Abstract
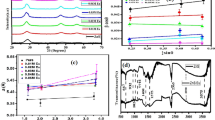
The present study demonstrates a red light-emitting nano-phosphor material tailored by doping europium (Eu+3) ions in zinc oxide (ZnO), prepared using a solution based co-precipitation method. Instead of using acetates or nitrates based precursor for Eu+3 doping, here we directly used europium oxide (Eu2O3) as a precursor. The precursor showed a limited amount of solubility only up to 3% in an alcoholic solution. No phase change of any kind in x-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns indicates effective Eu+3 doping in ZnO. Also, the broadening of the XRD peaks confirms the reduction of size to the nanoscale. Further, the optical properties of pure ZnO and Eu+3-doped ZnO are elucidated using UV–Visible and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy. A redshift of 10 nm in the absorption edge from pure ZnO to 3% Eu+3-doped ZnO concentration is detected, indicating that Eu+3 ions occupy impurity trap levels below the conduction band. A regular increase in the excitation wavelength from 190 nm to 270 nm confirms that 226 nm excitation wavelength is the onset point for the emission from Eu+3 ions. The Eu+3-doped ZnO nanoparticles exhibit two emission peaks at 584 nm and 613 nm corresponding to 5D0→7F1 and 5D0→7F2 transition of Eu+3 ions at low excitation wavelengths of 254 nm and 270 nm. Out of these two peaks, 613 nm peak was the most intense suggesting that mostly 5D0→7F2 transitions are taking place. The intensity ratio of 5D0→7F2 / 5D0→7F1 for both excitation wavelengths of 254 nm and 270 nm is always greater than one confirms the efficient emission of red color from Eu+3 ions. In addition to that, the samples exhibit a high color purity value of 83.78 %, with CIE coordinates (0.60, 0.40) lying closer to the ideal red color CIE coordinates at an excitation wavelength of 254 nm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.G. Yu, T.J. Marks, A. Facchetti, Metal oxides for optoelectronic applications. Nat. Mater. 15(4), 383–396 (2016)
L. Petti et al. Metal oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors for flexible electronics, (in English), Appl. Physics Rev Rev 3(2) 53 (2016), Art. no. 021303
M. Grundmann et al. Oxide bipolar electronics: materials, devices and circuits, J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 49(21), (2016), Art. no. 213001.
I. Choudhary, Deepak, Flexible substrate compatible solution processed P-N heterojunction diodes with indium-gallium-zinc oxide and copper oxide, Mater. Sci. Eng.: B. 218, 64-73 (2017)
J.H. Park et al., All-solution-processed, transparent thin-film transistors based on metal oxides and single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. C 1(9), 1840–1845 (2013)
R.F.P. Martins et al., Recyclable, flexible, low-power oxide electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23(17), 2153–2161 (2013)
S.K. Park, Y.H. Kim, J.I. Han, All solution-processed high-resolution bottom-contact transparent metal-oxide thin film transistors, J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 42(12), (2009) Art. no. 125102.
C.Y. Koo et al., Sol-gel derived Ga-In-Zn-O semiconductor layers for solution-processed thin-film transistors. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 53(1), 218–222 (2008)
C.D. Dimitrakopoulos, P.R.L. Malenfant, Organic thin film transistors for large area electronics, (in English). Adv. Mater. Rev. 14(2), 99 (2002)
H. Hosono, M. Yasukawa, H. Kawazoe, Novel oxide amorphous semiconductors: transparent conducting amorphous oxides. J Non-Cryst Solids 203, 334–344 (1996)
B. Ghanbari Shohany, A. Khorsand Zak, Doped ZnO nanostructures with selected elements—Structural, morphology and optical properties: A review. Ceram Int 46(5), 5507–5520 (2020)
J. Wang, R. Chen, L. Xiang, S. Komarneni, Synthesis, properties and applications of ZnO nanomaterials with oxygen vacancies: a review. Ceram Int 44(7), 7357–7377 (2018)
C.B. Ong, L.Y. Ng, A.W. Mohammad, A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81, 536–551 (2018)
A. Di Mauro, M.E. Fragalà, V. Privitera, G. Impellizzeri, ZnO for application in photocatalysis: from thin films to nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 69, 44–51 (2017)
S.K. Arya, S. Saha, J.E. Ramirez-Vick, V. Gupta, S. Bhansali, S.P. Singh, Recent advances in ZnO nanostructures and thin films for biosensor applications: Review. Analytica Chimica Acta 737, 1–21 (2012)
A. Wei, L. Pan, W. Huang, Recent progress in the ZnO nanostructure-based sensors. Mater. Sci. Eng.: B 176(18), 1409–1421 (2011)
A.B. Djurišić, A.M.C. Ng, X.Y. Chen, ZnO nanostructures for optoelectronics: Material properties and device applications. Progress Quantum Electron 34(4), 191–259 (2010)
S. Goel, B. Kumar, A review on piezo-/ferro-electric properties of morphologically diverse ZnO nanostructures. J. Alloys Comp. 816, 152491 (2020)
V.S. Bhati, M. Hojamberdiev, M. Kumar, Enhanced sensing performance of ZnO nanostructures-based gas sensors: A review. Energy Rep. 6, 46–62 (2020)
M. Alavi, A. Nokhodchi, An overview on antimicrobial and wound healing properties of ZnO nanobiofilms, hydrogels, and bionanocomposites based on cellulose, chitosan, and alginate polymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 227, 115349 (2020)
J. Liu, Y. Wang, J. Ma, Y. Peng, A. Wang, A review on bidirectional analogies between the photocatalysis and antibacterial properties of ZnO. J. Alloys Compd. 783, 898–918 (2019)
Y. Li et al., Study on the high magnetic field processed ZnO based diluted magnetic semiconductors. Ceram. Int. 45(16), 19583–19595 (2019)
R. Ahmad, S.M. Majhi, X. Zhang, T.M. Swager, K.N. Salama, Recent progress and perspectives of gas sensors based on vertically oriented ZnO nanomaterials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 270, 1–27 (2019)
P. Vishnukumar, S. Vivekanandhan, M. Misra, A.K. Mohanty, Recent advances and emerging opportunities in phytochemical synthesis of ZnO nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 80, 143–161 (2018)
R. Kumar, A. Umar, G. Kumar, H.S. Nalwa, Antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanomaterials: A review. Ceram. Int. 43(5), 3940–3961 (2017)
M. Norouzi et al., Thermoelectric energy harvesting using array of vertically aligned Al-doped ZnO nanorods. Thin Solid Films 619, 41–47 (2016)
A. Tsukazaki et al., Blue light-emitting diode based on ZnO. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44(21), 643–645 (2005)
S.H. Khan, B. Pathak, ZnO based Photocatalytic Degradation Of Persistent Pesticides: A comprehensive review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monitor. Manag. 100290 (2020).
C. Yi et al., Nanoscale ZnO-based photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Photodiagn. Photodynam. Ther. 30, 101694 (2020)
S. Kumar, G.-H. Kim, K. Sreenivas, R.P. Tandon, ZnO based surface acoustic wave ultraviolet photo sensor. J. Electroceram. 22(1), 198–202 (2009)
V.B. Raj, H. Singh, A.T. Nimal, M.U. Sharma, V. Gupta, Oxide thin films (ZnO, TeO2, SnO2, and TiO2) based surface acoustic wave (SAW) E-nose for the detection of chemical warfare agents. Sensors Actuators B: Chem 178, 636–647 (2013)
R. Singh, A. King, B.B. Nayak, Reddish emission of europium doped zinc oxide nanophosphor prepared through precipitation route using sodium borohydride. J. Alloys Compd. 792, 1191–1199 (2019)
V. Guckan, V. Altunal, A. Ozdemir, V. Tsiumra, Y. Zhydachevskyy, Z. Yegingil, Calcination effects on europium doped zinc oxide as a luminescent material synthesized via sol-gel and precipitation methods. J. Alloys Compd. 823, 153878 (2020)
M. Bian, H. Zhang, J. Zhang, Z. Li, Effects of post-annealing on photoluminescence of Eu-doped ZnO microsphere for single-component white-light materials. Optik 209, 164607 (2020)
E.H.H. Hasabeldaim, O.M. Ntwaeaborwa, R.E. Kroon, E. Coetsee, H.C. Swart, Photoluminescence and cathodoluminescence of spin coated ZnO films with different concentration of Eu3+ ions. Vacuum 169, 108889 (2019)
L.F. Koao, B.F. Dejene, H.C. Swart, S.V. Motloung, T.E. Motaung, Characterization of annealed Eu3+-doped ZnO flower-like morphology synthesized by chemical bath deposition method. Opt. Mater. 60, 294–304 (2016)
S.M. Ahmed, P. Szymanski, L.M. El-Nadi, M.A. El-Sayed, Energy-transfer efficiency in Eu-Doped ZnO Thin Films: The effects of oxidative annealing on the dynamics and the intermediate defect states. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(3), 1765–1772 (2014)
P.P. Pal, J. Manam, Structural and photoluminescence studies of Eu3+ doped zinc oxide nanorods prepared by precipitation method. J. Rare Earths 31(1), 37–43 (2013)
P. Dorenbos, E. van der Kolk, Location of lanthanide impurity levels in the III-V semiconductor GaN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89(6), 061122 (2006)
R.E.M. Khaidir et al., Exploring Eu3+-doped ZnO-SiO2 glass derived by recycling renewable source of waste rice husk for white-LEDs application. Results Phys. 15, 102596 (2019)
E. Hasabeldaim, O.M. Ntwaeaborwa, R.E. Kroon, H.C. Swart, Structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of Eu doped ZnO thin films prepared by spin coating. J. Mol. Struct. 1192, 105–114 (2019)
E. Wolska-Kornio, J. Kaszewski, B.S. Witkowski, Ł. Wachnicki, M. Godlewski, The effect of annealing on properties of europium doped ZnO nanopowders obtained by a microwave hydrothermal method. Opt. Mater. 59, 103–106 (2016)
J.-C. Sin, S.-M. Lam, Hydrothermal synthesis of europium-doped flower-like ZnO hierarchical structures with enhanced sunlight photocatalytic degradation of phenol. Mater. Lett. 182, 223–226 (2016)
S.A. Al Rifai, B.A. Kulnitskiy, Microstructural and optical properties of europium-doped zinc oxide nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74(12), 1733–1738 (2013)
J. Yang et al., Synthesis and optical properties of Eu-doped ZnO nanosheets by hydrothermal method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 14(3), 247–252 (2011)
P.A.M. Nascimento, A.J.S. Silva, A.B. Andrade, R.S. Silva, M.V.D.S. Rezende, Effects of X-ray irradiation on the luminescent properties of Eu-doped LiSrPO4 phosphors produced using the sol-gel method with glucose. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 113, 26–30 (2018)
K. Park, D.A. Hakeem, J.W. Pi, G.W. Jung, Emission enhancement of Eu3+-doped ZnO by adding charge compensators. J. Alloys Compd. 772, 1040–1051 (2019)
A.R. Khataee, A. Karimi, R.D.C. Soltani, M. Safarpour, Y. Hanifehpour, S.W. Joo, Europium-doped ZnO as a visible light responsive nanocatalyst: Sonochemical synthesis, characterization and response surface modeling of photocatalytic process. Appl. Catal. A: General 488, 160–170 (2014)
O. Lupan et al., Eu-doped ZnO nanowire arrays grown by electrodeposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 282, 782–788 (2013)
L. Luo et al., Enhanced ultraviolet lasing from europium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals. Opt. Mater. 32(9), 1066–1070 (2010)
R. Raji, R.G.A. Kumar, K.G. Gopchandran, Influence of local structure on luminescence dynamics of red emitting ZnO:Eu3+ nanostructures and its Judd-Ofelt analysis. J. Lumin. 205, 179–189 (2019)
A. Gulino, I. Fragala, Deposition and characterization of transparent thin films of zinc oxide doped with Bi and Sb. Chemi. of Mater. 14(1), 116–121 (2002)
X. Peng et al., Shape control of CdSe nanocrystals. Nature 404(6773), 59–61 (2000)
V. Srikant, D.R. Clarke, On the optical band gap of zinc oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 83(10), 5447–5451 (1998)
Ü. Özgür et al., A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 98(4), 041301 (2005)
L.V. Trandafilović, D.J. Jovanović, X. Zhang, S. Ptasińska, M.D. Dramićanin, Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by ZnO: Eu nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 203, 740–752 (2017)
D. Raoufi, Synthesis and photoluminescence characterization of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 134, 213–219 (2013)
A. Ghosh, R.N.P. Choudhary, Optical emission and absorption spectra of Zn–ZnO core-shell nanostructures. J. Exp. Nanosci. 5(2), 134–142 (2010)
H. Shahroosvand, M. Ghorbani-asl, Solution-based synthetic strategies for Eu doped ZnO nanoparticle with enhanced red photoluminescence. J. Lumin. 144, 223–229 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India. The authors also acknowledge the help of Dr. ML Singla senior scientist CSIO Chandigarh for helping out with PL measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, I., Shukla, R., Sharma, A. et al. Effect of excitation wavelength and europium doping on the optical properties of nanoscale zinc oxide. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 20033–20042 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04525-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04525-x