Abstract
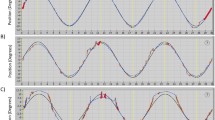
Eye–target synchronization is critical for effective smooth pursuit of a moving visual target. We apply the nonlinear dynamical technique of stochastic-phase synchronization to human visual pursuit of a moving target, in both normal and mild traumatic brain-injured (mTBI) patients. We observe significant fatigue effects in all subject populations, in which subjects synchronize better with the target during the first half of the trial than in the second half. The fatigue effect differed, however, between the normal and the mTBI populations and between old and young subpopulations of each group. In some cases, the younger (≤40 years old) normal subjects performed better than mTBI subjects and also better than older (>40 years old) normal subjects. Our results, however, suggest that further studies will be necessary before a standard of “normal” smooth pursuit synchronization can be developed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vanderploeg, R.D., Curtiss, G., Belanger, H.G.: Long-term neuropsychological outcomes following mild traumatic brain injury. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 11(3), 228–36 (2005)
Dockree, P.M., Bellgrove, M.A., O’Keeffe, F.M., Moloney, P., Aimola, L., Carton, S., Robertson, I.H.: Sustained attention in traumatic brain injury (TBI) and healthy controls: enhanced sensitivity with dual-task load. Exp. Brain Res. 168(1–2), 218–29 (2006)
Stuss, D.T., Pogue, J., Buckle, L., Bondar, J.: Characterization of stability of performance in patients with traumatic brain injury: variability and consistency on reaction time tests. Neuropsychology 8, 316–324 (1994)
Robertson, I.H., Manly, T., Andrade, J., Baddeley, B.T., Yiend, J.: ‘Oops!’: performance correlates of everyday attentional failures in traumatic brain injured and normal subjects. Neuropsychologia 35(6), 747–58 (1997)
Hetherington, C.R., Stuss, D.T., Finlayson, M.A.: Reaction time and variability 5 and 10 years after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 10(7), 473–86 (1996)
Suh, M., Kolster, R., Sarkar, R., McCandliss, B., Ghajar, J.: Deficits in predictive smooth pursuit after mild traumatic brain injury. Neurosci. Lett. 401(1–2), 108–13 (2006)
Suh, M., Basu, S., Kolster, R., Sarkar, R., McCandliss, B., Ghajar, J.: Increased oculomotor deficits during target blanking as an indicator of mild traumatic brain injury. Neurosci. Lett. 410(3), 203–7 (2006)
Arfanakis, K., Haughton, V.M., Carew, J.D., Rogers, B.P., Dempsey, R.J., Meyerand, M.E.: Diffusion tensor MR imaging in diffuse axonal injury. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 23, 794–802 (2002)
Povlishock, J.T., Katz, D.I.: Update of neuropathology and neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehab. 20, 75–94 (2005)
Gennarelli, T.A., Graham, D.I.: Neuropathology of the head injuries. Semin. Clin. Neuropsychiatry. 3(3), 160–175 (1998)
Smith, D.H., Meaney, D.F., Shull, W.H.: Diffuse axonal injury in head trauma. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 18, 307–316 (2003)
Kowler, E.: Cognitive expectations, not habits, control anticipatory smooth oculomotor pursuit. Vision Res. 29, 1049–1057 (1989)
Chen, Y., Holzman, P.S., Nakayama, K.: Visual and cognitive control of attention in smooth pursuit. Prog. Brain Res. 140, 255–265 (2002)
Hutton, S.B., Tegally, D.: The effects of dividing attention on smooth pursuit eye tracking. Exp. Brain Res. 163, 306–313 (2005)
Van Donkelaar, P., Drew, A.S.: The allocation of attention during smooth pursuit eye movements. Prog. Brain Res. 140, 267–77 (2002)
Hultsch, D.F., MacDonald, S.W.: Intraindividual variability in performance as a theoretical window onto cognitive aging. In: Dixon, R.A. (ed.) New Frontiers in Cognitive Aging, pp. 65–88. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2004)
Takeshita, D., Sato, Y.D., Bahar, S.: Transitions between multistable states as a model of epileptic seizure dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 75, 051925 (2007)
Weihberger, O., Bahar, S.: Frustration, drift, and antiphase coupling in a neural array. Phys. Rev. E 76, 011910 (2007)
Tass, P.A., Fieseler, T., Dammers, J., Dolan, K., Morosan, P., Majtanik, M., Boers, F., Muren, A., Zilles, K., Fink, G.R.: Synchronization tomography: a method for three-dimensional localization of phase synchronized neuronal populations in the human brain using magnetoencephalography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(8), 088101 (2003)
Goussard, Y., Martin, B., Stark, L.: A new quantitative indicator of visual fatigue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 34, 23–29 (1987)
Porcu, S., Ferrara, M., Urbani, L., Bellatreccia, A., Casagrande, M.: Smooth pursuit and saccadic eye movements as possible indicators of nighttime sleepiness. Physiol. Behav. 65, 437–443 (1998)
De Gennaro, L., Ferrara, M., Urbani, L., Bertini, M.: Oculomotor impairment after 1 night of total sleep deprivation: a dissociation between measures of speed and accuracy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 111, 1771–1778 (2000)
Zils, E., Sprenger, A., Heide, W., Born, J., Gais, S.: Differential effects of sleep deprivation on saccadic eye movements. Sleep 28, 1109–1115 (2005)
Madden, D.J.: Aging and visual attention. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 16(2), 70–74 (2007)
Cook, D.B., O’Connor, P.J., Lange, G., Steffener, J.: Functional neuroimaging correlates of mental fatigue induced by cognition among chronic fatigue syndrome patients and controls. NeuroImage 36, 108–122 (2007)
Pattyn, N., Neyt, X., Henderickx, D., Soetens, E.: Psychophysical investigation of vigilance decrement: boredom or cognitive fatigue? Physiol. Behav. 93, 369–378 (2008)
Pikovsky, A., Rosenblum, M., Kurths, J.: Synchronization: A Universal Concept in Nonlinear Sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Rosenblum, M.G., Pikovsky, A.S., Kurths, J.: Phase synchronization of chaotic oscillators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76(11), 1804–1807 (1996)
Rosenblum, M.G., Pikovsky, A.S., Kurths, J.: From phase to lag synchronization in coupled chaotic oscillators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78(22), 4193–4196 (1997)
Rosenblum, M., Pikovsky, A.S., Schäfer, C., Tass, P., Kurths, J.: Phase synchronization: from theory to data analysis (Chapter 9). In: Moss, F., Gielen, S., Hoff, A.J. (eds.) Handbook of Biological Physics: Neuro-informatics, vol. 4, pp. 279–321. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2001)
Rottach, K.G., Zivotofsky, A.Z., Das, V.E., Averbuch-Heller, L., Discenna, A.O., Poonyathalang, A., Leigh, R.J.: Comparison of horizontal, vertical and diagonal smooth pursuit eye movements in normal human subjects. Vision Res. 36(14), 2189–2195 (1996)
Schonewille, M., Luo, C., Ruigrok, T.J., Voogd, J., Schmolesky, M.T., Rutteman, M., Hoebeek, F.E., De Jeu, M.T., De Zeeuw, C.I.: Zonal organization of the mouse flocculus: physiology, input, and output. J. Comp. Neurol. 497(4), 670–82 (2006)
Bahar, S., Neiman, A., Wilkens, L.A., Moss, F.: Phase synchronization and stochastic resonance effects in the crayfish caudal photoreceptor. Phys. Rev. E 65, 050901(R) (2002)
Bahar, S.: Effect of light on stochastic phase synchronization in the crayfish caudal photoreceptor. Biol. Cybern. 89(3), 200–213 (2003)
Neiman, A.B., Russell, D.F.: Synchronization of noise-induced bursts in noncoupled sensory neurons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88(13), 138103 (2002)
Voss, H.U., McCandliss, B.D., Ghajar, J., Suh, M.: A quantitative synchronization model for smooth pursuit target tracking. Biol. Cybern. 96, 309–322 (2007)
Rodriguez, E., George, N., Lachaux, J.-P., Martinerie, J., Renault, B., Varela, F.J.: Perception’s shadow: long distance synchronization of human brain activity. Nature 397, 430–433 (1999)
Acknowledgements
SB is supported by NSF CAREER Grant no. PHY-0547647; JG and MS are supported by a grant from the James S. McDonnell Foundation to the Brain Trauma Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Contreras, R., Kolster, R., Voss, H.U. et al. Eye–Target Synchronization in Mild Traumatic Brain-injured Patients. J Biol Phys 34, 381–392 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-008-9092-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-008-9092-1