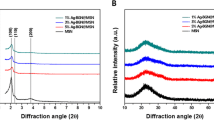
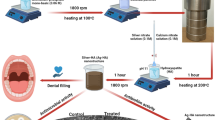
Abstract
The main purpose of this study was to investigate the substantivity of Ag–Ca–Si mesoporous nanoparticles (Ag-MCSNs) on dentin and its residual antibacterial effects against Enterococcus faecalis. Ag-MCSNs were fabricated and characterized, ion release profile and pH were tested, and the ability to inhibit planktonic E. faecalis as well as the cytotoxicity was evaluated. Dentin slices were medicated with Ca(OH)2 paste, 2 % chlorhexidine gel and Ag-MCSNs paste for 7 days and then irrigated. Dentin slices were then immersed in E. faecalis suspension for 6 days and then transferred to fresh brain heart infusion solution. The optical density value within 10 h after immersing and transferring were measured and compared among groups. Results indicated that Ag-MCSNs showed high pH, sustained Ag+–Ca2+–SiO3 2− ion release, and high substantivity on dentin. The Ag-MCSNs exhibited strong antibacterial effects against planktonic E. faecalis and much better residual inhibition effects against E. faecalis growth on dentin than Ca(OH)2 paste (P < 0.05). The Ag-MCSNs showed excellent antibacterial ability against E. faecalis and high substantivity on dentin, which might be developed to a new effective intra-canal medicament for human teeth.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nair PN. Pathogenesis of apical periodontitis and the causes of endodontic failures. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004;15:348–81.
Carr GB, Schwartz RS, Schaudinn C, Gorur A, Costerton JW. Ultrastructural examination of failed molar retreatment with secondary apical periodontitis: an examination of endodontic biofilms in an endodontic retreatment failure. J Endod. 2009;35:1303–9.
Love RM. Enterococcus faecalis–a mechanism for its role in endodontic failure. Int Endod J. 2001;34:399–405.
Mohammadi Z, Shalavi S, Yazdizadeh M. Antimicrobial activity of calcium hydroxide in endodontics: a review. Chonnam Med J. 2012;48:133–40.
Garcia-Caballero L, Quintas V, Prada-Lopez I, Seoane J, Donos N, Tomas I. Chlorhexidine substantivity on salivary flora and plaque-like biofilm: an in situ model. PLoS One. 2013;8:e83522.
Rahimi S, Janani M, Lotfi M, Shahi S, Aghbali A, Vahid Pakdel M, et al. A review of antibacterial agents in endodontic treatment. Iran Endod J. 2014;9:161–8.
Mohammadi Z, Abbott PV. Antimicrobial substantivity of root canal irrigants and medicaments: a review. Aust Endod J. 2009;35:131–9.
Kishen A. Advanced therapeutic options for endodontic biofilms. Endod Top. 2012;22:99–123.
Moritz M, Geszke-Moritz M. Mesoporous materials as multifunctional tools in biosciences: principles and applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2015;49C:114–51.
Fan W, Wu C, Han P, Zhou Y, Xiao Y. Porous Ca-Si-based nanospheres: a potential intra-canal disinfectant-carrier for infected canal treatment. Mater Lett. 2012;81:16–9.
Fan W, Wu D, Tay FR, Ma T, Wu Y, Fan B. Effects of adsorbed and templated nanosilver in mesoporous calcium-silicate nanoparticles on inhibition of bacteria colonization of dentin. Int J Nanomed. 2014;9:5217–30.
Wu C, Chang J, Fan W. Bioactive mesoporous calcium-silicate nanoparticles with excellent mineralization ability, osteostimulation, drug-delivery and antibacterial properties for filling apex roots of teeth. J Mater Chem. 2012;22:16801–9.
Fan W, Wu D, Ma T, Fan B. Ag-loaded mesoporous bioactive glasses against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm in root canal of human teeth. Dent Mater J. 2015;34:54–60.
Kasraei S, Sami L, Hendi S, Alikhani MY, Rezaei-Soufi L, Khamverdi Z. Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus. Restor Dent Endod. 2014;39:109–14.
Sre PRR, Reka M, Poovazhagi R, Kumar MA, Murugesan K. Antibacterial and cytotoxic effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using aqueous root extract of Erythrina indica lam. Spectrochim Acta A. 2014;135:1137–44.
Souza M, Cecchin D, Farina AP, Leite CE, Cruz FF, Pereira Cda C, et al. Evaluation of chlorhexidine substantivity on human dentin: a chemical analysis. J Endod. 2012;38:1249–52.
Moazami F, Sahebi S, Jamshidi D, Alavi A. The long-term effect of calcium hydroxide, calcium-enriched mixture cement and mineral trioxide aggregate on dentin strength. Iran Endod J. 2014;9:185–9.
White JD, Lacefield WR, Chavers LS, Eleazer PD. The effect of three commonly used endodontic materials on the strength and hardness of root dentin. J Endod. 2002;28:828–30.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81271130), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, China (Grant No. 2013CFB241) and the Innovation Seed Fund of Wuhan University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Wei Fan and Yujie Wu are the co-first authors with equal contributions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, W., Wu, Y., Ma, T. et al. Substantivity of Ag–Ca–Si mesoporous nanoparticles on dentin and its ability to inhibit Enterococcus faecalis . J Mater Sci: Mater Med 27, 16 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-015-5633-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-015-5633-x