Abstract
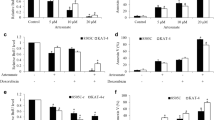
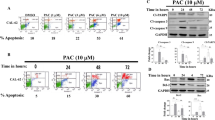
The clinical management of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma and follicular thyroid carcinoma is challenging and requires an alternative therapeutic strategy. Although atovaquone is an FDA-approved anti-malarial drug, studies has recently demonstrated its anti-cancer activities. In line with these efforts, our study shows that atovaquone is an attractive candidate for thyroid cancer treatment. We show that atovaquone significantly inhibits growth, migration and survival in a concentration-dependent manner in 8505C and FTC113 cells. Mechanistically, atovaquone inhibits mitochondrial complex III activity, leading to mitochondrial respiration inhibition and reduction of ATP production in thyroid cancer cells. The inhibitory effects of atovaquone is reversed in mitochondrial respiration-deficient 8505C ρ0 cells, confirming mitochondrial respiration as the mechanism of atovaquone’s action in thyroid cancer. In addition, atovaquone suppresses phosphorylation of STAT3 in thyroid cancer wildype but not ρ0 cells, demonstrating that STAT3 phosphorylation inhibition by atovaquone is a consequence of mitochondrial respiration inhibition. Notably, we further demonstrate that atovaquone significantly augments doxorubicin’s inhibitory effects via suppressing mitochondrial respiration and STAT3. Our findings suggest that atovaquone can be repurposed for thyroid cancer treatment. Our work also highlights that targeting mitochondrial respiration may represent potential therapeutic strategy in thyroid cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton TM, Fokas E, Kunz-Schughart LA, Folkes LK, Anbalagan S, Huether M, Kelly CJ, Pirovano G, Buffa FM, Hammond EM, Stratford M, Muschel RJ, Higgins GS, McKenna WG (2016) The anti-malarial atovaquone increases radiosensitivity by alleviating tumour hypoxia. Nat Commun 7:12308. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12308
Biagini GA, Fisher N, Berry N, Stocks PA, Meunier B, Williams DP, Bonar-Law R, Bray PG, Owen A, O'Neill PM, Ward SA (2008) Acridinediones: selective and potent inhibitors of the malaria parasite mitochondrial bc1 complex. Mol Pharmacol 73(5):1347–1355. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.108.045120
Birth D, Kao WC, Hunte C (2014) Structural analysis of atovaquone-inhibited cytochrome bc1 complex reveals the molecular basis of antimalarial drug action. Nat Commun 5:4029. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5029
Cabanillas ME, Zafereo M, Gunn GB, Ferrarotto R (2016) Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: treatment in the age of molecular targeted therapy. Journal of oncology practice / American Society of Clinical Oncology 12(6):511–518. https://doi.org/10.1200/JOP.2016.012013.
Chandel NS, Schumacker PT (1999) Cells depleted of mitochondrial DNA (rho0) yield insight into physiological mechanisms. FEBS Lett 454(3):173–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00783-8 [pii]
Chistiakov DA, Shkurat TP, Melnichenko AA, Grechko AV, Orekhov AN (2017) The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease: a brief review. Ann Med 50:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2017.1417631
Falloon J, Sargent S, Piscitelli SC, Bechtel C, LaFon SW, Sadler B et al (1999) Atovaquone suspension in HIV-infected volunteers: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and TMP-SMX interaction study. Pharmacotherapy 19(9):1050–1056
Fiorillo M, Lamb R, Tanowitz HB, Mutti L, Krstic-Demonacos M, Cappello AR, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP (2016) Repurposing atovaquone: targeting mitochondrial complex III and OXPHOS to eradicate cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 7(23):34084–34099. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9122.
Fry M, Pudney M (1992) Site of action of the antimalarial hydroxynaphthoquinone, 2-[trans-4-(4′-chlorophenyl) cyclohexyl]-3-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (566C80). Biochem Pharmacol 43(7):1545–1553
Gkouveris I, Nikitakis N, Karanikou M, Rassidakis G, Sklavounou A (2014) Erk1/2 activation and modulation of STAT3 signaling in oral cancer. Oncol Rep 32(5):2175–2182. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2014.3440
Harada Y, Ishii I, Hatake K, Kasahara T (2012) Pyrvinium pamoate inhibits proliferation of myeloma/erythroleukemia cells by suppressing mitochondrial respiratory complex I and STAT3. Cancer Lett 319(1):83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2011.12.034 S0304-3835(11)00793-2 [pii]
Hashiguchi K, Zhang-Akiyama QM (2009) Establishment of human cell lines lacking mitochondrial DNA. Methods Mol Biol 554:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-521-3_23
Jin S, Borkhuu O, Bao W, Yang YT (2016) Signaling pathways in thyroid Cancer and their therapeutic implications. Journal of clinical medicine research 8(4):284–296. https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr2480w
Johnson JM, Lai SY, Cotzia P, Cognetti D, Luginbuhl A, Pribitkin EA, Zhan T, Mollaee M, Domingo-Vidal M, Chen Y, Campling B, Bar-Ad V, Birbe R, Tuluc M, Martinez Outschoorn U, Curry J (2015) Mitochondrial metabolism as a treatment target in anaplastic thyroid Cancer. Semin Oncol 42(6):915–922. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2015.09.025
Kondo T, Ezzat S, Asa SL (2006) Pathogenetic mechanisms in thyroid follicular-cell neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 6(4):292–306. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1836
Lee J, Chang JY, Kang YE, Yi S, Lee MH, Joung KH, Kim KS, Shong M (2015) Mitochondrial energy metabolism and thyroid cancers. Endocrinol Metab 30(2):117–123. https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.117
Momtazi-Borojeni AA, Abdollahi E, Ghasemi F, Caraglia M, Sahebkar A (2017) The novel role of pyrvinium in cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol 233:2871–2881. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26006
Nikiforov YE, Nikiforova MN (2011) Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7(10):569–580. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.142
Qureshi R, Yildirim O, Gasser A, Basmadjian C, Zhao Q, Wilmet JP, Désaubry L, Nebigil CG (2015) FL3, a synthetic Flavagline and ligand of Prohibitins, protects cardiomyocytes via STAT3 from doxorubicin toxicity. PLoS One 10(11):e0141826. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141826
Saiselet M, Floor S, Tarabichi M, Dom G, Hebrant A, van Staveren WC et al (2012) Thyroid cancer cell lines: an overview. Front Endocrinol 3:133. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2012.00133
Sipos JA, Mazzaferri EL (2010) Thyroid cancer epidemiology and prognostic variables. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 22(6):395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2010.05.004
Song L, Turkson J, Karras JG, Jove R, Haura EB (2003) Activation of Stat3 by receptor tyrosine kinases and cytokines regulates survival in human non-small cell carcinoma cells. Oncogene 22(27):4150–4165. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206479
Srivastava IK, Rottenberg H, Vaidya AB (1997) Atovaquone, a broad spectrum antiparasitic drug, collapses mitochondrial membrane potential in a malarial parasite. J Biol Chem 272(7):3961–3966
Wegrzyn J, Potla R, Chwae YJ, Sepuri NB, Zhang Q, Koeck T et al (2009) Function of mitochondrial Stat3 in cellular respiration. Science 323(5915):793–797. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1164551
Weinberg SE, Chandel NS (2015) Targeting mitochondria metabolism for cancer therapy. Nat Chem Biol 11(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1712
Xiang W, Cheong JK, Ang SH, Teo B, Xu P, Asari K et al (2015) Pyrvinium selectively targets blast phase-chronic myeloid leukemia through inhibition of mitochondrial respiration. Oncotarget 6(32):33769–33780. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5615.
Xiang M, Kim H, Ho VT, Walker SR, Bar-Natan M, Anahtar M, Liu S, Toniolo PA, Kroll Y, Jones N, Giaccone ZT, Heppler LN, Ye DQ, Marineau JJ, Shaw D, Bradner JE, Blonquist T, Neuberg D, Hetz C, Stone RM, Soiffer RJ, Frank DA (2016) Gene expression-based discovery of atovaquone as a STAT3 inhibitor and anticancer agent. Blood 128(14):1845–1853. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-07-660506
Xiao M, Zhang L, Zhou Y, Rajoria P, Wang C (2016) Pyrvinium selectively induces apoptosis of lymphoma cells through impairing mitochondrial functions and JAK2/STAT5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 469(3):716–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.059
Yang F, Teves SS, Kemp CJ, Henikoff S (2014) Doxorubicin, DNA torsion, and chromatin dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1845(1):84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2013.12.002
Zhou J, Duan L, Chen H, Ren X, Zhang Z, Zhou F, Liu J, Pei D, Ding K (2009) Atovaquone derivatives as potent cytotoxic and apoptosis inducing agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19(17):5091–5094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.07.044
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Grant from the Health Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Grant No. 216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 369 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Z., Yan, X., Lu, L. et al. Atovaquone enhances doxorubicin’s efficacy via inhibiting mitochondrial respiration and STAT3 in aggressive thyroid cancer. J Bioenerg Biomembr 50, 263–270 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-018-9755-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-018-9755-y