Abstract
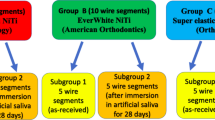
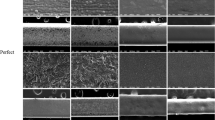
The objective of the article is to study surface topographic changes and nickel release in lingual orthodontic archwires in vitro. Stainless steel (SS), nickel–titanium (NiTi) and copper–nickel–titanium (CuNiTi) lingual orthodontic archwires were studied using atomic absorption spectrometry for nickel release after immersion in a saline solution. Surface roughness changes were measured using atomic force microscopy. Differences between groups were analyzed using independent sample t-tests. Statistically significant changes in roughness were seen in all archwires except NiTi. Surface changes were most severe in the CuNiTi alloy. SS archwires released the highest amount of nickel. In conclusion, only roughness changes in CuNiTi archwires seemed to be clinically significant. The amount of nickel released for all archwires tested is below the levels known to cause cell damage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daems J, Celis JP, Willems G. Morphological characterization of as-received and in vivo orthodontic stainless steel archwires. Eur J Orthod. 2009;31:260–5.
McCann HC. Inorganic components of salivary secretions. In: Harris RS, editor. Art and science of dental caries research. New York: Academic Press; 1968. p. 55–70.
Walker MP, White RJ, Kula KS. Effect of fluoride prophylactic agents on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium-based orthodontic wires. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2005;127:662–9.
Kaneko K, Yokoyama K, Moriyama K, Asaoka K, Sakai J. Degradation in performance of orthodontic wires caused by hydrogen absorption during short-term immersion in 2.0% acidulated phosphate fluoride solution. Angle Orthod. 2004;74:487–95.
Yokohama K, Kaneko K, Ogawa T, Moriyama K, Asaoka K, Sakai J. Hydrogen embrittlement of work-hardened Ni–Ti alloy in fluoride solutions. Biomaterials. 2005;26:101–8.
Schiff N, Grosgogeat B, Lissac M, Dalard F. Influence of fluoridated mouthwashes on corrosion resistance of orthodontic wires. Biomaterials. 2004;25:4535–42.
Ogawa T, Yokoyama K, Asaoka K, Sakai J. Hydrogen absorption behavior of beta-titanium alloy in acid fluoride solutions. Biomaterials. 2004;25:2419–25.
Kaneko K, Yokoyama K, Moriyama K, Asaoka K, Sakai J, Nagumo M. Delayed fracture of beta titanium orthodontic wire in fluoride aqueous solutions. Biomaterials. 2003;24:2113–20.
House K, Sernetz F, Dymock D, Sandy JR, Ireland AJ. Corrosion of orthodontic appliances-should we care? Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2008;133:584–92.
Verstrynge A, van Humbeeck J, Willems G. In vitro evaluation of the material characteristics of stainless steel and beta-titanium orthodontic wires. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2006;130:460–70.
Kim H, Johnson JW. Corrosion of stainless steel, nickel-titanium, coated nickel-titanium, and titanium orthodontic wires. Angle Orthod. 1999;69:39–44.
Pereira MC, Pereira ML, Sousa JP. Histological effects of iron accumulation on mice liver and spleen after administration of a metallic solution. Biomaterials. 1999;20:2193–8.
Bourauel C, Fries T, Drescher D, Plietsch R. Surface roughness of orthodontic wires via atomic force microscopy, laser specular reflectance, and profilometry. Eur J Orthod. 1998;20:79–92.
Schiff N, Boinet M, Morgon L, Lissac M, Dalard F, Grosgeat B. Galvanic corrosion between orthodontic wires and brackets in flouride mouthwashes. Eur J Orthod. 2006;28:298–304.
Oh K-T, Kim K-N. Ion release and cytotoxicity of stainless steel wires. Eur J Orthod. 2005;27:533–40.
Fischer-Brandies H, Es-Souni M, Kock N, Raetzke K, Bock O. Transformation behavior, chemical composition, surface topography and bending properties of five selected 0.016×0.022″ NiTi archwires. J Orofac Orthop. 2003;64:88–99.
McKay GC, Macnair R, MacDonald C, Grant MH. Interactions of orthopaedic metals with an immortalized rat osteoblast cell line. Biomaterials. 1996;17:1339–44.
Kerosuo H, Kullaa A, Kerosuo E, Kanerva L, Hensten-Petterson A. Nickel allergy in adolescents in relation to orthodontic treatment and piercing of ears. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1996;109:148–54.
Berger-Gorbet M, Broxup B, Rivard C, Yahia L’H. Biocompatibility testing of Ni–Ti screw using immuno histochemistry on sections containing metallic implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 1996;32:243–8.
Bass JK, Fine H, Cisnero CJ. Nickel hypersensitivity in the prosthodontics patient. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1993;103:280–5.
Grimsdottir MR, Hensten-Pettersen A, Kulmann A. Proliferation of nickel sensitive human lymphocytes by corrosion products of orthodontic appliances. Biomaterials. 1994;15:1157–60.
International Agency for Research on Cancer. Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans. Lyon, France: IARC; 1996.
Zhou D, Salnikow K, Costa M. Cap43, a novel gene specifically induced by Ni2+ compounds. Cancer Res. 1998;58:2182–9.
Salnikow K, Gao M, Voitkun V, Huang X, Costa M. Altered oxidative stress responses in nickel-resistant mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1994;24:6407–12.
Grimsdottir MR, Hensten-Pettersen A, Kulmann A. Cytotoxic effect of orthodontic appliances. Eur J Orthod. 1992;14:47–53.
Ryhanen J, Niemi E, Serlo W, Niemela E, Sandvik P, Pernu H, et al. Biocompatibility of nickel-titanium shape memory metal and its corrosion behavior in human cell cultures. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;35:451–7.
Schwaninger B, Sarkar NK, Foster BE. Effect of long-term immersion corrosion on the flexural properties of nitinol. Am J Orthod. 1982;82:45–9.
Kurz C, Swartz ML, Andreiko C. Lingual orthodontics: a status report. Part 2: research and development. J Clin Orthod. 1982;16:735–40.
Fujita K. New orthodontic treatment with lingual bracket and mushroom archwire appliance. Am J Orthod. 1979;76:657–75.
Fujita K. Multilingual bracket and mushroom arch wire technique. A clinical report. Am J Orthod. 1982;82:120–40.
Widu F, Drescher D, Junker R, Bourauel C. Corrosion and biocompatibility of orthodontic wires. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1999;10:275–81.
Drescher D, Bourauel C, Schumacher HA. Frictional forces between bracket and archwire. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1989;96:397–404.
Barrett RD, Bishara SE, Quinn JK. Biodegradation of orthodontic appliances, I biodegradation of nickel and chromium in vitro. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1993;103:8–14.
Park HY, Shearer TR. In vitro release of nickel and chromium from simulated orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod. 1983;84:156–9.
Kerosuo H, Moe G, Kleven E. In vitro release of nickel and chromium from different types of simulated orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod. 1995;65:111–6.
Jia W, Beatty MW, Reinhardt RA, Petro TM, Cohen DM, Maze CR, et al. Nickel release from orthodontic arch wires and cellular immune response to various nickel concentrations. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;48:488–95.
Grimsdottir MR, Gjerdet NR, Hensten-Pettersen A. Composition and in vitro corrosion of orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1992;101:525–32.
Delescluse J, Dinet Y. Nickel allergy in Europe: the new European legislation. Dermatology. 1994;189(2):56–7.
Vreeburg KJJ, de Groot K, von Blomberg BME, Scheper RJ. Induction of immunological tolerance by oral administration of nickel and chromium. J Dent Res. 1984;63:124–8.
Hwang CJ, Shin JS, Cha JY. Metal release from simulated fixed orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2001;120:383–9.
Gil FJ, Solano E, Peña J, Engel E, Mendoza A, Planell JA. Microstructural, mechanical and cytotoxicity evaluation of different NiTi and NiTiCu shape memory alloys. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004;15:1181–5.
Locci P, Marinucci L, Lilli C, Belcastro S, Staffolani N, Bellocchio S, et al. Biocompatibility of alloys used in orthodontics evaluated by cell culture tests. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51:561–8.
Fahmy B, Cormier SA. Copper oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in airway epithelial cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2009; Aug 19 (Epub ahead of print).
Karlsson HL, Gustafsson J, Cronholm P, Möller L. Size-dependent toxicity of metal oxide particles—a comparison between nano and micrometer size. Toxicol Lett. 2009;188:112–8.
Quinn JF, Crane S, Harris C, Wadsworth TL. Copper in Alzheimer’s disease: too much or too little? Expert Rev Neurother. 2009;9:631–7.
Michelberger DJ, Eadie RL, Faulkner MG, Glover KE, Prasad NG, Major PW. The friction and wear patterns of orthodontic brackets and archwires in the dry state. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2000;118:662–74.
Berradja A, Willems G, Celis JP. Tribological behaviour of orthodontic archwires under dry and wet sliding conditions in vitro. Aust Orthod J. 2006;22:11–9.
Berradja A, Bratu F, Benea L, Willems G, Celis JP. Effect of sliding wear on tribocorrosion behaviour of stainless steel in a Ringer’s solution. Wear. 2006;261:987–93.
Acknowledgements
The present study was funded through a research grant of the Universitat de Barcelona (Facultat d’Odontologia). We would like to acknowledge the help provided in the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya by Dr. José María Manero and Fernando Villar in obtaining the images for the present study. The photo in Fig. 1 was kindly donated by Dr. A. Hayes (St Louis, MO, USA). We are especially grateful to Dr. Gregory Stylianos Antonarakis from the Division of Orthodontics of the Université de Genève for proof reading this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suárez, C., Vilar, T., Gil, J. et al. In vitro evaluation of surface topographic changes and nickel release of lingual orthodontic archwires. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 21, 675–683 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3898-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3898-7