Abstract
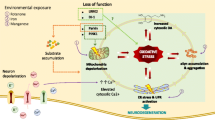
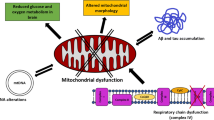
Complex factors contribute to the appearance of Parkinson’s disease (PD), but with a constant mitochondrial involvement. There are two interdependent conditions in PD: brain mitochondrial dysfunction and brain mitochondrial oxidative damage. Mitochondrial dysfunction and reduced complex I activity are recognized in substantia nigra and in frontal cortex in PD patients. The molecular mechanism involved in the inactivation of complex I is likely accounted by the sum of ONOO− mediated reactions, reactions with free radical intermediates of the lipid peroxidation process and amine-aldehyde adduction reactions. The inhibitory effects on complex I lead synergistically to denaturation of the protein structure and to further increases of O −2 and ONOO− production at the vicinity of complex I. An adaptive response in PD patients has been described with increases in mtNOS activity, mitochondrial mass and mitochondrial biogenesis. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the human frontal cortex is to be considered a factor contributing to impaired cognition in PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JD Jr, Odunze IN (1991) Free Radic Biol Med 10:161–169
Bender A, Krishnan KJ, Morris CM, Taylor GA, Reeve AK, Perry RH, Jaros E, Hersheson JS, Betts J, Klopstock T, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM (2006) Nat Genet 38:515–517
Bougria M, Vitorica J, Cano J, Machado A (1995) Eur J Pharmacol 291:407–415
Boveris A, Cadenas E (2000) IUBMB Life 50:245–250
Boveris A, Chance B (1973) Biochem J 134:707–716
Boveris A, Navarro A (2008) IUBMB Life 60:308–314
Boveris A, Stoppani AO (1971) Arch Biochem Biophys 142:150–156
Boveris A, Valdez LB, Zaobornyj T, Bustamante J (2006) Biochim Biophys Acta 1757:535–542
Brown GC, Borutaite V (2004) Biochim Biophys Acta 1658:44–49
Carreras MC, Franco MC, Peralta JG, Poderoso JJ (2004) Mol Aspects Med 25:125–139
Cassarino DS, Halvorsen EM, Swerdlow RH, Abramova NN, Parker WD Jr, Sturgill TW, Bennett JP Jr (2000) J Neurochem 74:1384–1392
Cutler RG (1991) Am J Clin Nutr 53:373S–379S
de Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Lancet Neurol 5:525–535
Dennis J, Bennett JP Jr (2003) J Neurosci Res 72:76–88
Eve DJ, Nisbet AP, Kingsbury AE, Hewson EL, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Marsden CD, Foster OJ (1998) Brain Res Mol Brain Res 63:62–71
Forno LS (1996) J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:259–272
Gatto EM, Riobo NA, Carreras MC, Chernavsky A, Rubio A, Satz ML, Poderoso JJ (2000) Nitric Oxide 4:534–539
Gomez C, Bandez MJ, Navarro A (2007) Front Biosci 12:1079–1093
Gonzalez-Flecha B, Cutrin JC, Boveris A (1993) J Clin Invest 91:456–464
Good PF, Hsu A, Werner P, Perl DP, Olanow CW (1998) J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:338–342
Hensley K, Kotake Y, Sang H, Pye QN, Wallis GL, Kolker LM, Tabatabaie T, Stewart CA, Konishi Y, Nakae D, Floyd RA (2000) Carcinogenesis 21:983–989
Ischiropoulos H (2009) Arch Biochem Biophys 484:117–121
Jellinger KA, Mizuno Y (2003) Parkinson’s disease. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 159–187
Keeney PM, Xie J, Capaldi RA, Bennett JP Jr (2006) J Neurosci 26:5256–5264
Kwong JQ, Beal MF, Manfredi G (2006) J Neurochem 97:1659–1675
Lam PY, Yin F, Hamilton RT, Boveris A, Cadenas E (2009) Free Radic Res 43:431–439
Liu Q, Raina AK, Smith MA, Sayre LM, Perry G (2003) Mol Aspects Med 24:305–313
Mann VM, Cooper JM, Krige D, Daniel SE, Schapira AH, Marsden CD (1992) Brain 115(Pt 2):333–342
McNamara P, Durso R, Harris E (2007) Cognit Neuropsychiatry 12:285–300
Mizuno Y, Ohta S, Tanaka M, Takamiya S, Suzuki K, Sato T, Oya H, Ozawa T, Kagawa Y (1989) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:1450–1455
Navarro A, Boveris A (2008) Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1534–1544
Navarro A, Torrejon R, Bandez MJ, Lopez-Cepero JM, Boveris A (2005) Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 289:E1101–E1109
Navarro A, Lopez-Cepero JM, Bandez MJ, Sanchez-Pino MJ, Gomez C, Cadenas E, Boveris A (2008) Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R501–R509
Navarro A, Boveris A, Bandez MJ, Sanchez-Pino MJ, Gomez C, Muntane G, Ferrer I (2009) Free Radic Biol Med 46:1574–1580
Nisoli E, Falcone S, Tonello C, Cozzi V, Palomba L, Fiorani M, Pisconti A, Brunelli S, Cardile A, Francolini M, Cantoni O, Carruba MO, Moncada S, Clementi E (2004) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:16507–16512
Poon HF, Frasier M, Shreve N, Calabrese V, Wolozin B, Butterfield DA (2005) Neurobiol Dis 18:492–498
Raha S, Robinson BH (2000) Trends Biochem Sci 25:502–508
Riobo NA, Clementi E, Melani M, Boveris A, Cadenas E, Moncada S, Poderoso JJ (2001) Biochem J 359:139–145
Riobo NA, Schopfer FJ, Boveris AD, Cadenas E, Poderoso JJ (2002) Free Radic Biol Med 32:115–121
Schapira AH (2008) Lancet Neurol 7:97–109
Schapira AH, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Jenner P, Clark JB, Marsden CD (1989) Lancet 1:1269
Schapira AH, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Clark JB, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1990a) J Neurochem 54:823–827
Schapira AH, Mann VM, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Daniel SE, Jenner P, Clark JB, Marsden CD (1990b) J Neurochem 55:2142–2145
Tolmasoff JM, Ono T, Cutler RG (1980) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:2777–2781
Turrens JF (2003) J Physiol 552:335–344
Valdez LB, Alvarez S, Lores-Arnaiz S, Schopfer F, Boveris A (2000) Free Radic Biol Med 29:349–356
Valdez LB, Zaobornyj T, Boveris A (2006) Biochim Biophys Acta 1757:166–172
Walker JE (1992) Q Rev Biophys 25:253–324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navarro, A., Boveris, A. Brain mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in Parkinson’s disease. J Bioenerg Biomembr 41, 517–521 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-009-9250-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-009-9250-6