Abstract
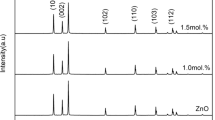
The rod-like (Bi, Co) co-doped ZnO powders were directly synthesized by refluxing method and the effect of reaction time on its structure and optical properties was explored. These powders were consolidated into dense varistors discs by compaction, sintering, and evaluated for their non-linear I–V characteristics. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results revealed that the doped ZnO nanopowders have a hexagonal wurtzite structure and the Bi2O3 phase is found. The half-height width of the (002) plane of the ZnO phase decreases as the reaction time increases, which indicates the improvement of the crystal quality. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) results show that the samples present a uniform rod-like structure. As the refluxing time increases from 2 to 4 h, the average length of ZnO composites increases from 900 to 2250 nm and decreases to 530 nm for 6 h. The presence of functional groups and the chemical bonding is confirmed by Fourier transformation infrared spectra (FTIR). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) demonstrates that Bi element is successfully doped into ZnO in the trivalent valence state while Co element in the form of divalent and trivalent states. The Z-2 varistor ceramics sintered in air at 1200 °C for 2 h showed the highest nonlinear coefficient of 30.8 and the strongest breakdown voltage of 282.8 V/mm. These studies demonstrate the feasibility of direct synthesis of doped ZnO powders for varistor ceramics by refluxing method.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
P. Kumar, P.C. Pandey, J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 80, 342 (2016)
Y.A. Kumar, H.J. Kim, Energies 11, 3285 (2018)
R. Appiah-Ntiamoah, A.F. Baye, B.T. Gadisa, M.W. Abebe, H. Kim, J. Hazard. Mater. 373, 459 (2019)
T.T. Liu, M.H. Wang, H.P. Zhang, J. Electron. Mater. 45, 4412 (2016)
R. Kumar, A. Umar, R. Kumar, M.S. Chauhan, Y. Al-Hadeethi, Ceram. Int. 47, 6201 (2021)
M. Tiemann, F. Marlow, J. Hartikainen, Ö Weiss, M. Lindén, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 1463 (2008)
M. Shuai, Z. Xu, R. Chu, J. Hao, L. Cheng, G. Li, J. Mater. Sci-Mater. Electron. 25, 3878 (2014)
A. Galdámez-Martínez, B. Yang, G. Santana, S.S. Reiner, A. Dutt, Int. J. Hydrogen. Energy 45, 31942 (2020)
R. Lamba, A. Umar, S.K. Mehta, S.K. Kansal, Talanta 131, 490 (2015)
S. Anas, R.V. Mangalaraja, M. Poothayal, S.K. Shukla, S. Ananthakumar, Acta. Mater. 55, 5792 (2007)
J. Ungula, B.F. Dejene, H.C. Swart, Phys. B 535, 251 (2018)
F. Li, X. Huang, Y. Jiang, L. Liu, Z. Li, Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 437 (2009)
M.H. Wang, Z. Fu, B. Zhang, Y. Chao, Mater. Lett. 142, 64 (2015)
A.J. Reddy, M.K. Kokila, H. Nagabhushana, R.P.S. Chakradhar, C. Shivakumara, J.L. Rao, B.M. Nagabhushana, J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 5349 (2011)
M. Gharagozlou, S. Naghibi, Mater. Res. Bull. 84, 71 (2016)
G.P. Singh, P. Kaur, S. Kaur, D.P. Singh, Phys. B 407, 4168 (2012)
J. Rao, A. Yu, C. Shao, X. Zhou, ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 4, 5346 (2012)
G. Vijayaprasath, R. Murugan, S. Asaithambi, G.A. Babu, P. Sakthivel, T. Mahalingam, Y. Hayakawa, G. Ravi, Appl. Phys. A122(2), 122 (2016) 1
K. Raja, P.S. Ramesh, D. Geetha. Spectrochim. Acta. A 131, 183 (2014)
J.F. Moulder, J. Chastain, R.C. King, Chem. Phys. Lett. 220(1), 7 (1992)
M. Chen, X. Wang, Y.H. Yu, Z.L. Pei, X.D. Bai, C. Sun, R.F. Huang, L.S. Wen, Appl. Surf. Sci. 158, 134 (2000)
H. Bai, Y. Sun, Z. Xu, R. Chu, J. Hao, H. Li, C. Chen, C. Hu, G. Li, Mater. Lett. 209, 115 (2017)
S. Wan, W. Lu, X. Wang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 319 (2010)
Y. Shi, Q.G. Liu, Y. Chen, M.H. Wang, J. Electron. Mater. 50, 5891 (2021)
Funding
This research was partially supported by the grant from Changzhou University with KYCX20-2566 and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province with KYCX21-2858.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. YS performed Material preparation, data collection, and analysis, QGL made contribution to the creation of new software used in the work, YC made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work, and MHW revised the work critically for important intellectual content. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YS and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Liu, QG., Chen, Y. et al. Synthesis and properties of rod-like ZnO composite powders by the reflux method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 3556–3565 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07548-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07548-0