Abstract
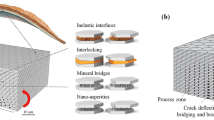
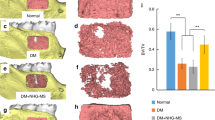
This paper considers the use of bioinspired functionally graded structures in the design of dental multi-layers that are more resistant to sub-surface crack nucleation. Unlike existing dental crown restorations that give rise to high stress concentration, the functionally graded layers (between crown materials and the joins that attach them to dentin) are shown to promote significant reductions in stress and improvements in the critical crack size. Special inspiration is drawn from the low stress concentrations associated with the graded distributions in the dentin-enamel-junction (DEJ). The implications of such functionally graded structures are also discussed for the design of dental restorations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. A. MALAMENT and S. S. SOCRANSKY, Survival of Dicor glass-ceramic dental restorations over 14 years: Part 1. Survival of Dicor complete coverage restorations and effect of internal surface acid etching, tooth position, gender and age. J. Prosthet. Dent. 81 (1999) 23–32.
J. R. KELLY, Ceramics in restorative and prosthetic dentistry. Ann. Rev. in Mater. Scie. 27 (1997) 443–468.
B. R. LAWN, Y. DENG, I. K. LLOYD, M. N. JANAL, E. D. REKOW and V. P. THOMPSON, Material design of ceramic-based layer structures for crown. J. Dent. Res. 81 (2002) 433–438.
W. O. SOBOYEJO, R. WANG, N. KATSUBE, R. SEGHI, C. PAGEDAS, P. SKRABA, D. R. MUMM and A. G. EVANS, Contact damage of model dental multilayers: Experiments and finite element simulations. Key Eng. Mater. 198–199 (2001) 135–178.
Y. DENG, B. R. LAWN and I. K. LLOYD, Damage characterization of brittle materials in ceramic-based crown-like layer structures. Key Eng. Mater. 224–226 (2002) 453–458.
E. D. REKOW and V. P. THOMPSON, Clinical performance—a reflection of damage accumulation in ceramic dental crowns. Key Eng. Mater. 198–199 (2001) 115–134.
W. J. O’BRIEN, “Dental Materials and Their Selection,” 2nd edition. (Quintessence Publishing Co.: Chicago 1997).
H. FONG, M. SARIKAYA, S. N. WHITE and M. L. SNEAD, Nano-mechanical properties profiles across dentin-enamel junction of human incisor teeth. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 7 (2000) 119–128.
G. W. MARSHALL Jr., M. BALOOCH, R. R. GALLAGHER, S. A. GANSKY and S. J. MARSHALL, Mechanical properties of the dentinoenamel junction: AFM studies of nanohardness, elastic modulus, and fracture. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 54 (2001) 87–95.
R. Z. WANG and S. WEINER, Strain-structure relations in human teeth using Moiré fringes. J. Biomech. 31 (1998) 135–141.
N. MEREDITH, M. SHERRIFF, D. J. SETCHELL and S. A. V. SWANSON, Measurement of the microhardness of Young”s modulus of human enamel and dentin using an indentation technique. Arch. Oral. Boil. 41 (1996) 53–545.
J. H. KINNEY, M. BALOOCH, S. J. MARSHALL, G. W. MARSHALL and T. P. WEIHS, Hardness and Young’s modulus of human peritubular and intertubular dentin. Arch. Oral. Biol. 41 (1996) 9–13.
L. E. TAM, E. PULVER, D. MCCOMB and D. C. SMITH, Physical properties of proprietary light-cured lining materials. Oper. Dent. 16 (1991) 210–217.
J.-H. KIM and G. H. PAULINO, An accurate scheme for mixed-mode fracture analysis of functionally graded materials using the interaction integral and micromechanics models. International J. Numer. Meth. Engi. 58 (2003) 1457–1497.
M. C. WALTERS, G. H. PAULINO, and R. H. DODDS Jr., Stress-intensity factors for surface cracks in functionally graded materials under mode-I thermomechanical loading. Inte. J. Sol. Struct. 41 (2004) 1081–1118.
Y. MURAKAMI (editor-in-Chief), “Stress Intensity Factors Handbook,” vol. 1 (Pergamon, Oxford 1987).
G. H. PAULINO, Z. H. JIN and R. H. DODDS, Failure of functionally graded materials. In “Comprehensive Structural Integrity,” (Elsevier Science, 2003) pp. 607–644.
J.-H. KIM and G. H. PAULINO, An accurate scheme for mixed-mode fracture analysis of functionally graded materials using the interaction integral and micromechanics models. Inte. J. Numer. Meth. Eng., 58 (2003) 1457–1497.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, M., Wang, R., Thompson, V. et al. Bioinspired design of dental multilayers. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 18, 57–64 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0662-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0662-0