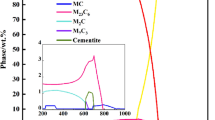
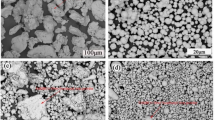
Abstract
The influence of P content on Curie temperature, magnetic properties and microstructures of Fe81.5Si3B10+xP3.5−xC0.2Cu0.8Nb1 (x = 0, 1, 2, and 3 at.%) alloys subjected to magnetic field annealing has been studied. Here, the decrease in P content can improve Curie temperature of alloys from about 575 to 584 K, which increases the operating temperature of magnetic device. Via optimal field annealing technique, the amorphous alloy with x = 3 exhibits good soft magnetic properties, including saturation magnetic flux density of 1.53 T, high effective permeability above 12,000, low coercivity below 3 A/m, and low core loss around 0.18 W/kg. The hysteresis loops show that tuning down the content of P relative to B can increase the saturation magnetic flux density of alloy system. Besides, the investigation about the microstructures of alloys annealed at optimal conditions indicates that longitudinal magnetic field annealing can improve the stability of amorphous phase, thereby ensuring the amorphous structure annealed at a higher annealing temperature compared with the general annealing for alloys.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Xu, Y.Z. Yang, Q.S. Yan, C.F. Fan, F.T. Hou, Z.W. Xie, Effect of microalloying on crystallization behavior, magnetic properties and bending ductility of high Fe content FeSiBCuPC alloys. J. Alloy Compd. 777, 499–505 (2019)
F. Wang, A. Inoue, Y. Han, S.L. Zhu, F.L. Kong, E. Zanaeva, G.D. Liu, E. Shalaan, F. Al-Marzouki, A. Obaid, Excellent soft magnetic Fe-Co-B-based amorphous alloys with extremely high saturation magnetization above 1.85 T and low coercivity below 3 A/m. J. Alloy Compd. 711, 132–142 (2017)
A. Urata, H. Matsumoto, S. Sato, A. Makino, High Bs nanocrystalline alloys with high amorphous-forming ability. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 07A324-1-07A324-3 (2009)
H.R. Lashgari, D. Chu, S.S. Xie, H.D. Sun, M. Ferry, S. Li, Composition dependence of the microstructure and soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys: a review study. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 391, 61–82 (2014)
F. Wang, A. Inoue, Y. Han, F.L. Kong, S.L. Zhu, E. Shalaan, F. Al-Marzouki, A. Obaid, Soft magnetic Fe-Co-based amorphous alloys with extremely high saturation magnetization exceeding 1.9 T and low coercivity of 2 A/m. J. Alloy Compd. 723, 376–384 (2017)
A. Takeuchi, A. Inoue, Mixing enthalpy of liquid phase calculated by miedema’s scheme and approximated with sub-regular solution model for assessing forming ability of amorphous and glassy alloys. Intermetallics 18, 1779–1789 (2010)
A. Takeuchi, A. Inoue, Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 12, 2817–2829 (2005)
B. Majumdar, D. Akhtar, Structure and coercivity of nanocrystalline Fe–Si–B–Nb–Cu alloys. Bull. Mater. Sci. 28, 395–399 (2005)
K.G. Pradeep, G. Herzer, P. Choi, D. Raabe, Atom probe tomography study of ultrahigh nanocrystallization rates in FeSiNbBCu soft magnetic amorphous alloys on rapid annealing. Acta Mater. 68, 295–309 (2014)
B.S. Berry, W.C. Pritchet, Magnetic annealing and directional ordering of an amorphous ferromagnetic alloy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 34, 1022–1025 (1975)
S. Kwon, S. Kim, H. Yim, Improvement of saturation magnetic flux density in Fe–Si–B–Nb–Cu nanocomposite alloys by magnetic field annealing. Curr. Appl. Phys. 20, 37–42 (2020)
Y. Yoshizawa, K. Yamauchi, Effects of magnetic field annealing on magnetic properties in ultrafine crystalline Fe–Cu–Nb–Si–B alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 25, 3324–3326 (1989)
H. Li, A.N. He, A.D. Wang, L. Xie, Q. Li, C.L. Zhao, G.Y. Zhang, P.B. Chen, Improvement of soft magnetic properties for distinctly high Fe content amorphous alloys via longitudinal magnetic field annealing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471, 110–115 (2019)
I. Škorvánek, J. Marcin, J. Turčanová, J. Kováč, P. Švec, Improvement of soft magnetic properties in Fe38Co38Mo8B15Cu1 amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys by heat treatment in external magnetic field. J. Alloy. Compd. 504, S135–S138 (2010)
M. Ghanaatshoar, N. Nabipour, M.M. Tehranchi, S.M. Hamidi, S.M. Mohseni, The influence of laser annealing in the presence of longitudinal weak magnetic field on asymmetrical magnetoimpedance response of CoFeSiB amorphous ribbons. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354, 5150–5152 (2008)
X.H. Zhang, Y.Q. Dong, A.N. He, L. Xie, F.S. Li, L. Chang, H.Y. Xiao, H. Li, T. Wang, Improvement of SMPs in Fe–Si–B–P–C–Cu–Nb alloys via harmonizing P and B. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 506, 199757 (2020)
Y.S. Tyan, L.E. Toth, Slater pauling magnetization curve in transition metal phosphides. J. Electron. Mater. 3, 1–6 (1974)
Y. Kakehashi, O. Hosohata, Curie-temperature “Slater-Pauling Curve". J. Phys. Colloque 49, C8–C73 (1988)
C. Takahashi, M. Ogura, H. Akai, First-principles calculation of the Curie temperature Slater-Pauling curve. J. Phys.-Condens. Matter. 19, 365233 (2007)
M.Q. Zuo, S.Y. Meng, Q. Li, H.X. Li, C.T. Chang, Y.F. Sun, Effect of metalloid elements on magnetic properties of Fe-based bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 83, 83–86 (2017)
S.Y. Meng, H.B. Ling, Q. Li, J.J. Zhang, Development of Fe-based bulk metallic glasses with high saturation magnetization. Scripta Mater. 81, 24–27 (2014)
Z.Q. Liu, M.J. Shi, T. Zhang, Composition dependences and optimization of the magnetic properties of Fe-based metallic glasses. Mater. Res. Express 1, 046110 (2014)
R.C. O’Handley, D.S. Boudreaux, Magnetic properties of transition metal-metalloid glasses a charge transfer model. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 45, 607–615 (1978)
H. Kronműller, M. Fähnle, M. Domann, H. Grimm, R. Grimm, B. Grőger, Magnetic properties of amorphous ferromagnetic alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 13, 53–70 (1979)
H.Y. Xiao, A.D. Wang, J.W. Li, A.N. He, T. Liu, Y.Q. Dong, H. Guo, X.C. Liu, Structural evolutionary process and interrelation for FeSiBNbCuMo nanocrystalline alloy. J. Alloy Compd. 821, 153487 (2020)
E.N. Zanaeva, A.I. Bazlov, D.A. Milkova, A.Y. Churyumov, A. Inoue, N.Y. Tabachkova, F. Wang, F.L. Kong, S.L. Zhu, High-frequency soft magnetic properties of Fe–Si–B–P–Mo–Cu amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 526, 119702 (2019)
Y. Han, F.L. Kong, F.F. Han, A. Inoue, S.L. Zhu, E. Shalaan, F. Al-Marzouki, New Fe-based soft magnetic amorphous alloys with high saturation magnetization and good corrosion resistance for dust core application. Intermetallics 76, 18–25 (2016)
H. Matsumoto, A. Urata, Y. Yamada, A. Inoue, Novel FePBNbCr glassy alloys “SENNTIX” with good soft-magnetic properties for high efficiency commercial inductor cores. J. Alloy Compd. 509, S193–S196 (2011)
J. Xu, Y.Z. Yang, W. Li, X.C. Chen, The effect of introduction of carbon on the glass forming ability and magnetic properties of melt-spun Fe–Si–B–Cu–C alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 447, 167–170 (2016)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number U1704159), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.51771083), and the S&T Innovation 2025 Major Special Program (Grant Number 2018B10084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuhang Zhang, Yaqiang Dong and Fushan Li contributed the central idea, and wrote the first draft. Aina He and Jiawei Li contributed to improve the manuscript. Liang Chang contributed to provide the component ideas. Changjiu Wang, Qiang Chi and Xiaoxue Shui completed the remain refining experiment. All authors have contributed to the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Dong, Y., Wang, C. et al. Influence of P content on SMPs in Fe–Si–B–P–C–Cu–Nb amorphous alloys under longitudinal field annealing. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 7198–7208 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05428-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05428-1