Abstract
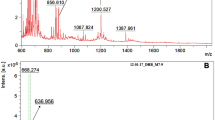
Ion trap mass spectrometry (ITMS) was used to obtain further qualitative information about the chemical composition of humic-like substances (HULIS) in atmospheric particulate matter. Particles ≤10 μm (PM10) were collected on quartz fiber filters for 24 h in the region of Basel (Switzerland) and extracted with water. HULIS were separated from inorganic salts by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and detected by electrospray ionization in the negative ion mode (ESI(−)). Series of consecutive fragment ion spectra (MSn) were recorded by ITMS. Full scan mass spectra of the extracts showed a mass distribution pattern characteristic for HULIS. Different molecular ions were selected from this pattern for further fragmentations. Among them the molecular ion m/z 299 was considered as representative and intensively studied. Many MS2 and MS3 fragment spectra contained a fragment m/z 97 and a neutral loss of 80 u. Time-of-flight (TOF) MS and deuterium exchange experiments identified m/z 97 as hydrogen sulfate. MS2 and MS3 fragment spectra supported the existence of sulfate covalently bound to HULIS. The fragmentation behavior of sulfated HULIS could be confirmed by model compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brimblecombe, P., 1996: Air Composition & Chemistry, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Cappiello, A., De Simoni, E., Fiorucci, C., Mangani, F., Palma, P., Trufelli, H., Decesari, S., Facchini, M. C., and Fuzzi, S., 2003: Molecular characterization of the water-soluble organic compounds in fogwater by ESI-MS/MS, Environ. Sci. Technol. 37, 1229–1240.
Facchini, M. C., Fuzzi, S., Zappoli, S., Andracchio, A., Gelencser, A., Kiss, G., Krivacsy, Z., Meszaros, E., Hansson, H.-C., Alsberg, T., and Zebühr, Y., 1999: Partitioning of the organic aerosol component between fog droplets and interstitial air, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 26821–26832.
Fuzzi, S., Decesari, S., Facchini, M. C., Matta, E., and Mircea, M., 2001: A simplified model of the water soluble organic component of atmospheric aerosols, Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 4079–4082.
Fuzzi, S., Facchini, M. C., Decesari, S., Matta, E., and Mircea, M., 2002: Soluble organic compounds in fog and cloud droplets: What have we learned over the past few years? Atmos. Environ. 64, 89–98.
Jacobson, M. C., Hansson, H.-C., Noone, K. J., and Charlson, R. J., 2000: Organic Atmospheric Aerosols: Review and State of the Science, Review of Geophysics 38, 267–294.
Kalberer, M., Paulsen, D., Sax, M., Steinbacher, M., Dommen, J., Prevot, A. S. H., Fisseha, R., Weingartner, E., Frankevich, V., Zenobi, R., and Baltensperger, U., 2004: Identification of polymers as major components of atmospheric organic aerosols, Science 303, 1659–1662.
Kiss, G., Gelencser, A., Hoffer, A., Krivacsy, Z., Meszaros, E., Molnar, A., and Varga, B., 2000: Chemical characterisation of water soluble organic compounds in tropospheric fine aerosol, Proc. Conf. on Nucleation and Atmospheric Aerosols, 761–764.
Kiss, G., Varga, B., Gelencser, A., Krivacsy, Z., Molnar, A., Alsberg, T., Persson, L., Hansson, H.-C., and Facchini, M.C., 2001: Characterisation of polar organic compounds in fog water, Atmos. Environ. 35, 2193–2200.
Kiss, G., Tombácz, E., Varga, B., Alsberg, T., and Persson, L., 2003: Estimation of the average molecular weight of humic-like substances isolated from fine atmospheric aerosol, Atmos. Environ. 37, 3783–3794.
Krivacsy, Z., Hoffer, A., Sarvari, Z., Temesi, D., Baltensperger, U., Nyeki, S., Weingartner, E., Kleefeld, S., and Jennings, S. G., 2001: Role of organic and black carbon in the chemical composition of atmospheric aerosol at European background sites, Atmos. Environ. 35, 6231–6244.
Limbeck, A., and Puxbaum, H., 1999: Organic acids in continental background aerosols, Atmos. Environ. 33, 1847–1852.
Novakov, T., and Penner, J. E., 1993: Large contribution of organic aerosols to cloud-condensation-nuclei concentrations, Nature 365, 823–826.
Saxena, P. and Hildemann, L. M., 1996: Water-soluble organics in atmospheric particles: A critical review of the literature and application of thermodynamics to identify candidate compounds, J. Atmos. Chem. 24, 57–109.
Seinfeld, J. H. and Pandis, S. N., 1998: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Suzuki, Y., Kawakami, M., and Akasaka, K., 2001: 1H NMR application for characterizing water-soluble organic compounds in urban atmospheric particles, Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 2656–2664.
These, A. and Reemtsma, T., 2003: Limitations of electrospray ionization of fulvic and humic acids as visible from size exclusion chromatography with organic carbon and mass spectrometric detection, Anal. Chem. 75, 6275–6281.
UNEP, 2003: Global Environment Outlook 3 – GEO 2003, Earthscan Publication Ltd, London.
Varga, B., Kiss, G., Ganszky, I., Gelencser, A., and Krivacsy, Z., 2001: Isolation of water-soluble organic matter from atmospheric aerosol, Talanta 55, 561–572.
Zappoli, S., Andracchio, A., Fuzzi, S., Facchini, M. C., Gelencser, A., Kiss, G., Krivacsy, Z., Molnar, A., Meszaros, E., Hansson, H.-C., Rosman, K., and Zebühr, Y., 1999: Inorganic, organic and macromolecular components of fine aerosol in different areas of Europe in relation to their water solubility, Atmos. Environ. 33, 2733–2743.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romero, F., Oehme, M. Organosulfates – A New Component of Humic-Like Substances in Atmospheric Aerosols?. J Atmos Chem 52, 283–294 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-005-0594-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-005-0594-y