Abstract
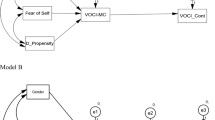
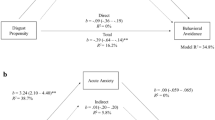
Contamination aversion is implicated in a range of psychological disorders, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder and health anxiety. Despite broad implications, the core mechanisms mediating contamination aversion are mixed and have not clearly been elucidated. The present studies are psychometric investigations of the components of contamination aversion and tests of the different mechanisms that mediate the severity of these components. In Study 1, items from existing measures of contamination aversion were compiled into one measure and administered to a large sample of nonclinical participants (N = 1,286). Exploratory factor analyses demonstrated a two-factor structure, with one factor comprised of items related to intrinsically (direct) contaminated objects and the other factor comprised of items related to extrinsically (indirect) contaminated objects. In Study 2, items were added and confirmatory factor analyses supported a two-factor model in another large nonclinical sample (N = 612). In Study 3 (N = 471), structural modeling demonstrated distinct relations between the two factors and affective and cognitive constructs. Affective constructs related more to aversions toward more directly contaminated objects and situations while cognitive constructs related more to aversions toward more indirectly contaminated objects and situations. The present studies help clarify and articulate the unique roles of cognition and affect in specific contamination aversions, and, as such, have important implications for conceptual modeling of contamination-related psychopathology.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A list of all items comprising the initial 59-item CAS is available upon request from the first author.
References
Abramowitz, J. S., Deacon, B. J., Olatunji, B. O., Wheaton, M. G., Berman, N. C., Losardo, D., et al. (2010). Assessment of obsessive-compulsive symptom dimensions: development and evaluation of the dimensional obsessive-compulsive scale. Psychological Assessment, 22, 180–198.
Adams, T., Cisler, J., Brady, R., & Lohr, J. (2012). The effects of cognitive and affective priming on law of contagion appraisals. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology, 3, 470–478.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2007). AMOS (Version 7) [Computer software]. Chicago: SPSS.
Armstrong, T., & Olatunji, B. O. (2010). Orienting and maintenance of gaze in contamination-based OCD: biases for disgust and fear cues. Behavior Research and Therapy 48, 402–408.
Burns, G. L., Keortge, S. G., Formea, G. M., & Sternberger, L. G. (1996). Revision of the Padua Inventory of obsessive compulsive disorder symptoms: distinctions between worry, obsessions, and compulsions. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 34, 163–173.
Cisler, J. M., & Olatunji, B. O. (2010). Components of attentional biases in contamination fear: evidence for difficulty in disengagement. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 48, 74–78.
Cisler, J. M., Olatunji, B. O., Sawchuk, C. N., & Lohr, J. M. (2008). Specificity of emotional maintenance processes among contamination fears and blood-injection-injury fears. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 22, 915–923.
Cisler, J. M., Olatunji, B. O., & Lohr, J. M. (2009a). Disgust, fear, and the anxiety disorders: a critical review. Clinical Psychology Review, 29, 34–46.
Cisler, J. M., Olatunji, B. O., & Lohr, J. M. (2009b). Disgust sensitivity and emotion regulation potentiate the effect of disgust propensity on spider fear, blood-injection-injury fear, and contamination fear. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 40, 219–229.
Cisler, J. M., Adams, T. G., Brady, R. E., Bridges, A. J., Lohr, J. M., & Olatunji, B. O. (2010a). Unique affective and cognitive processes in contamination appraisals: implications for contamination fear. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 25, 28–35.
Cisler, J. M., Olatunji, B. O., Feldner, M. T., & Forsyth, J. P. (2010b). Emotion regulation and the anxiety disorders: an integrative review. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 32, 68–82.
Cisler, J. M., Brady, R. E., Olatunji, B. O., & Lohr, J. M. (2010c). Disgust and obsessive beliefs in contamination-related OCD. Cognitive Therapy and Research 34, 439–448.
Clark, D. M. (1986). A cognitive approach to panic. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 24, 461–470.
Cougle, J. R., Wolitzky-Taylor, K. B., Lee, H., & Telch, M. J. (2007). Mechanisms of change in ERP treatment of compulsive hand washing: does primary threat make a difference? Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45, 1449–1459.
Cudeck, R. (2000). Exploratory factor analysis. In H. E. A. Tinsley & S. D. Brown (Eds.), Handbook of applied multivariate statistics and mathematical modeling (pp. 265–296). San Diego: Academic.
Curtis, V., Aunger, R., & Rabie, T. (2004). Evidence that disgust evolved to protect from risk of disease. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences, 271, 131–133.
Deacon, B., & Olatunji, B. O. (2007). Specificity of disgust sensitivity in the prediction of behavioral avoidance in contamination fear. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45, 2110–2120.
Denys, D., de Geus, F., van Megen, H. J. G. M., & Westenberg, H. G. M. (2004). Symptom dimensions in obsessive-compulsive disorder: factor analysis on a clinician-rated scale and a self-report measure. Psychopathology, 37, 181–189.
Duncan, L. A., Schaller, M., & Park, J. H. (2009). Perceived vulnerability to disease: development and validation of a 15-item self-report instrument. Personality and Individual Differences, 47, 541–546.
Floyd, F. J., & Widaman, K. F. (1995). Factor analysis in the development and refinement of clinical assessment instruments. Psychological Assessment, 7, 286–299.
Foa, E. B., Kozak, M. J., Salkovskis, P. M., Coles, M. E., & Amir, N. (1998). The validation of a new obsessive-compulsive scale: the obsessive-compulsive inventory. Psychological Assessment, 10, 206–214.
Foa, E. B., Huppert, J. D., Leiberg, S., Langner, R., Kichic, R., Hajcak, G., et al. (2002). The obsessive-compulsive inventory: development and validation of a short version. Psychological Assessment, 14, 485–496.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18, 39–50.
Frazer, J. G. (1922). The golden bough. New York: Macmillan. Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/196/.
Goodman, W. K., Price, L. H., Rasmussen, S. A., Mazure, C., Fleischmann, R. L., Hill, C. L., et al. (1989). The yale-brown obsessive compulsive scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Archives of General Psychiatry, 46, 1006–1011.
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: Development, factor structure, and initial validation of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 36, 41–54.
Gross, J. J. (1998). The emerging field of emotion regulation: an integrative review. Review of General Psychology, 2, 271–299.
Gross, J. J. (1999). Emotion regulation: past, present, future. Cognition and Emotion, 13, 551–573.
Haidt, J., McCauley, C., & Rozin, P. (1994). Individual differences in sensitivity to disgust: A scale sampling seven domains of disgust elicitors. Personality and Individual Differences, 16, 701–713.
Hodgson, R., & Rachman, S. (1977). Obsessional compulsive complaints. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 15, 389–395.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1–55.
Jones, M. K., & Menzies, R. G. (1997). The cognitive mediation of obsessive–compulsive handwashing. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 35, 843–850.
Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
Laposa, J. M., & Rector, N. A. (2009). Cognitive bias to symptom and obsessive belief threat cues in obsessive-compulsive disorder. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 197, 599–605.
McKay, D., & Moretz, M. W. (2009). The intersection of disgust and contamination fear. In B. Olatunji & D. Mckay (Eds.), Disgust and its disorders: Theory, assessment, and treatment implications (pp. 211–227). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
McKay, D., & Tsao, S. D. (2005). A treatment most foul: handling disgust in cognitive-behavior therapy. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 19, 355–367.
Moretz, M. W., & Mckay, D. (2008). Disgust sensitivity as a predictor of obsessive-compulsive contamination sympotoms and associated cognitions. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 22, 707–715.
Nemeroff, C., & Rozin, P. (1994). The contagion concept in adult thinking in the United States: transmission of germs and of interpersonal influence. Ethos, 22, 158–186.
Oaten, M., Stevenson, R. J., & Case, T. I. (2009). Disgust as a disease-avoidance mechanism. Psychological Bulletin, 135, 303–321.
Obsessive Compulsive Cognitions Working Group. (1997). Cognitive assessment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 35, 667–681.
Obsessive Compulsive Cognitions Working Group. (2005). Psychometric validation of the obsessive belief questionnaire and interpretation of intrusions inventory—Part II: factor analyses and testing of a brief version. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 43, 1527–1542.
Ochsner, K. N., & Gross, J. J. (2008). Cognitive emotion regulation: insights from social cognitive and affective neuroscience. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 17, 153–158.
Olatunji, B. O., & Broman-Fulks, J. J. (2009). Latent structure of aversion: taxometric exploration. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 23, 87–92.
Olatunji, B. O., & McKay, D. (2007). Disgust and psychiatric illness: have we remembered? The British Journal of Psychiatry, 190, 457–459.
Olatunji, B. O., & Sawchuk, C. N. (2005). Disgust: characteristic features, social manifestations, and clinical implications. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 24, 932–962.
Olatunji, B. O., Sawchuk, C. N., Lohr, J. M., & de Jong, P. J. (2004). Disgust domains in the prediction of contamination fear. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 42, 93–104.
Olatunji, B. O., Lohr, J. M., Sawchuk, C. N., & Tolin, D. F. (2007). Multimodal assessment of disgust in contamination-related obsessive-compulsive disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45, 263–276.
Olatunji, B. O., Williams, N., Lohr, J. M., Connolly, K., Cisler, J., & Meunier, S. (2007). Structural differentiation of disgust from trait anxiety in the prediction of specific anxiety disorder symptoms. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45, 3002–3017.
Olatunji, B. O., Williams, N. L., Tolin, D. F., Abramowitz, J. S., Sawchuk, C. N., Lohr, J. M., et al. (2007). The disgust scale: item analysis, factor structure, and suggestions for refinement. Psychological Assessment, 19, 281–297.
Olatunji, B. O., Cisler, J., McKay, D., & Phillips, M. L. (2010). Is disgust associated with psychopathology? Emerging research in the anxiety disorders. Psychiatry Research, 175, 1–10.
Rachman, S. (2004). Fear of contamination. Behavior Research and Therapy, 42, 1227–1255.
Rachman, S. (2006). Fear of contamination: Assessment and treatment. New York: Oxford University Press Inc.
Radomsky, A., & Rachman, S. (1999). Memory bias in obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Behavior Research and Therapy, 37, 605–618.
Rozin, P., & Fallon, A. E. (1987). A perspective on disgust. Psychological Review, 94, 23–41.
Rozin, P., Haidt, J., McCauley, C., Dunlop, L., & Ashmore, M. (1999). Individual differences in disgust sensitivity: comparisons and evaluations of paper-and-pencil versus behavioral measures. Journal of Research in Personality, 33, 330–351.
Sanavio, E. (1988). Obsessions and compulsions: the Padua Inventory. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 26, 169–177.
Siegal, M., Fadda, R., & Overton, P. G. (2011). Contamination sensitivity and the development of disease-avoidant behaviour. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 366, 3427–3432.
Stopa, L., & Clark, D. M. (1993). Cognitive processes in social phobia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 31, 255–267.
Taylor, S., Zvolensky, M., Cox, B., Deacon, B., Heimberg, R., Ledley, D., et al. (2007). Robust dimensions of anxiety sensitivity: development and initial validation of the Anxiety Sensitivity Index—3. Psychological Assessment, 19, 176–188.
Thordarson, D. S., Radomsky, A. S., Rachman, S., Shafran, R., Sawchuk, C. N., & Hakstian, R. A. (2004). The Vancouver Obsessional Compulsive Inventory (VOCI). Behaviour Research and Therapy, 42, 1289–1314.
Tolin, D. F., Woods, C. M., & Abramowitz, J. S. (2003). Relationship between obsessive beliefs and obsessive-compulsive symptoms. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 27, 657–669.
Tolin, D. F., Worhunsky, P., & Maltby, N. (2004). Sympathetic magic in contamination-related OCD. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 35, 193–205.
Tolin, D. F., Brady, R. E., & Hannan, S. (2008). Obsessional beliefs and symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder in a clinical sample. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 30, 31–42.
Toronchuk, J. A., & Ellis, G. F. R. (2007). Disgust: sensory affect or primary emotional system. Cognition and Emotion, 21, 1799–1818.
Tsao, S. D., & Mckay, D. (2004). Behavioral avoidance tests and disgust in contamination fears: distinctions from trait anxiety. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 42, 207–216.
van Overveld, W. J. M., de Jong, P. J., Peters, M. L., Cavanagh, K., & Davey, G. C. L. (2006). Disgust propensity and disgust sensitivity: separate constructs that are differentially related to specific fears. Personality and Individual Differences, 41, 1241–1252.
Wells, A. (1995). Meta-cognition and worry: a cognitive model of generalized anxiety disorder. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 23, 301–320.
Woody, S. R., & Teachman, B. A. (2000). Intersection of disgust and fear: normative and pathological views. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 7, 291–311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adams, T.G., Cisler, J.M., Brady, R.E. et al. Preliminary Psychometric Evidence for Distinct Affective and Cognitive Mechanisms Mediating Contamination Aversion. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 35, 375–388 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-013-9343-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-013-9343-8