Abstract
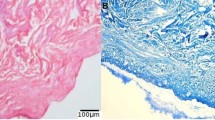
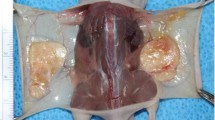
Soft tissue augmentation using acellular dermal matrix has gained popularity to overcome the shortcomings of autogenous and alloplastic materials. Sometimes it needs multilayered stacking to obtain enough volume. In this study, we investigated the efficacy of multilayered implantation using acellular dermal matrix (MatriDerm®) for soft tissue augmentation. MatriDerm was implanted subdermally on each side of the dorsum of nude mice (n = 20), stacked two layers thick in the control group and three layers thick in the experimental group. Alterations of thickness, degree of angiogenesis, and collagen and elastin fiber syntheses were observed over 40 days. Three-layered implantation with MatriDerm maintained its volume similarly as in two-layered implantation, although the thickness decreased after 30 days in both groups. At the early stage of implantation, angiogenesis and collagen and elastin fiber syntheses occurred fluently on the central portion, which is the farthest away from the surface in contact with the host tissue. Collagen and elastin fibers became more concentrated over time, and the original structure of MatriDerm could not be maintained due to being replaced with newly formed collagen and elastin fibers 40 days after implantation. Multilayered implantation with MatriDerm is considered appropriate for tissue ingrowth and can be used as a substitute for soft tissue augmentation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sclafani AP, Romo T, Jacono AA, McCormick S, Cocker R, Parker A. Evaluation of acellular dermal graft in sheet (AlloDerm) and injectable (micronized AlloDerm) forms for soft tissue augmentation. Clinical observations and histological analysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2000;2:130–6.
Tham C, Lai Y, Weng C, Chen Y. Silicone augmentation rhinoplasty in an Oriental population. Ann Plast Surg. 2005;54:1–5.
Sherris DA, Oriel BS. Human acellular dermal matrix grafts for rhinoplasty. Aesthet Surg J. 2011;31:95S–100S.
Achauer BM, VanderKam VM, Celikoz B, Jacobson DG. Augmentation of facial soft-tissue defects with Alloderm dermal graft. Ann Plast Surg. 1998;41:503–7.
Biesman BS, Wesley RE, Klippenstein KA, Termin P, Elson ML. Histopathologic evaluation of a new dermal allograft following explantation. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:985–8.
Baxter RA. Intracapsular allogenic dermal grafts for breast implant-related problems. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;112:1692–6.
Cole PD, Stal D, Sharabi SE, Hicks J, Hollier LH. A comparative, long-term assessment of four soft tissue substitutes. Aesthet Surg J. 2011;31:674–81.
Hwang K, Hwang JH, Park JH, Kim DJ, Shin YH. Experimental study of autologous cartilage, acellular cadaveric dermis, lyophilized bovine pericardium, and irradiated bovine tendon: applicability to nasal tip plasty. J Craniofac Surg. 2007;18:551–8.
Wong AK, Schonmeyr B, Singh P, Carlson DL, Li S, Mehrara BJ. Histologic analysis of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in acellular human dermis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121:1144–52.
Cervelli V, Brinci L, Spallone D, Tati E, Palla L, Lucarini L, De Angelis B. The use of MatriDerm® and skin grafting in post-traumatic wounds. Int Wound J. 2011;8:400–5.
Garramone CE, Lam B. Use of AlloDerm in primary nipple reconstruction to improve long-term nipple projection. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119:1663–8.
Nahabedian MY. Acellular dermal matrices in primary breast reconstruction: principles, concepts, and indications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130:44S–53S.
Haslik W, Kamolz LP, Manna F, Hladik M, Rath T, Frey M. Management of full-thickness skin defects in the hand and wrist region: first long-term experiences with the dermal matrix Matriderm. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63:360–4.
Yannas IV, Burke JF. Design of an artificial skin. I. Basic design principles. J Biomed Mater Res. 1980;14:65–81.
Sclafani AP, Romo T, Jacono AA, McCormick SA, Cocker R, Parker A. Evaluation of acellular dermal graft (AlloDerm) sheet for soft tissue augmentation: a 1-year follow-up of clinical observations and histological findings. Arch Fac Plast Surg. 2001;3:101–3.
Gryskiewicz JM. Dorsal augmentation with AlloDerm. Semin Plast Surg. 2008;22:90–103.
Tobin HA, Karas ND. Lip augmentation using an alloderm graft. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998;56:722–7.
Lee JH, Park KR, Kim TG, Ha JH, Chung KJ, Kim YH, Lee SJ, Kang SH. A Comparative study of CG CryoDerm and AlloDerm in direct-to-implant immediate breast reconstruction. Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40:374–9.
Carlson TL, Lee KW, Pierce LM. Effect of cross-linked and non-cross-linked acellular dermal matrices on the expression of mediators involved in wound healing and matrix remodeling. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131:697–705.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2011-0022012, Lee WJ and No. 2013R1A1A1009764, Lee DW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.W., Lee, M.C., Roh, H. et al. Multilayered implantation using acellular dermal matrix into nude mice. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 25, 2669–2676 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5281-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5281-6