Abstract
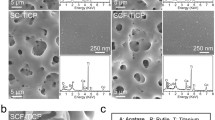
Ti-based implants sometimes fail to integrate with surrounding bone tissue due to insufficiency of new bone formation and surface bonding. To overcome this problem, this research focused on establishing a sustained bone growth factor delivery system by applying anodized TiO2 nanotube arrays and PLGA film on the titanium implant surface. TiO2 nanotube arrays were made by anodic oxidation method, and were then filled with rhBMP2 by vacuum freeze-drying. Next, PLGA was deposition on the surface of this material. The designed system was characterized, pharmacokinetic release rate of rhBMP2 was determined. Adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation activity of osteoblasts cultured on the new surfaces and traditional titanium surfaced were compared. SEM showed that a surface of TiO2 nanotube arrays were successfully generated. PLGA membranes of 50 nm, 250 nm, 800 nm thickness were successfully deposited on the surfaces of TiO2 nanotube layers by using 1%, 3%, 10% PLGA solutions. PLGA film of 250 nm thickness showed ideally controlled release of rhBMP2, lasting for 4 weeks. Furthermore, 250 nm thickness PLGA film improved osteoblast adhesion, proliferation, and levels of alkaline phosphatase. In conclusion, the PLGA film / TiO2 nanotube growth factor delivery system can effectively sustain the release of rhBMP-2, and promote proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niinomi M. Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2008;1(1):30–42.
Ardura JA, Portal‐Núñez S, Lozano D, Gutiérrez‐Rojas I, Sánchez‐Salcedo S, López‐Herradón A, et al. Local delivery of parathyroid hormone‐related protein‐derived peptides coated onto a hydroxyapatite‐based implant enhances bone regeneration in old and diabetic rats. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(8):2060–70.
Oates TW, Galloway P, Alexander P, Green AV, Huynh-Ba G, Feine J, et al. The effects of elevated hemoglobin A 1c in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on dental implants. J Am Dent Assoc. 2014;145(12):1218–26.
Gómez‐Moreno G, Aguilar‐Salvatierra A, Rubio Roldán J, Guardia J, Gargallo J, Calvo‐Guirado JL. Peri‐implant evaluation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a 3‐year study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(9):1031–5.
Bagherifard S, Ghelichi R, Khademhosseini A, Guagliano M. Cell response to nanocrystallized metallic substrates obtained through severe plastic deformation. ACS Appl Mater & Interfaces. 2014;6(11):7963–85.
Kalemaj Z, Scarano A, Valbonetti L, Rapone B, Grassi FR. Bone Response to Four Dental Implants with Different Surface Topographies: A Histologic and Histometric Study in Minipigs. Int J Periodontics & Restor Dent. 2016;36(5):745–54.
Liu W, Su P, Chen S, Wang N, Wang J, Liu Y, et al. Antibacterial and osteogenic stem cell differentiation properties of photoinduced TiO2 nanoparticle-decorated TiO2 nanotubes. Nanomedicine. 2015;10(5):713–23.
Balasundaram G, Yao C, Webster TJ. TiO2 nanotubes functionalized with regions of bone morphogenetic protein‐2 increases osteoblast adhesion. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;84(2):447–53.
Lee K, Mazare A, Schmuki P. One-dimensional titanium dioxide nanomaterials: nanotubes. Chemical Reviews. 2014;114(19):9385–454.
Salou L, Hoornaert A, Louarn G, Layrolle P. Enhanced osseointegration of titanium implants with nanostructured surfaces: an experimental study in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2015;11:494–502.
Justin D, Jin S, Frandsen C, Brammer K, Bjursten L, Oh S, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of implant surfaces treated with titanium oxide (TiO2) nanotube arrays to enhance osseointegration between arthroplasty implants and surrounding bone. Bone Jt J. 2016;98(SUPP8):71.
Brammer KS, Frandsen CJ, Jin S. TiO 2 nanotubes for bone regeneration. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(6):315–22.
Kumeria T, Mon H, Aw MS, Gulati K, Santos A, Griesser HJ, et al. Advanced biopolymer-coated drug-releasing titania nanotubes (TNTs) implants with simultaneously enhanced osteoblast adhesion and antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2015;130:255–63.
Lee J-K, Cho L-R, Um H-S, Chang B-S, Cho K-S. Bone formation and remodeling of three different dental implant surfaces with Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 in a rabbit model. Int J Oral & Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(2):424–30.
James AW, LaChaud G, Shen J, Asatrian G, Nguyen V, Zhang X, et al. A review of the clinical side effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B: Rev. 2016;22(4):284–97.
Zara JN, Siu RK, Zhang X, Shen J, Ngo R, Lee M, et al. High doses of bone morphogenetic protein 2 induce structurally abnormal bone and inflammation in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(9-10):1389–99.
Yang HS, La W-G, Bhang SH, Jeon J-Y, Lee JH, Kim B-S. Heparin-conjugated fibrin as an injectable system for sustained delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(4):1225–33.
Bai Y, Yin G, Huang Z, Liao X, Chen X, Yao Y, et al. Localized delivery of growth factors for angiogenesis and bone formation in tissue engineering. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;16(2):214–23.
Bae IH, Yun KD, Kim HS, Jeong BC, Lim HP, Park SW, et al. Anodic oxidized nanotubular titanium implants enhance bone morphogenetic protein‐2 delivery. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater. 2010;93(2):484–91.
Xu Y, Kim CS, Saylor DM, Koo D. Polymer degradation and drug delivery in PLGA‐based drug–polymer applications: A review of experiments and theories. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater. 2016;105(6):1692–716.
Qi R, Guo R, Zheng F, Liu H, Yu J, Shi X. Controlled release and antibacterial activity of antibiotic-loaded electrospun halloysite/poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) composite nanofibers. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2013;110:148–55.
Meng ZX, Xu XX, Zheng W, Zhou HM, Li L, Zheng YF, et al. Preparation and characterization of electrospun PLGA/gelatin nanofibers as a potential drug delivery system. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2011;84(1):97–102.
Zodrow KR, Schiffman JD, Elimelech M. Biodegradable polymer (PLGA) coatings featuring cinnamaldehyde and carvacrol mitigate biofilm formation. Langmuir. 2012;28(39):13993–9.
Meng H-W, Chien EY, Chien H-H. Dental implant bioactive surface modifications and their effects on osseointegration: a review. Biomark Res. 2016;4(1):24.
W-q Yu, Qiu J, Zhang F-q. In vitro corrosion study of different TiO 2 nanotube layers on titanium in solution with serum proteins. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2011;84(2):400–5.
Samadi N, Abbadessa A, Di Stefano A, Van Nostrum C, Vermonden T, Rahimian S, et al. The effect of lauryl capping group on protein release and degradation of poly (d, l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) particles. J Control Release. 2013;172(2):436–43.
Kim BS, Kang H-J, Park J-Y, Lee J. Fucoidan promotes osteoblast differentiation via JNK-and ERK-dependent BMP2–Smad 1/5/8 signaling in human mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Mol Med. 2015;47(1):e128.
Funding
This study was funded by Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (S30206 and T0202), Science and Technology committee of Shanghai (08DZ2271100, ZZjdyx13107, and 15XD1502500), National Natural Science Funds of China (81300912), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (ZR2017BH030), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M561942).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, S., Zhang, Y., Zeng, D. et al. PLGA film/Titanium nanotubues as a sustained growth factor releasing system for dental implants. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 29, 141 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-018-6138-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-018-6138-1