Abstract
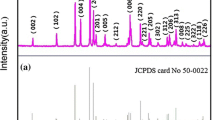
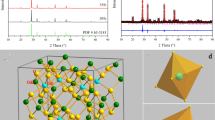
Rare earth ions doped up-conversion luminescent materials have attracted massive attention owing to their unique nonlinear optical properties of converting multiple low-energy photons into high-energy photons and potential application in many fields, especially in information storage and anti-counterfeiting. In this paper, the red-to-green emission ratio of NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+ phosphors was adjusted through power density, pulse width and frequency. The results displayed that the red-to-green emission ratio enhanced with power density, pulse width and frequency increasing. The increase was not obvious with the increase of power density because of the combined effect of two-photon up-conversion processes and the increase rate of nonradiative relaxation process 2H11/2/4S3/2 → 4F9/2 (Er3+). The ratio changes with pulse width and frequency were originated to different non-steady-state up-conversion processes of red and green emissions. The ratio can also be changed from 0.75 to 0.98 by inducing Mn2+ ions in NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+ phosphors, which is cause by the energy transfers among the energy levels 2H11/2/4S3/2 (Er3+), 4T1 (Mn2+), and 4F9/2 (Er3+). All methods of tuning the ratio of red-to-green emissions can be used in fields of information storage and optical encryption.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
G. Chen, H. Qiu, P.N. Prasad, X. Chen, Chem. Rev. 114, 5161 (2014)
X. Li, R. Wang, F. Zhang, Nano Lett. 14, 3634 (2014)
M. Ding, D. Chen, Z. Wan, Y. Zhou, J. Zhong, J. Xi, Z. Ji, J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 5372 (2015)
J. Park, K. Kim, E.J. Jo, W. Kim, H. Kim, R. Lee, J. Lee, J. Jo, M.G. Kim, G.Y. Jung, Nanoscale 11, 22813 (2019)
M. Runowski, P. Wozny, N. Stopikowska, Q. Guo, S. Lis, ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11, 4131 (2019)
W. You, D. Tu, R. Li, W. Zheng, X. Chen, Nano Res. 12, 1417 (2019)
F. Heine, E. Heumann, T. Danger, T. Schweizer, G. Huber, B. Chai, Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 383 (1994)
S. Yu, D. Jang, H. Yuan, W.T. Huang, M. Kim, F. Marques Mota, R.S. Liu, H. Lee, S. Kim, D.H. Kim, ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 13, 58422 (2021)
H. Jia, D. Li, D. Zhang, Y. Dong, S. Ma, M. Zhou, W. Di, W. Qin, A.C.S. Appl, Mater. Inter. 13, 4402 (2021)
J. Zuo, W. Wang, D. Zhang, X. Wang, Y. Ma, P. Li, Y. Li, W. Sun, Y. Zhang, L. Tu, Y. Chang, Q. Li, H. Zhang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 575, 151701 (2022)
Z. Li, Q. Han, T. Yan, Z. Huang, Y. Song, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Alloy Compd. 904, 164009 (2022)
T. Zheng, M. Runowski, N. Stopikowska, M. Skwierczyńska, S. Lis, P. Du, L. Luo, J. Alloy. Compd. 890, 161830 (2022)
D. Zhang, S. Liang, S. Yao, H. Li, J. Liu, Y. Geng, X. Pu, Sep. Purif. Technol. 248, 117040 (2020)
T. Blumenthal, J. Meruga, P.S. May, J. Kellar, W. Cross, K. Ankireddy, S. Vunnam, Q.N. Luu, Nanotechnology 23, 185305 (2012)
M. You, J. Zhong, Y. Hong, Z. Duan, M. Lin, F. Xu, Nanoscale 7, 4423 (2015)
A. Baride, J.M. Meruga, C. Douma, D. Langerman, G. Crawford, J.J. Kellar, W.M. Cross, P.S. May, RSC Adv. 5, 101338 (2015)
K. Huang, N.M. Idris, Y. Zhang, Small 12, 836 (2016)
H. Zhang, Y. Fan, P. Pei, C. Sun, L. Lu, F. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 58, 10153 (2019)
H. Suo, Q. Zhu, X. Zhang, B. Chen, J. Chen, F. Wang, Mater. Today Phys. 21, 100520 (2021)
X. Fu, S. Fu, Q. Lu, J. Zhang, P. Wan, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, C.H. Chen, W. Li, H. Wang, Q. Mei, Nat. Commun. 13, 1 (2022)
B. Cao, Y. Bao, Y. Liu, J. Shang, Z. Zhang, Y. He, Z. Feng, B. Dong, Chem. Eng. J. 385, 123906 (2020)
H. Rijckaert, S. Premcheska, S. Mohanty, J. Verduijn, A. Skirtach, A.M. Kaczmarek, Phys. B 626, 413453 (2022)
Y. Feng, Z. Li, Q. Li, J. Yuan, L. Tu, L. Ning, H. Zhang, Light: Sci. Appl. 10, 1 (2021)
G.S. Yi, G.M. Chow, Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 2324 (2006)
C. Homann, L. Krukewitt, F. Frenzel, B. Grauel, C. Würth, U. Resch-Genger, M. Haase, Angew Chem. Int. Edit. 57, 8765 (2018)
J. Li, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, L. Li, H. Hao, Nanomaterials 11, 2660 (2021)
W. Liu, W. Zhang, R. Liu, G. Li, New J. Chem. 45, 9818 (2021)
Q. Shao, G. Zhang, L. Ouyang, Y. Hu, Y. Dong, J. Jiang, Nanoscale 9, 12132 (2017)
K. Lingeshwar Reddy, R. Balaji, A. Kumar, V. Krishnan, Small 14, 18 (2018)
Q. Xiao, X. Dong, X. Yin, H. Wang, H. Zhong, B. Dong, X. Luo, Mater. Res. Bull. 141, 111326 (2021)
T. Gao, X. Zhu, X.J. Wu, B. Zhang, H.L. Liu, J. Phys. Chem. C 125, 732 (2021)
S. Li, L. Tan, W. Wang, Z. Chen, S. Kang, C. Gao, C. Lin, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 106, 1015 (2023)
W. Gao, H. Zheng, Q. Han, E. He, F. Gao, R. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 5327 (2014)
Funding
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12004217) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. ZR201910230199 and ZR201910230202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MZ: implemented the research scheme and wrote the manuscript. HH: reviewed and edited the article. LL: reviewed and edited the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving humans and animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Hao, H. & Li, L. Effect of excitation condition and Mn2+ doping on the red-to-green emission ratio in NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+ phosphors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 869 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10263-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10263-7