Abstract
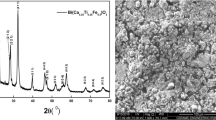
We have investigated the structural, magnetic, dielectric, and magnetodielectric properties of brownmillerite-structured polycrystalline KBiFe2O5 (KBFO) sample synthesized using conventional solid-state reaction route. Monoclinic structure with P2/c space group is determined from Rietveld refined X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. Temperatures-dependent magnetic and dielectric data show a broad hump around 510 °C, indicating the existence of magnetodielectric effect in KBFO. Room-temperature M–H hysteresis measurement possesses a weak ferromagnetic order (MR = 0.006 emu/g and Hc = 1100 Oe) originating from the canted Fe3+ moments due to antiferromagnetic ordering. This canted Fe3+ moment is also reflected in magnetic field variation of magnetodielectric (MD) measurement at room temperature, in which MD does not trace the original path by reversing the field. The highest magnetodielectric response is obtained to be ~ − 1.8% at room temperature. Modulus and complex impedance spectrum analysis attributes the bulk contribution to the observed room-temperature magnetodielectric at high frequency (> 10 kHz) and extrinsic contribution (< 10 kHz) at low frequency. The presence of temperature-dependent and non-Debye (β < 1) type of relaxation in prepared sample is confirmed from the extracted grain (Rg) and grain boundary (Rgb) contribution at different temperature. The frequency-dependent ac conductivity at different temperature follows Jonscher’s power law. The extracted power exponent “n” is decreased with increase in temperature. This behavior (n \(\propto\)1/T) suggests that the ac conduction mechanism of KBFO follows correlated barrier hoping (CBH) model.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Vopson, Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 40, 223 (2015)
J.F. Scott, NPG Asia Mater. 5, 72 (2013)
W. Eerenstein et al., Nature 442, 759 (2006)
M. Fiebig, Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 16046 (2016)
V. Sharma et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 012901 (2015)
S. Tanasescu et al., Solid State Ionics 134, 265 (2000)
H. D’Hondt et al., Chem. Mater 20, 7188 (2008)
D.S. Vavilapalli et al., ASC Omega 3, 16643 (2018)
G. Zhang et al., Sci. Rep. 3, 1265 (2013)
M. Zhang et al., J. Alloys. Compd. 699, 561 (2017)
M.A. Jalaja et al., Mater. Res. Bull. 88, 9 (2017)
G. Zhang et al., Adv. Electron. Mater. 1, 1600498 (2017)
M.A. Jalaja et al., Mater. Res. Express 4, 016401 (2017)
B. Mettout et al., Phys. Rev. B 93, 195123 (2016)
H.M. Rietveld, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 22, 65 (1969)
L. Patterson, Phys. Rev. 56, 978 (1939)
K. Momma et al., J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41, 653 (2008)
D.L. Wood et al., Phys. Rev. B 5, 3144 (1972)
S.R. Mohapatra et al., J. Appl. Phys. 122, 134103 (2017)
A. Pal et al., J. Appl. Phys. 123, 014102 (2018)
G. Catalan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 102902 (2006)
M. K. Singh, J. Appl. Phys. 111, 014113 (2012)
J. Liu et al., Phys. Rev. B 70, 144106 (2004)
P. Uniyal et al., J. Phys. 21, 405901 (2009)
P.R. Mandal et al., Phys. B 448, 68 (2014)
S.R. Mohapatra et al., J. Mater. Sci. 3645, 27 (2016)
R. Grhardt, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 55, 1491 (1994)
S.R. Mohapatra et al., Ceram. Int. 42, 12352 (2016)
A. Shukla et al., J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70, 1401 (2009)
K.P. Padmasree et al., Solid State Ionics 475, 177 (2006)
C.C. Wang et al., J. Appl. Phys. 113, 094103 (2013)
M.M. Hoque et al., J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30, 311 (2014)
K. Jonscher, Nature 673, 267 (2006)
V. Thakur et al., AIP Adv. 5, 087110 (2015)
Acknowledgements
AKS acknowledges the Board of Research in Nuclear Science (BRNS), Mumbai (Sanction No: 2012/37P/40/BRNS/2145), the UGC- DAE-CSR Mumbai (Sanction No: CRS-M-187, 225), and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi (Sanction No: SR/FTP/PS-187/2011), for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrakanta, K., Jena, R., Pal, P. et al. Evidence of room-temperature magnetodielectric effect in brownmillerite KBiFe2O5 through magnetic, complex dielectric, and impedance study. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 15875–15884 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04149-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04149-1