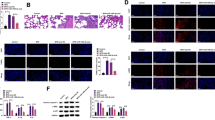
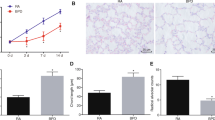
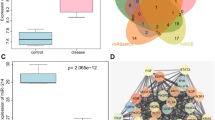
Abstract
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is characterized by impaired vascular and alveolar development, and the underlying molecular mechanisms have remained elusive. MicroRNAs are important players in various biological functions including the pathogenesis of BPD. The present study aimed to examine the expression of miR-203a-3p in the peripheral blood of BPD patients and elucidate the mechanisms underlying miR-203a-3p-mediated progression of BPD. We examined the expression of miR-203a-3p in the peripheral blood of BPD patients and found that miR-203a-3p was up-regulated in the patients. Additionally, the mRNA expression levels of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha were down-regulated in the BPD patients. Further in vitro studies showed that miR-203a-3p suppressed the expression of VEGFA in RLE-6TN cells by targeting the VEGFA 3′ untranslated region. Overexpression of miR-203a-3p inhibited the viability of RLE-6TN cells and induced cell apoptosis, whereas the knockdown of miR-203a-3p exerted opposite effects. VEGFA treatment significantly attenuated the increase in the RLE-6TN cell apoptotic rates induced by miR-203a-3p overexpression; while VEGFA knockdown significantly increased the cell apoptotic rates of RLE-6TN cells, which was partially reversed by the treatment with miR-203a-3p inhibitor. Furthermore, miR-203a-3p was up-regulated, whereas VEGFA was down-regulated in the lung tissues of BPD rats, and sequestration of the expression of miR-203a-3p prevented hyperoxia-induced lung damage, increased VEGFA mRNA and protein expression levels, and promoted the protein expression of ERK, PI3K, and p38 in the lung tissues of BDP rats. In summary, the findings of our study indicate that miR-203a-3p knockdown alleviates hyperoxia-induced lung tissue damage in the BPD rat model, and its effect may be associated with the up-regulation of VEGF.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated in this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Ameis D, Khoshgoo N, Iwasiow BM, Snarr P, Keijzer R (2017) MicroRNAs in lung development and disease. Paediatr Respir Rev 22:38–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prrv.2016.12.002
Arora S, Dev K, Agarwal B, Das P, Syed MA (2018) Macrophages: their role, activation and polarization in pulmonary diseases. Immunobiology 223(4–5):383–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2017.11.001
Asikainen TM, Ahmad A, Schneider BK, Ho WB, Arend M, Brenner M, Günzler V, White CW (2005) Stimulation of HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, and VEGF by prolyl 4-hydroxylase inhibition in human lung endothelial and epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 38(8):1002–1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.12.004
Bancalari E, Jain D (2018) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: can we agree on a definition? Am J Perinatol 35(6):537–540. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1637761
Bhatt AJ, Pryhuber GS, Huyck H, Watkins RH, Metlay LA, Maniscalco WM (2001) Disrupted pulmonary vasculature and decreased vascular endothelial growth factor, Flt-1, and TIE-2 in human infants dying with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164(10 Pt 1):1971–1980. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2101140
Brener Dik PH, Nino Gualdron YM, Galletti MF, Cribioli CM, Mariani GL (2017) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: incidence and risk factors. Arch Argent Pediatr 115(5):476–482. https://doi.org/10.5546/aap.2017.eng.476
Cai W, Liu S, Liu Z, Hou S, Lv Q, Cui H et al (2020) Downregulation of lung miR-203a-3p expression by high-altitude hypoxia enhances VEGF/notch signaling. Aging (Albany NY) 12(5):4247–4267. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102878
Chen L, Gao H, Liang J, Qiao J, Duan J, Shi H, Zhen T, Li H, Zhang F, Zhu Z, Han A (2018) miR-203a-3p promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting PDE4D. Am J Cancer Res 8(12):2387–2401
Cheng H, Wu B, Wang L, Hu T, Deng Z, Li D (2020) Insights into the expression profiles and functions of circRNAs in a newborn hyperoxia-induced rat bronchopulmonary dysplasia model. J Gene Med 22:e3163. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.3163
Claesson-Welsh L, Welsh M (2013) VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J Intern Med 273(2):114–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12019
Day CL, Ryan RM (2017) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: new becomes old again! Pediatr Res 81(1–2):210–213. https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2016.201
Durrani-Kolarik S, Pool CA, Gray A, Heyob KM, Cismowski MJ, Pryhuber G, Lee LJ, Yang Z, Tipple TE, Rogers LK (2017) miR-29b supplementation decreases expression of matrix proteins and improves alveolarization in mice exposed to maternal inflammation and neonatal hyperoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 313(2):L339–l349. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00273.2016
Gentle SJ, Lal CV (2019) Predicting BPD: lessons learned from the airway microbiome of preterm infants. Front Pediatr 7:564. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2019.00564
Kunig AM, Balasubramaniam V, Markham NE, Morgan D, Montgomery G, Grover TR, Abman SH (2005) Recombinant human VEGF treatment enhances alveolarization after hyperoxic lung injury in neonatal rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289(4):L529–L535. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00336.2004
Lal CV, Olave N, Travers C, Rezonzew G, Dolma K, Simpson A, Halloran B, Aghai Z, Das P, Sharma N, Xu X, Genschmer K, Russell D, Szul T, Yi N, Blalock JE, Gaggar A, Bhandari V, Ambalavanan N (2018) Exosomal microRNA predicts and protects against severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely premature infants. JCI Insight 3(5):e93994. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.93994
Levesque BM, Kalish LA, Winston AB, Parad RB, Hernandez-Diaz S, Phillips M, Zolit A, Morey JA, Gupta M, Mammoto A, Ingber DE, van Marter LJ (2013) Low urine vascular endothelial growth factor levels are associated with mechanical ventilation, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and retinopathy of prematurity. Neonatology 104(1):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1159/000351040
Liu HY, Zhang YY, Zhu BL, Feng FZ, Zhang HT, Yan H, Zhou B (2019) MiR-203a-3p regulates the biological behaviors of ovarian cancer cells through mediating the Akt/GSK-3beta/snail signaling pathway by targeting ATM. J Ovarian Res 12(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-019-0532-2
Liu X, Li K, Zhang F, Zhang Y, Deng C, Guo C (2020) Ablation of glutaredoxin 1 promotes pulmonary angiogenesis and alveolar formation in hyperoxia-injured lungs by modifying HIF-1alpha stability and inhibiting the NF-kappaB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 525:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.129
Maniscalco WM, Watkins RH, Pryhuber GS, Bhatt A, Shea C, Huyck H (2002) Angiogenic factors and alveolar vasculature: development and alterations by injury in very premature baboons. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282(4):L811–L823. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00325.2001
Principi N, Di Pietro GM, Esposito S (2018) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical aspects and preventive and therapeutic strategies. J Transl Med 16(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1417-7
Samadi P, Saki S, Dermani FK, Pourjafar M, Saidijam M (2018) Emerging ways to treat breast cancer: will promises be met? Cell Oncol (Dordr) 41(6):605–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0409-1
Sudhadevi T, Ha AW, Ebenezer DL, Fu P, Putherickal V, Natarajan V, Harijith A (2020) Advancements in understanding the role of lysophospholipids and their receptors in lung disorders including bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1865(7):158685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158685
Syed M, Das P, Pawar A, Aghai ZH, Kaskinen A, Zhuang ZW, Ambalavanan N, Pryhuber G, Andersson S, Bhandari V (2017) Hyperoxia causes miR-34a-mediated injury via angiopoietin-1 in neonatal lungs. Nat Commun 8(1):1173. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01349-y
Thebaud B, Ladha F, Michelakis ED, Sawicka M, Thurston G, Eaton F et al (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor gene therapy increases survival, promotes lung angiogenesis, and prevents alveolar damage in hyperoxia-induced lung injury: evidence that angiogenesis participates in alveolarization. Circulation 112(16):2477–2486. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.105.541524
Wang Z, Zhao Z, Yang Y, Luo M, Zhang M, Wang X, Liu L, Hou N, Guo Q, Song T, Guo B, Huang C (2018) MiR-99b-5p and miR-203a-3p function as tumor suppressors by targeting IGF-1R in gastric cancer. Sci Rep 8(1):10119. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27583-y
Xu JZ, Shao CC, Wang XJ, Zhao X, Chen JQ, Ouyang YX, Feng J, Zhang F, Huang WH, Ying Q, Chen CF, Wei XL, Dong HY, Zhang GJ, Chen M (2019) circTADA2As suppress breast cancer progression and metastasis via targeting miR-203a-3p/SOCS3 axis. Cell Death Dis 10(3):175. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1382-y
Yang Y, Qiu J, Kan Q, Zhou XG, Zhou XY (2013) MicroRNA expression profiling studies on bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Genet Mol Res 12(4):5195–5206. https://doi.org/10.4238/2013.October.30.4
Yin R, Yuan L, Ping L, Hu L (2016) Neonatal bronchopulmonary dysplasia increases neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus through the HIF-1alpha and p53 pathways. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 220:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2015.09.011
Zhang Y, Dong X, Lingappan K (2019) Role of HIF-1alpha-miR30a-Snai1 Axis in neonatal Hyperoxic lung injury. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2019:8327486–8327489. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8327486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BW and DL conceived the study; LC and YW performed the data analysis and the experiments; TH edited the manuscript. All the authors approved the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shenzhen People’s Hospital.
Statement of human and animal rights
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shenzhen People’s Hospital. Human blood samples were obtained from these patients and written informed consent was obtained from the guardians of the patients.
Statement of informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplemental Figure S1
MiR-203a-3p was regulated by HIF-1α signaling in RLE-6TN cells. (A) TargetScan analysis of the predicted binding sites between miR-203a-3p and HIF-1α 3’UTR. (B and C) qRT-PCR analysis of HIF-1α expression in RLE-6TN cells after being transfected with mimics-NC, miR-203a-3p mimics, inhibitor NC or miR-203a-3p inhibitor. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of miR-203a-3p expression in RLE-6TN cells after being treated with HIF-1α activator (DMOG). N = 3. *P < 0.05. (PNG 5473 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, H., Chen, L., Wei, Y. et al. Knockdown of miR-203a-3p alleviates the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia partly via the up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A. J Bioenerg Biomembr 53, 13–23 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-020-09863-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-020-09863-3