Abstract
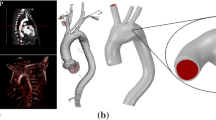
The response of wall stress to the elasticity of each layer in the aorta wall was investigated to understand the role of the different elastic properties of layers in the aortic dissection. The complex mechanical interaction between blood flow and wall dynamics in a three-dimensional arch model of an aorta was studied by means of computational coupled fluid-structure interaction analysis. The results show that stresses in the media layer are highest in three layers and that shear stress is concentrated in the media layer near to the adventitia layer. Hence, the difference in the elastic properties of the layers could be responsible for the pathological state in which a tear splits across the tunica media to near to the tunica adventitia and the dissection spreads along the laminar planes of the media layer where it is near the adventitia layer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thubrikar, M.J., Agali, P., Robicsek, F.: Wall stress as a possible mechanism for the development of transverse intimal tears in aortic dissections. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 23, 127–134 (1999)
Svensson, L.G., Grawford, E.S.: Aortic dissection and aortic aneurysm surgery: clinical observations, experimental investigations, and statistical analyses. Part II. Curr. Probl. Surg. 29, 913–1057 (1992)
Doroghazi, R.M., Slater, E.E.: Aortic Dissection, (p. 38.). McGraw-Hill, New York, NY (1983)
Roberts, W.C.: Aortic dissection: anatomy consequences and causes. Am. Heart J. 101, 195–214 (1981)
Jamieson, W.R.E., Munro, A.I., Miyagishima, R.T., Allen, P., Tyers, G.F.O., Gerein, A.N.: Aortic dissection: early diagnosis and surgical management are the keys to survival. Can. J. Surg. 25, 145–149 (1982)
Desanctis, R.W., Doroghazi, R.M., Austen W.G., Buckley, M.J.: Aortic dissection. N. Engl. J. Med. 317, 1060–1067 (1987)
Slater, E.E., Desanctis, R.W.: The clinical recognition of dissecting aortic aneurysm. Amer. J. Med. 60, 625–633 (1976)
Tam, A.S.M., Sapp, M.C., Roach, M.R.: The effect of tear depth on the propagation of aortic dissections in isolated porcine thoracic aorta. J. Biomech. 31, 673–676 (1998)
Yee, C.A.: Aortic dissection: the tear that kills. Nurs. Manage. 35, 25–32 (2004)
Di Martino, E.S., Guadagni, G., Fumero, A., Ballerini, G., Spirito, R., Biglioli, P., Redaelli, A.: Fluid-structure interaction within realistic three-dimensional models of the aneurysmatic aorta as a guidance to assess the risk of rupture of the aneurysm. Med. Eng. Phys. 23, 647–655 (2001)
Giannakoulas, G., Giannoglou, G., Soulis, J., Farmakis, T., Papadopoulou, S., Parcharidis G., Louridas, G.: A computational model to predict aortic wall stresses in patients with systolic arterial hypertension. Med. Hypotheses 65(6), 1191–1195 (2005)
MacLean, N.F., Dudek, N.L., Roach, M.R.: The role of radial elastic properties in the development of aortic dissections. J. Vasc. Surg. 29, 703–710 (1999)
Humphrey, J.D.: Mechanics of the arterial wall: review and directions. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 23, 1–162 (1995)
Holzapfel, G.A., Gasser, T.C., Ogden, R.W.: A new constitutive framework for arterial wall mechanics and comparative study of material models. J. Elast. 61, 1–48 (2000)
Engel, N.: Abdominal aortic aneurysm and low back pain. Dyn. Chiropr. 14(16) (1996)
Ganong, W.F.: Review of Medical Physiology. Lange Medical, Los Altos, CA (1963)
Shiotani, S., Kohno, M., Ohashi, N., Yamazaki, K., Nakayama, H., Ito, Y., Kaga, K., Ebashi, T., Itai, Y.: Hyperattenuating aortic wall on postmortem computed tomography. Radiat. Med. 20(4), 201–206 (2002)
Riley, W.A., Barnes, R.W., Evans, G.W., Burke, G.L.: Ultrasonic measurements of the elastic modulus of the common carotid artery: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Stroke 23, 952–956 (1992)
Schulze-Bauer, C.A., Morth, C., Holzapfel, G.A.: Passive biaxial mechanical response of aged human iliac arteries. J. Biomech. Eng. 125(3), 395–406 (2003)
Bloom W, Fawcett D.W.: A Textbook of Histology. 12th ed. Chapman & Hall, New York, NY (1994)
Driessen, N.J.B., Wilson, W., Bouten, C.V.C., Baaijens, F.P.T.: A computational model for collagen fibre remodeling in the arterial wall. J. Theor. Biol., 226, 53–64 (2004)
Xie, J., Zhou, J., Fung, Y.C.: Bending of blood vessel wall: stress–strain laws of the intima-media and adventitial layers. J. Biomech. Eng. 117, 136–145 (1995)
Fischer, E.I., Armentano, R.L., Pessana, F.M., Graf, S., Romero, L., Christen, A.I., Simon, A., Levenson, J.: Endothelium-dependent arterial wall tone elasticity modulated by blood viscosity. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 282, 389–394 (2002)
FIDAP Theory Manual, v.8.7.2, Fluent Inc., Lebanon, N.H. Apr. (2003)
Liepsch, D., Moravec, S., Baumgart, R.: Some flow visualization and laser-doppler velocity measurements in a true-to-scale elastic model of a human aortic arch – a new model technique. Biorheology 29, 563–580 (1992)
Perktold, K., Resch, M., Florian, H.: Pulsatile non-Newtonian flow characteristics in a three-dimensional human carotid bifurcation model. J. Biomech. Eng. 113, 464–475 (1991)
Endo, S., Sohara, Y., Karino, T.: Flow patterns in dog aortic arch under a steady flow condition simulating mid-systole. Heart Vessels 11, 180–191 (1996)
Shahcheraghi, N., Dwyer, H.A., Cheer, A.Y., Barakat, A.I., Rutaganira, T.: Unsteady and three-dimensional simulation of blood flow in the human aortic arch. J. Biomech. Eng. 124, 378–387 (2002)
Moayeri, M.S., Zendehbudi, G.R.: Effect of elastic property of the wall on flow characteristics through arterial stenoses. J. Biomech. 36, 525–535 (2003)
Torii, R., Oshima, M., Kobayashi, T., Takagi, K.: Influence of wall deformation on wall shear stress distribution of intracranial artery. In: Summer Bioengineering Conference, Sonesta Beach Resort, Key Biscayne, FL, 25–29 June 2003 (pp. 493–494)
Ku, D.N., Giddens, D.P., Zarins, C.K., Glagov, S.: Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation: positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 5, 293–302 (1985)
Moore, J.E., Xu, C., Glagov, S., Zarins, C.K., Ku, D.N.: Fluid wall shear stress measurements in a model of the human abdominal aorta: oscillatory behavior and relationship to atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 110, 225–240 (1994)
Angouras, D., Sokolis, D.P., Dosios, T., Kostomitsopoulos, N., Boudoulas, H., Skalkeas, G., Karayannacos, P.E.: Effect of impaired vasa vasorum flow on the structure and mechanics of the thoracic aorta: implications for the pathogenesis of aortic dissection. Eur. J. Cardio-thorac. Surg. 17, 468–473 (2000)
Okamoto, R.J., Xu, H.D., Kouchoukos, N.T., Moon, M.R., Sundt, T.M.: The influence of mechanical properties on wall stress and distensibility of the dilated ascending aorta. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 126, 842–850 (2003)
Carsten, J.B., Michel, R.L., Mano, J.T., Gabor, S., Francis, R., Siegfried, H.: Increased aortic wall stress in aortic insufficiency: clinical data and computer model. Eur. J. Cardio-thorac. Surg. 27, 270–275 (2005)
Nevitt, M.P., Ballard, D.J., Hallet, J.W.: Prognosis of abdominal aortic aneurysms: a population-based study. N. Engl. J. Med. 321, 1009–1014 (1989)
McNamara, J.J., Pressler, V.: Natural history of atherosclerotic thoracic aortic aneurysms. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 26, 468–473 (1978)
Michael, W.C., Margot, R.R.: The strength of the aortic media and its role in the propagation of aortic dissection. J. Biomech. 23, 579–588 (1990)
Liepsch, D.: An introduction to biofluid mechanics – basic models and applications. J. Biomech. 35, 415–435 (2002)
Hirst, A., Johns, V., Kime, W.: Dissecting aneurysms of the aorta: a review of 505 cases. Medicine 37, 217–279 (1958)
Xie, L., Shih, H.J., Freedman, L.: Aortic dissection. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 128, 599–600 (2004)
Vilacosta I., San Romàn J.A.: Acute aortic syndrome. Heart 85, 365–368 (2001)
Uchida, K., Imoto, K., Takahashi, M., Suzuki, S., Isoda, S., Sugiyama, M., Kondo, J., Takanashi, Y.: Pathologic characteristics and surgical indications of superacute type A intramural hematoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 79, 1518–1521 (2005)
Coady, M.A., Rizzo, J.A., Elefteriades, J.A.: Pathologic variants of thoracic aortic dissections. Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers and intramural hematomas. Cardiol. Clin. 17, 637–657 (1999)
Maltzahn, W.W.V., Warriyar, R.G., Keitzer, W.F.: Experimental measurements of elastic properties of media and adventitia of bovine carotid arteries. J. Biomech. 17, 839–848 (1984)
Macleod, R.I., Soames, J.V.: Intimal cushions in the lingual artery of neonates and children. Arch. Oral. Biol. 30, 745–747 (1985)
Wheat, M.W.: Acute dissection of the aorta. Cardiovasc. Clin. 17, 241–262 (1987)
O’Gara, P.T., DeSanctis, R.W.: Acute aortic dissection and its variants: toward a common diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Circulation 92, 1376–1378 (1995)
Wolinsky, H., Glagov, S.: A lamellar unit of aortic medial structure and function in mammals. Circ. Res. 20, 409–421 (1967)
van Baardwijk, C., Roach, M.R.: Factors in the propagation of aortic dissections in canine thoracic aortas. J. Biomech. 20, 67–73 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, F., Guo, Z., Sakamoto, M. et al. Fluid-structure Interaction within a Layered Aortic Arch Model. J Biol Phys 32, 435–454 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-006-9027-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-006-9027-7