Abstract
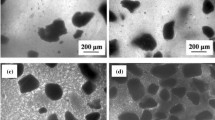
In this study, ZnO varistors with different particle sizes were added into the epoxy resin to fabricate ZnO varistor-Epoxy composites. The effect of ZnO filler size on the dynamic mechanical, thermal, and dielectric properties of ZnO varistor-Epoxy composites was investigated. As the temperature ranges from − 60 to 110 °C, 20 vol% ZnO varistor-Epoxy composites with different ZnO particle sizes represent the glassy state, the glass transition state and rubbery state. When ZnO particle size increases from 70 to 255 μm, the storage modulus of ZnO varistor-Epoxy composites is significantly improved from 1681 MPa to 2755 MPa at room temperature, and the maximum value of damping factor fluctuates between 0.55 and 0.60. As the frequency increases from 0.1 to 20 Hz, both the storage modulus and the maximum value of damping factor are raised. In addition, the coefficient of thermal expansion decreases from 5.06 × 10− 5 K− 1 to 4.45 × 10− 5 K− 1, whereas the filler size has little influence on the glass transition temperature of composites. Besides, both the dielectric constant and dielectric loss in the frequency range from 103 to 106 Hz vary in a small range with the increase of the ZnO filler size. With the increase of frequency, both the dielectric constant and dielectric loss gradually decrease. However, as the temperature increases, the dielectric constant and dielectric loss show an opposite trend.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author [Heng Tian], upon reasonable request.
References
L.G. Virsberg, P.H. Ware, IEEE T Power Syst Pas 86, 1129–1135 (1967)
A. Can-Ortiz, L. Laudebat, Z. Valdez-Nava, S. Diaham, Polymers-Basel 13, 1370 (2021)
B.X. Du, Z.L. Li, Z.R. Yang, IEEE T Dielect El In 23, 3108–3116 (2016)
Z.H. Yang, P.H. Hu, S.J. Wang, J.W. Zha, Z.C. Guo, Z.M. Dang, IEEE Trans Dielect Elec Ins 24, 1735–1742 (2017)
T.T. Wang, X.J. Li, M.Y. Liu, G.C. Li, W. Xiao, S.J. Chen, C.C. Hao, Y.H. Wei, M.L. Fu, Q.Q. Lei, Mater. Res. Express 7, 125302 (2020)
A. Roberts, IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag 11, 26–31 (1995)
D. Weida, C. Richter, M. Clemens, IEEE Trans Dielect Elec Ins 18, 1262–1267 (2011)
R. Abd-Rahman, A. Haddad, N. Harid, H. Griffiths, IEEE Trans Dielect Elec Ins 19, 705–713 (2012)
X.L. Zhao, X. Yang, J. Hu, H. Wang, H.Y. Yang, Q. Li, J.L. He, Z.L. Xu, X.X. Li, IEEE Trans Dielect Elec Ins 26, 1253–1260 (2019)
B.X. Du, H.C. Liang, J. Li, IEEE Trans Dielect Elec Ins 26, 801–809 (2019)
L. Donzel, F. Greuter, T. Christen, IEEE Electr. Ins. Mag 27, 18–29 (2011)
X.L. Zhao, X. Yang, J. Hu, Q. Li, J.L. He, Compos. Sci. Technol. 175, 151–157 (2019)
J.Y. Guo, X.L. Wang, Z.D. Jia, J. Wang, C. Chen, Molecules 23, 1–16 (2018)
C.Y. Liu, X.Q. Zheng, P. Peng, IEEE T Plasma Sci 43, 3727–3733 (2015)
X. Wang, J.K. Nelson, L.S. Schadler, H. Hillborg, IEEE Trans Dielect Elec Ins 17, 1687–1696 (2010)
F.Q. Tian, Q.Q. Lei, X. Wang, Y. Wang, IEEE Trans Dielect Elec Ins 19, 763–769 (2012)
M. Perlman, A. Kumar, R. Coelho, B. Aladenize, IEEE Trans. Elect. Insulation 26, 323–325 (1991)
A.S. Blivi, F. Bedoui, S. Weigand, D. Kondo, Polym. Eng. Sci. 60, 1773–1784 (2020)
G. Suriati, M. Mariatti, A. Azizan, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 22, 56–63 (2011)
J.J. Tian, Y.C. Cao, H. Tian, Y.H. Xu, G.D. Wang, Y.J. Feng, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 32, 13029–13039 (2021)
P.K. Arya, V. Mathur, D. Patidar, Phase Transit. 90, 695–702 (2017)
S.K. Esthappan, R. Joseph, Prog Rubber Plast Re 30, 211–219 (2014)
A.R. Shah, M.N. Prabhakar, H.F. Wang, J. Song, Polym Compos. 39, 2420–2430 (2018)
P. Khoshnoud, A.Z. Nidal, J. Vinyl Addit. Techn 25, 134–143 (2019)
P. Sabarinathan, K. Rajkumar, V.E. Annamalai, K. Vishal, Polym Compos. 41, 3309–3321 (2020)
A. Kufel, S. Kuciel. Mater 12, 2557 (2019)
Y.Z. Tang, P. Zhang, M.X. Zhu, J.C. Li, Y.X. Li, Z.G. Wang, L.S. Huang, Materials 12, 1–12 (2019)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Scientific Research Projects of Henan Colleges and Universities (Grant No. 20B430005 and Grant No. 21A510004), the Doctoral Fund Project of Henan Polytechnic University (Grant No. B2020-45 and Grant No. B2019-20), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (Grant No. NSFRF210451), the Henan Province Scientific and Technological Project (Grant No. 222102230026).
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Scientific Research Projects of Henan Colleges and Universities (Grant No. 20B430005 and Grant No. 21A510004), the Doctoral Fund Project of Henan Polytechnic University (Grant No. B2020-45 and Grant No. B2019-20), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (Grant No. NSFRF210451), the Henan Province Scientific and Technological Project (Grant No. 222102230026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HT, JT, and YF. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JT and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Wu, Y., Tian, J. et al. The effect of ZnO particle size on the dynamic mechanical, thermal, and dielectric properties of ZnO varistor-Epoxy composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 22388–22399 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09016-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09016-9