber. In: Restelli, G., Angeletti, G. (eds.) Physico-Chemical Behaviour of Atmospheric Pollutants, pp. 277–282. Springer, Dordrecht (1990)
Behnke, W., Holländer, W., Koch, W., Nolting, F., Zetzsch, C.: A smog chamber for studies of the photochemical degradation of chemicals in the presence of aerosols. Atmos. Environ. (1988). doi:10.1016/0004-6981(88)90341-1
Bleicher, S., Buxmann, J.C., Sander, R., Riedel, T.P., Thornton, J.A., Platt, U., Zetzsch, C.: The influence of nitrogen oxides on the activation of bromide and chloride in salt aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. (2014). doi:10.5194/acpd-14-10135-2014
Buxmann, J., Balzer, N., Bleicher, S., Platt, U., Zetzsch, C.: Observations of bromine explosions in smog chamber experiments above a model salt pan. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. (2012). doi:10.1002/kin.20714
Buxmann, J., Bleicher, S., Platt, U., von Glasow, R., Sommariva, R., Held, A., Zetzsch, C., Ofner, J.: Consumption of reactive halogen species from sea-salt aerosol by secondary organic aerosol: slowing down bromine explosion. Environ. Chem. (2015). doi:10.1071/EN14226
Byrne, R.H., Kester, D.R.: Solubility of hydrous ferric oxide and iron speciation in seawater. Mar. Chem. (1976). doi:10.1016/0304-4203(76)90012-8
Cwiertny, D.M., Young, M.A., Grassian, V.H.: Chemistry and photochemistry of mineral dust aerosol. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. (2008). doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.59.032607.093630
Delmelle, P., Lambert, M., Dufrêne, Y., Gerin, P., Óskarsson, N.: Gas/aerosol–ash interaction in volcanic plumes: new insights from surface analyses of fine ash particles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. (2007). doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.04.052
Duce, R.A., Tindale, N.W.: Atmospheric transport of iron and its deposition in the ocean. Limnol. Oceangr. (1991). doi:10.4319/lo.1991.36.8.1715
Duggen, S., Croot, P., Schacht, U., Hoffmann, L.: Subduction zone volcanic ash can fertilize the surface ocean and stimulate phytoplankton growth: evidence from biogeochemical experiments and satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. (2007). doi:10.1029/2006GL027522
Erickson, D.J., Seuzaret, C., Keene, W.C., Gong, S.L.: A general circulation model based calculation of HCl and ClNO2 production from sea salt dechlorination: reactive chlorine emissions inventory. J. Geophys. Res. (1999). doi:10.1029/98JD01384
Gliß, J., Bobrowski, N., Vogel, L., Pöhler, D., Platt, U.: OClO and BrO observations in the volcanic plume of Mt. Etna – implications on the chemistry of chlorine and bromine species in volcanic plumes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. (2015). doi:10.5194/acp-15-5659-2015
Graedel, T.E., Keene, W.C.: The budget and cycle of earth’s natural chlorine. Pure Appl. Chem. (1996). doi:10.1351/pac199668091689
Herrmann, H., Majdik, Z., Ervens, B., Weise, D.: Halogen production from aqueous tropospheric particles. Chemosphere (2003). doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00202-9
Ito, A., Feng, Y.: Role of dust alkalinity in acid mobilization of iron. Atmos. Chem. Phys. (2010). doi:10.5194/acp-10-9237-2010
Jeong, D., Kim, K., Choi, W.: Accelerated dissolution of iron oxides in ice. Atmos. Chem. Phys. (2012). doi:10.5194/acp-12-11125-2012
Jickells, T.D., Spokes, L.J.: Atmospheric iron inputs to the oceans. IUPAC Ser. Analytical Phys. Chem. Environ. Syst. 7, 85–122 (2001)
Keene, W.C., Savoie, D.L.: The pH of deliquesced sea-salt aerosol in polluted marine air. Geophys. Res. Lett. (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL01591
Keene, W.C., Sander, R., Pszenny, A.A., Vogt, R., Crutzen, P.J., Galloway, J.N.: Aerosol pH in the marine boundary layer. J. Aerosol Sci. (1998). doi:10.1016/S0021-8502(97)10011-8
Keene, W.C., Khalil, M., Aslam, K., Erickson, D.J., McCulloch, A., Graedel, T.E., Lobert, J.M., Aucott, M.L., Gong, S.L., Harper, D.B., Kleiman, G., Midgley, P., Moore, R.M., Seuzaret, C., Sturges, W.T., Benkovitz, C.M., Koropalov, V., Barrie, L.A., Li, Y.F.: Composite global emissions of reactive chlorine from anthropogenic and natural sources: reactive chlorine emissions inventory. J. Geophys. Res. (1999). doi:10.1029/1998JD100084
Kester, D.R., Duedall, I.W., Connors, D.N., Pytkowicz, R.M.: Preparation of artificial seawater. Limnol. Oceangr. (1967). doi:10.4319/lo.1967.12.1.0176
Kiwi, J., Lopez, A., Nadtochenko, V.: Mechanism and kinetics of the OH-radical intervention during Fenton oxidation in the presence of a significant amount of radical scavenger (Cl−). Environ. Sci. Technol. (2000). doi:10.1021/es991406i
Knipping, E.M., Lakin, M.J., Foster, K.L., Jungwirth, P., Tobias, D.J., Gerber, R.B., Dabdub, D., Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.: Experiments and simulations of ion-enhanced interfacial chemistry on aqueous NaCl aerosols. Science (2000). doi:10.1126/science.288.5464.301
Kolb, C.E., Cox, R.A., Abbatt, J.P.D., Ammann, M., Davis, E.J., Donaldson, D.J., Garrett, B.C., George, C., Griffiths, P.T., Hanson, D.R., Kulmala, M., McFiggans, G., Pöschl, U., Riipinen, I., Rossi, M.J., Rudich, Y., Wagner, P.E., Winkler, P.M., Worsnop, D.R., O’ Dowd, C.D.: An overview of current issues in the uptake of atmospheric trace gases by aerosols and clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. (2010). doi:10.5194/acp-10-10561-2010
Kuma, K., Nishioka, J.U., Matsunaga, K.: Controls on iron(III) hydroxide solubility in seawater: the influence of pH and natural organic chelators. Limnol. Oceangr. (1996). doi:10.4319/lo.1996.41.3.0396
Lim, M., Chiang, K., Amal, R.: Photochemical synthesis of chlorine gas from iron(III) and chloride solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2006.03.005
Liu, X., Millero, F.J.: The solubility of iron in seawater. Mar. Chem. (2002). doi:10.1016/S0304-4203(01)00074-3
Luo, C., Mahowald, N., Bond, T., Chuang, P.Y., Artaxo, P., Siefert, R., Chen, Y., Schauer, J.: Combustion iron distribution and deposition. Glob Biogeochem. Cycles (2008). doi:10.1029/2007GB002964
Machulek, A., Vautier-Giongo, C., Moraes, J.E.F., Nascimento, C.A.O., Quina, F.H.: Laser flash photolysis study of the photocatalytic step of the photo-Fenton reaction in saline solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. (2006). doi:10.1562/2005-05-28-RA-548
Machulek, A., Moraes, J.E.F., Vautier-Giongo, C., Silverio, C.A., Friedrich, L.C., Nascimento, C.A.O., Gonzalez, M.C., Quina, F.H.: Abatement of the inhibitory effect of chloride anions on the photo-Fenton process. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2007). doi:10.1021/es071884q
Mahowald, N.M., Engelstaedter, S., Luo, C., Sealy, A., Artaxo, P., Benitez-Nelson, C., Bonnet, S., Chen, Y., Chuang, P.Y., Cohen, D.D., Dulac, F., Herut, B., Johansen, A.M., Kubilay, N., Losno, R., Maenhaut, W., Paytan, A., Prospero, J.M., Shank, L.M., Siefert, R.L.: Atmospheric iron deposition: global distribution, variability, and human perturbations. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. (2009). doi:10.1146/annurev.marine.010908.163727
Meskhidze, N.: Dust and pollution: a recipe for enhanced ocean fertilization? J. Geophys. Res. (2005). doi:10.1029/2004JD005082
Miller, W.L., King, D., Lin, J., Kester, D.R.: Photochemical redox cycling of iron in coastal seawater. Mar. Chem. (1995). doi:10.1016/0304-4203(95)00027-O
Nadtochenko, V.A., Kiwi, J.: Photolysis of FeOH2+ and FeCl2+ in aqueous solution. Photodissociation kinetics and quantum yields. Inorg. Chem. (1998). doi:10.1021/ic9804723
Pignatello, J.J., Liu, D., Huston, P.: Evidence for an additional oxidant in the photoassisted Fenton reaction. Environ. Sci. Technol. (1999). doi:10.1021/es980969b
Prescher, C., McCammon, C., Dubrovinsky, L., Moss, A.: A program for analyzing energy-domain Mössbauer spectra from conventional and synchrotron sources. J. Appl. Crystallogr. (2012). doi:10.1107/S0021889812004979
Rossi, M.J.: Heterogeneous reactions on salts. Chem. Rev. 103, 4823–4882 (2003)
Rubasinghege, G., Lentz, R.W., Scherer, M.M., Grassian, V.H.: Simulated atmospheric processing of iron oxyhydroxide minerals at low pH: roles of particle size and acid anion in iron dissolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. (2010). doi:10.1073/pnas.0910809107
Santschi, C., Rossi, M.J.: Uptake of CO2, SO2, HNO3 and HCl on calcite (CaCO3) at 300 K: mechanism and the role of adsorbed water. J. Phys. Chem. A (2006). doi:10.1021/jp056312b
Schroth, A.W., Crusius, J., Sholkovitz, E.R., Bostick, B.C.: Iron solubility driven by speciation in dust sources to the ocean. Nat. Geosci. (2009). doi:10.1038/ngeo501
Sedwick, P.N., Sholkovitz, E.R., Church, T.M.: Impact of anthropogenic combustion emissions on the fractional solubility of aerosol iron: evidence from the Sargasso Sea. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. (2007). doi:10.1029/2007GC001586
Shi, Z., Krom, M.D., Bonneville, S., Baker, A.R., Jickells, T.D., Benning, L.G.: Formation of iron nanoparticles and increase in iron reactivity in mineral dust during simulated cloud processing. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2009). doi:10.1021/es901294g
Shi, Z., Krom, M.D., Jickells, T.D., Bonneville, S., Carslaw, K.S., Mihalopoulos, N., Baker, A.R., Benning, L.G.: Impacts on iron solubility in the mineral dust by processes in the source region and the atmosphere: a review. Aeolian Res. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.aeolia.2012.03.001
Sholkovitz, E.R., Sedwick, P.N., Church, T.M., Baker, A.R., Powell, C.F.: Fractional solubility of aerosol iron: synthesis of a global-scale data set. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.gca.2012.04.022
Siefert, R.L., Johansen, A.M., Hoffmann, M.R., Pehkonen, S.O.: Measurements of trace metal (Fe, Cu, Mn, Cr) oxidation states in fog and stratus clouds. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. (1998). doi:10.1080/10473289.1998.10463659
Sullivan, R.C., Guazzotti, S.A., Sodeman, D.A., Prather, K.A.: Direct observations of the atmospheric processing of Asian mineral dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. (2007a). doi:10.5194/acp-7-1213-2007
Sullivan, R.C., Guazzotti, S.A., Sodeman, D.A., Tang, Y., Carmichael, G.R., Prather, K.A.: Mineral dust is a sink for chlorine in the marine boundary layer. Atmos. Environ. (2007b). doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.05.047
Supeno, Supeno, P.: Sonochemical formation of nitrate and nitrite in water. Ultrason. Sonochem. (2000). doi:10.1016/S1350-4177(99)00043-7
Svensson, R., Ljungström, E., Lindqvist, O.: Kinetics of the reaction between nitrogen dioxide and water vapour. Atmos. Environ. (1987). doi:10.1016/0004-6981(87)90315-5
Tilgner, A., Bräuer, P., Wolke, R., Herrmann, H.: Modelling multiphase chemistry in deliquescent aerosols and clouds using CAPRAM3.0i. J. Atmos. Chem. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10874-013-9267-4
Tobo, Y., Zhang, D., Nakata, N., Yamada, M., Ogata, H., Hara, K., Iwasaka, Y.: Hygroscopic mineral dust particles as influenced by chlorine chemistry in the marine atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. (2009). doi:10.1029/2008GL036883
Tobo, Y., Zhang, D., Matsuki, A., Iwasaka, Y.: Asian dust particles converted into aqueous droplets under remote marine atmospheric conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. (2010). doi:10.1073/pnas.1008235107
Vogt, R., Crutzen, P.J., Sander, R.: A mechanism for halogen release from sea-salt aerosol in the remote marine boundary layer. Nature (1996). doi:10.1038/383327a0
Wahner, A., Mentel, T.F., Sohn, M.: Gas-phase reaction of N2O5 with water vapor: Importance of heterogeneous hydrolysis of N2O5 and surface desorption of HNO3 in a large Teflon chamber. Geophys. Res. Lett. (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL51596
Wang, W.-N., Purwanto, A., Lenggoro, I.W., Okuyama, K., Chang, H., Jang, H.D.: Investigation on the correlations between droplet and particle size distribution in ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. (2008). doi:10.1021/ie070821d
Wang, R., Balkanski, Y., Boucher, O., Bopp, L., Chappell, A., Ciais, P., Hauglustaine, D., Peñuelas, J., Tao, S.: Sources, transport and deposition of iron in the global atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. (2015). doi:10.5194/acp-15-6247-2015
Wittmer, J., Bleicher, S., Zetzsch, C.: Iron(III)-induced activation of chloride and bromide from modeled saltpans. J. Phys. Chem. A (2015a). doi:10.1021/jp508006s
Wittmer, J., Bleicher, S., Ofner, J., Zetzsch, C.: Iron(III)-induced activation of chloride from artificial sea salt aerosol. Environ. Chem. (2015b). doi:10.1071/EN14279
Zetzsch, C., Behnke, W.: Heterogeneous reactions of chlorine compounds. In: Niki, H., Becker, K.H. (eds.) The Tropospheric Chemistry of Ozone in the Polar Regions, pp. 291–306. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (1993)
Zetzsch, C.: Simulation of atmospheric photochemistry in the presence of solid airborne aerosols. In: Dechema-Monographien, vol 104. pp 187–213. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, Germany (1987)
Zhang, D., Iwasaka, Y.: Chlorine deposition on dust particles in marine atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. (2001). doi:10.1029/2001GL013333
Zhu, X., Prospero, J.M., Millero, F.J., Savoie, D.L., Brass, G.W.: The solubility of ferric ion in marine mineral aerosol solutions at ambient relative humidities. Mar. Chem. (1992). doi:10.1016/0304-4203(92)90069-M
Zhu, X., Prospero, J.M., Savoie, D.L., Millero, F.J., Zika, R.G., Saltzman, E.S.: Photoreduction of iron(III) in marine mineral aerosol solutions. J. Geophys. Res. (1993). doi:10.1029/93JD00202
Zhuang, G., Yi, Z., Duce, R.A., Brown, P.R.: Chemistry of iron in marine aerosols. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles (1992). doi:10.1029/92GB00756
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Dr. Catherine McCammon, BGI Bayreuth, Germany, for the Mössbauer spectroscopy of our samples, Johannes Thiessen for the BET analysis, Dipl.-Ing. Franz D. Oeste and Dr. Sergej Bleicher for advice, and Agnes Bednorz and Andrej Einhorn for technical support. This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) within research unit 763 (HALOPROC) grant ZE792/5-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wittmer, J., Zetzsch, C. Photochemical activation of chlorine by iron-oxide aerosol. J Atmos Chem 74, 187–204 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-016-9336-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-016-9336-6