Abstract
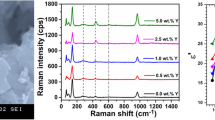
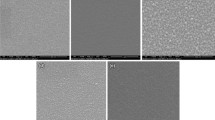
We report on synthesizing rare-earth yttrium oxide-doped ZnO nanoparticles through high-energy planetary milling approach. The impact of varying dopant content in the 3.0, 5.0 to 7.0 wt% range on microstructural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO nanoparticles has been successfully explored. The XRD data showed the existence of a hexagonal wurtzite ZnO phase along with Y2O3 impurity peaks, and the SEM micrographs divulge the development of semi-spherical nanoparticles. The incorporation of Y2O3 dopant in ZnO lattice has been supported by EDS, XPS and Raman analysis. The frequency and composition dependence of dielectric parameters was investigated and interpreted according to the Maxwell Wagner model. The data revealed non-monotonic dependence of the dielectric constant (εr), dielectric loss (tan δ) and AC conductivity and impedance of ZnO with varying dopant content. The variation of the shape of the impedance semicircles and the equivalent circuits between pure and doped ZnO samples prove increased grain boundary resistance due to Y2O3 incorporation. The study reveals that Yttrium-doped ZnO nanostructures are possible potential candidates for application in electronic devices if the dopant’s content is controlled.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that all data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ü. Özgür et al., A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 98(4), 11 (2005)
Z.L. Wang, Zinc oxide nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 16(25), R829 (2004)
X. Wang et al., Large-scale synthesis of six-nanometer-wide ZnO nanobelts. J. Phys. Chem. B 108(26), 8773–8777 (2004)
X. Li et al., Facile preparation of ZnO/Ag2CO3 heterostructured nanorod arrays with improved photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 125, 96–102 (2019)
J. Yang et al., Tunable deep-level emission in ZnO nanoparticles via yttrium doping. J. Alloys Compd. 509(8), 3606–3612 (2011)
M. Gao et al., Enhancement of optical properties and donor-related emissions in Y-doped ZnO. Superlattices Microstruct. 52(1), 84–91 (2012)
S. Anandan, S. Muthukumaran, Influence of Yttrium on optical, structural and photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanopowders by sol–gel method. Opt. Mater. 35(12), 2241–2249 (2013)
O. Kaygili et al., Structural and dielectric properties of yttrium-substituted hydroxyapatites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 47, 333–338 (2015)
M.A. Yousuf et al., The impact of yttrium cations (Y3+) on structural, spectral and dielectric properties of spinel manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45(8), 10936–10942 (2019)
S.-K. Kim et al., Highly efficient yttrium-doped ZnO nanorods for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 365, 136–142 (2016)
S. Heo et al., Effects of Y contents on surface, structural, optical, and electrical properties for Y-doped ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 558, 27–30 (2014)
T. Jun et al., Bias stress stable aqueous solution derived Y-doped ZnO thin film transistors. J. Mater. Chem. 21(35), 13524–13529 (2011)
W. Guo et al., Hollow, porous, and yttrium functionalized ZnO nanospheres with enhanced gas-sensing performances. Sens. Actuators B 178, 53–62 (2013)
H.W. Choi et al., Improved performance of ZnO nanostructured bulk heterojunction organic solar cells with nanowire-density modified by yttrium chloride introduction into solution. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 117, 273–278 (2013)
S. Das, T. Alford, Optimization of the zinc oxide electron transport layer in P 3 HT: PC 61 BM based organic solar cells by annealing and yttrium doping. RSC Adv. 5(57), 45586–45591 (2015)
P. Wang et al., The electronic structures and optical properties of yttrium-doped zinc oxide with zinc interstitial defects calculated by first-principles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 36, 36–42 (2015)
B. Zhao et al., Influence of yttrium dopant on the properties of anatase nanoparticles and the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(22), 14836–14842 (2015)
X.-W. Li et al., Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar pure copper/1350 aluminum alloy butt joints by friction stir welding. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(6), 1298–1306 (2012)
M. Irfan, A. Shakoor, Structural, electrical and dielectric properties of dodecylbenzene sulphonic acid doped polypyrrole/nano-Y2O3 composites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30(4), 1287–1292 (2020)
C. Mrabet et al., Physical properties of La-doped NiO sprayed thin films for optoelectronic and sensor applications. Ceram. Int. 42(5), 5963–5978 (2016)
C. Wu, Y.C. Zhang, Q. Huang, Solvothermal synthesis of N-doped ZnO microcrystals from commercial ZnO powder with visible light-driven photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 119, 104–106 (2014)
P. Swarthmore, Powder diffraction file, joint committee on powder diffraction standards. International Center for Diffraction Data. Card, pp. 3–0226 (1972)
P. Kumar et al., Investigation of phase segregation in yttrium doped zinc oxide. Ceram. Int. 41(5), 6734–6739 (2015)
R. Joshi et al., Structural, optical and ferroelectric properties of V doped ZnO. Appl. Nanosci. 4(5), 531–536 (2014)
Z.-Y. Ye et al., Structural, electrical, and optical properties of Ti-doped ZnO films fabricated by atomic layer deposition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8(1), 1–6 (2013)
J. Yang et al., Low-temperature growth and optical properties of Ce-doped ZnO nanorods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(5), 2646–2650 (2008)
N. Sinha et al., Y-doped ZnO nanosheets: gigantic piezoelectric response for an ultra-sensitive flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator. Ceram. Int. 44(7), 8582–8590 (2018)
C.S. Barrett, Structure of metals (McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., New York, 1943)
J. Zheng et al., Enhanced UV emission of Y-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(18), 6735–6738 (2012)
V. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B. Dole, Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 6(1), 6 (2012)
S. Kumar, V. Singh, A. Tanwar, Structural, morphological, optical and photocatalytic properties of Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(2), 2166–2173 (2016)
T.C. Damen, S. Porto, B. Tell, Raman effect in zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. 142(2), 570 (1966)
L. Bergman et al., Raman analysis of the configurational disorder in Al x Ga 1–x N films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71(15), 2157–2159 (1997)
S. Sharma, G. Exarhos, Raman spectroscopic investigation of ZnO and doped ZnO films, nanoparticles and bulk material at ambient and high pressures. In: Diffusion and Defect Data Part B Solid State Phenomena. (1997) Sci Tech Publications Ltd.
A. Ubaldini, M.M. Carnasciali, Raman characterisation of powder of cubic RE2O3 (RE= Nd, Gd, Dy, Tm, and Lu), Sc2O3 and Y2O3. J. Alloy. Compd. 454(1–2), 374–378 (2008)
N. Basavegowda et al., Sonochemical green synthesis of yttrium oxide (Y 2 O 3) nanoparticles as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for the construction of biologically interesting 1, 3-thiazolidin-4-ones. Catal. Lett. 147(10), 2630–2639 (2017)
L. Mariscal-Becerra et al., Structural and luminescent analysis of hafnium-doped yttrium oxide and yttrium-doped hafnium oxide powders and doped with trivalent europium and terbium ions. J. Nanophoton. 12(3), 036013 (2018)
T. Ngo-Duc et al., Vertical ZnO nanowire growth on metal substrates. Nanotechnology 23(19), 194015 (2012)
S.K. Sharma et al., Diameter and density controlled growth of yttrium functionalized zinc oxide (YZO) nanorod arrays by hydrothermal. Curr. Appl. Phys. 15, S82–S88 (2015)
G. Ingo et al., XPS studies on cerium, zirconium and yttrium valence states in plasma-sprayed coatings. Surf. Interface Anal. 16(1–12), 515–519 (1990)
A. Modwi et al., Structural and electrical characterization of Ba/ZnO nanoparticles fabricated by co-precipitation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 1–12 (2019)
A. Farea et al., Structure and electrical properties of Co0. 5CdxFe2. 5− xO4 ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 464(1–2), 361–369 (2008)
M. Ahmed, E. Ateia, S. El-Dek, Rare earth doping effect on the structural and electrical properties of Mg–Ti ferrite. Mater. Lett. 57(26–27), 4256–4266 (2003)
S. Bernik, S. Macek, B. Ai, Microstructural and electrical characteristics of Y2O3-doped ZnO–Bi2O3-based varistor ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21(10–11), 1875–1878 (2001)
J. He, J. Hu, Y. Lin, ZnO varistors with high voltage gradient and low leakage current by doping rare-earth oxide. Sci. China Ser. E: Technol. Sci. 51(6), 693–701 (2008)
J. He et al., AC ageing characteristics of Y2O3-doped ZnO varistors with high voltage gradient. Mater. Lett. 65(17–18), 2595–2597 (2011)
E. Luna-Arredondo et al., Indium-doped ZnO thin films deposited by the sol–gel technique. Thin Solid Films 490(2), 132–136 (2005)
Z. Yin et al., Structural, magnetic properties and photoemission study of Ni-doped ZnO. Solid State Commun. 135(7), 430–433 (2005)
A. Yildiz et al., Ni doping effect on electrical conductivity of ZnO nanocrystalline thin films. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 22(9), 1473–1478 (2011)
M.N. Siddique, A. Ahmed, P. Tripathi, Electric transport and enhanced dielectric permittivity in pure and Al doped NiO nanostructures. J. Alloy. Compd. 735, 516–529 (2018)
S. Elliott, A theory of ac conduction in chalcogenide glasses. Phil. Mag. 36(6), 1291–1304 (1977)
E. Kohnke, Electrical and optical properties of natural stannic oxide crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 23(11), 1557–1562 (1962)
M. Buraidah et al., Ionic conductivity by correlated barrier hopping in NH4I doped chitosan solid electrolyte. Physica B 404(8–11), 1373–1379 (2009)
A.K. Jonscher, Dielectric relaxation in solids. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 32(14), R57 (1999)
S. Elliott, AC conduction in chalcogenide glasses, in Structure and bonding in noncrystalline solids. (Springer, Boston, 1986), pp. 251–284
C. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83(1), 121 (1951)
I. Gul et al., Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Co1− xZnxFe2O4 synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 311(2), 494–499 (2007)
R. Zamiri et al., Er doped ZnO nanoplates: synthesis, optical and dielectric properties. Ceram. Int. 40(1), 1635–1639 (2014)
C. Fanggao et al., Effect of gadolinium substitution on dielectric properties of bismuth ferrite. J. Rare Earths 24(1), 273–276 (2006)
H. Frohlick, Theory of Dielectrics (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1956)
M. Ghosh, C. Rao, Solvothermal synthesis of CdO and CuO nanocrystals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 393(4–6), 493–497 (2004)
C. Liu, X. Zu, W. Zhou, Magnetic interaction in Co-doped SnO2 nano-crystal powders. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 18(26), 6001 (2006)
M. Kotkata, F. Abdel-Wahab, H. Maksoud, Investigations of the conduction mechanism and relaxation properties of semiconductor Sm doped a-Se films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39(10), 2059 (2006)
M.M. Hassan et al., Structural and frequency dependent dielectric properties of Fe3+ doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(12), 3952–3958 (2012)
R. Zamiri et al., Structural and dielectric properties of Al-doped ZnO nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 40(4), 6031–6036 (2014)
F. Alam et al., Synthesis, structural, optical and electrical properties of in-situ synthesized polyaniline/silver nanocomposites. Funct. Mater. Lett. 5(03), 1250026 (2012)
N. Divya, P. Aparna, P. Pradyumnan, Dielectric properties of Er 3+ doped ZnO nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 5(08), 287 (2015)
A. Zankat et al., Frequency and temperature dependent electrical properties of ZnO–SnO2 nanocomposites. Physica B 617, 413140 (2021)
H. Wang et al., Effect of sintering process on the electrical properties and microstructure of Ca-doped ZnO varistor ceramics. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 133, 105880 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University, Saudi Arabia, Grant No. (20-13-12-017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest or any competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toghan, A., Modwi, A., Mostafa, A.M. et al. Insight of yttrium doping on the structural and dielectric characteristics of ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 18167–18179 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08673-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08673-0