Abstract
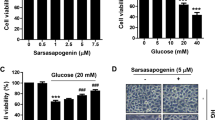
Asiaticoside, the major bioactive constituent purified from Centella asiatica, is a pentacyclic triterpene saponin with sugar moieties (glucose-glucose-rhamnose). Its biological activities including anti-inflammation and antioxidant have been widely reported. This study aimed to investigate the role of asiaticoside in diabetic retinopathy (DR). Human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells ARPE-19 were induced by high glucose. Then, cell survival rate, expression of inflammatory factors, oxidative stress, and apoptosis were measured by MTT method, western blot, oxidative stress detection kits and TUNEL respectively. To uncover the underlying mechanism, the levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP) and protein kinase A (PKA) were measured by Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and PKA activities were detected by the Kemptide phosphorylation assay. Furthermore, cAMP inhibitor SQ22536 was also used to validate the mechanism. Asiaticoside suppressed the inflammation and apoptosis of ARPE-19 cells, and the activities of cAMP and PKA were inhibited upon HG induction while again released after further administration of asiaticoside. However, these effects were all abolished by SQ22536. In conclusion, we have demonstrated in this paper that asiaticoside ameliorates high glucose-induced inflammation and apoptosis of RPE cells by activating cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. asiaticoside-mediated activation of cAMP/PKA signaling pathway may serve as a potential target for the management of DR.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aizu Y, Oyanagi K, Hu J, Nakagawa H (2002) Degeneration of retinal neuronal processes and pigment epithelium in the early stage of the streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Neuropathology 22:161–170
Cheng Y, Yu X, Zhang J, Chang Y, Xue M, Li X, Lu Y, Li T, Meng Z, Su L, Sun B, Chen L (2019) Pancreatic kallikrein protects against diabetic retinopathy in KK Cg-A(y)/J and high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced mouse models of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 62:1074–1086
Dang JW, Lei XP, Li QP, Dong WB (2019) Asiaticoside attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in vitro and in vivo. Iran J Basic Med Sci 22:797–805
Fan L, Li X, Liu T (2020) Asiaticoside Inhibits Neuronal Apoptosis and Promotes Functional Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. J Mol Neurosci 70:1988–1996
Huang J, Gu S, Chen M, Zhang SJ, Jiang Z, Chen X, Jiang C, Liu G, Radu RA, Sun X, Vollrath D, Du J, Yan B, Zhao C (2019) Abnormal mTORC1 signaling leads to retinal pigment epithelium degeneration. Theranostics 9:1170–1180
In Vivo Wound Healing Studies (2016) Prog Drug Res 71:151–157
Krebs EG, Beavo JA (1979) Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 48:923–959
Lengeler KB, Davidson RC, D’Souza C, Harashima T, Shen WC, Wang P, Pan X, Waugh M, Heitman J (2000) Signal transduction cascades regulating fungal development and virulence. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:746–785
Liu D, Homan LL, Dillon JS (2004) Genistein acutely stimulates nitric oxide synthesis in vascular endothelial cells by a cyclic adenosine 5’-monophosphate-dependent mechanism. Endocrinology 145:5532–5539
Miller RA, Chu Q, Xie J, Foretz M, Viollet B, Birnbaum MJ (2013) Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP. Nature 494:256–260
Pandey MK, Sung B, Ahn KS, Kunnumakkara AB, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB (2007) Gambogic acid, a novel ligand for transferrin receptor, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis through modulation of the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Blood 110(10):3517–3525
Shukla A, Rasik AM, Dhawan BN (1999) Asiaticoside-induced elevation of antioxidant levels in healing wounds. Phytother Res 13:50–54
Song MK, Roufogalis BD, Huang TH (2012) Reversal of the Caspase-Dependent Apoptotic Cytotoxicity Pathway by Taurine from Lycium barbarum (Goji Berry) in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells: Potential Benefit in Diabetic Retinopathy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:323784.
Steinle JJ (2020) Review: Role of cAMP signaling in diabetic retinopathy. Mol vis 26:355–358
Stitt AW, Lois N, Medina RJ, Adamson P, Curtis TM (2013) Advances in our understanding of diabetic retinopathy. Clin Sci (lond) 125:1–17
Sun J, Qian P, Kang Y, Dai HB, Wang FZ, Wang HY, Zhou H, Gao Q, Zhou YB (2021) Adrenomedullin 2 attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in microglia cells by receptor-mediated cAMP-PKA pathway. Neuropeptides 85:102109.
Ucgun NI, Zeki-Fikret C, Yildirim Z (2020) Inflammation and diabetic retinopathy. Mol vis 26:718–721
Wang L, Guo T, Guo Y, Xu Y (2020) Asiaticoside produces an antidepressant-like effect in a chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in mice, involving reversion of inflammation and the PKA/pCREB/BDNF signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 22:2364–2372
Wijeweera P, Arnason JT, Koszycki D, Merali Z (2006) Evaluation of anxiolytic properties of Gotukola–(Centella asiatica) extracts and asiaticoside in rat behavioral models. Phytomedicine 13:668–676
Xu HZ, Le YZ (2011) Significance of outer blood-retina barrier breakdown in diabetes and ischemia. Invest Ophthalmol vis Sci 52:2160–2164
Yang H, Yang L (2016) Targeting cAMP/PKA pathway for glycemic control and type 2 diabetes therapy. J Mol Endocrinol 57:R93–R108
Yang Q, Li S, Zhou Z, Fu M, Yang X, Hao K, Liu Y (2020) HDAC6 inhibitor Cay10603 inhibits high glucose-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in retinal pigment epithelial cells via regulating NF-kappaB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Gen Physiol Biophys 39:169–177
Yin Z, Yu H, Chen S, Ma C, Ma X, Xu L, Ma Z, Qu R, Ma S (2015) Asiaticoside attenuates diabetes-induced cognition deficits by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Behav Brain Res 292:288–299
Zhang Z, Li X, Li D, Luo M, Li Y, Song L, Jiang X (2017) Asiaticoside ameliorates β-amyloid-induced learning and memory deficits in rats by inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis and reducing inflammatory factors. Exp Ther Med 13:413–420
Zhang T, Dai J, Ye W, Cai L, Wei J, Chen M, Huang X, Wang X (2020) Asiaticoside attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in A2aR(-/-) mice by promoting the BMP7/Smad1/5 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 527:662–667
Zhu Q, Zeng J, Li J, Chen X, Miao J, Jin Q, Chen H (2020) Effects of Compound Centella on Oxidative Stress and Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Pathway Expression in Diabetic Kidney Disease Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020:9817932
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Meng, X. & Liu, K. The modulation of cAMP/PKA pathway by asiaticoside ameliorates high glucose-induced inflammation and apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Bioenerg Biomembr 54, 9–16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09929-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-021-09929-w