Abstract
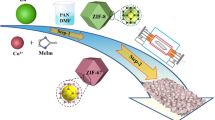
To improve the microwave absorption performance of functional coatings, metal–organic framework (MOF)-based nanocomposites were synthesized via a simple method, including a two-step cooling process. Derived from the ZIF-67 precursor, the nanocomposites consist of C, Co, and C3O4, and all the three chemical constituents are effectively combined in nanometer scale. By varying the heat treatment temperature, the structural architecture and chemical composition of the nanocomposites are carefully tailored to achieve the outstanding microwave absorption properties, in particular, for low frequencies. These properties are mainly boosted by the distinguished attenuation performance and an optimal impedance matching condition. When the heat treatment temperature is 800 °C, the sample (CCCO-800, CCCO for Carbon–Cobalt–Cobalt Oxide) possesses the best microwave absorption performance in this research. The maximum reflection loss (RL) of CCCO-800 can reach − 84.75 dB at 6.61 GHz, and the effective absorption bandwidth (RL < -10 dB) can be as wide as 8.5 GHz. With the absorber thickness ranging from 1.0 to 5.0 mm, the effective absorption bandwidth of CCCO-800 can cover one half of S band and the whole C, X, and Ku bands. These results show that with an appropriate process control, the nanocomposite absorber can achieve remarkable microwave absorption performance, which makes this type of nanocomposite promising as a functional coating for both civil and military applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Liu, C. Hao, L. He, C. Yang, Y. Chen, C. Jiang, R. Yu, Yolk–shell structured Co-C/Void/Co9S8 composites with a tunable cavity for ultrabroadband and efficient low-frequency microwave absorption. Nano Res. 11(8), 4169–4182 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2006-z
F. Shahzad, M. Alhabeb, C.B. Hatter, B. Anasori, S. Man Hong, C.M. Koo, Y. Gogotsi, Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 353(6304), 1137–1140 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aag2421
Z. Chen, C. Xu, C. Ma, W. Ren, H.-M. Cheng, Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 25(9), 1296–1300 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201204196
J. Ma, M. Zhan, K. Wang, Ultralightweight silver nanowires hybrid polyimide composite foams for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7(1), 563–576 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/am5067095
B. Zhao, X. Guo, W. Zhao, J. Deng, G. Shao, B. Fan, Z. Bai, R. Zhang, Yolk–shell Ni@SnO2 composites with a designable interspace to improve the electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(42), 28917–28925 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b10886
Y. Zhang, W. Hao, Absorbing material advance and influence to military stealth technology. New Chem. Mater. 40(1), 13–15 (2012)
J. Xu, W. Zhou, F. Luo, D. Zhu, J. Su, S. Jiang, Research progress on radar stealth technique and radar absorbing materials. Mater. Rev. 28(5), 46–49 (2014)
A. Wang, W. Wang, C. Long, W. Li, J. Guan, H. Gu, G. Xu, Facile preparation, formation mechanism and microwave absorption properties of porous carbonyl iron flakes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2(19), 3769–3776 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC00108G
S. Motojima, Y. Noda, S. Hoshiya, Y. Hishikawa, Electromagnetic wave absorption property of carbon microcoils in 12–110 GHz region. J. Appl. Phys. 94(4), 2325–2330 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1589603
J. Joo, C.Y. Lee, High frequency electromagnetic interference shielding response of mixtures and multilayer films based on conducting polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 88(1), 513–518 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.373688
X. Huang, J. Zhang, M. Lai, T. Sang, Preparation and microwave absorption mechanisms of the NiZn ferrite nanofibers. J. Alloy. Compd. 627, 367–373 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.11.235
H. Zhao, Y. Cheng, W. Liu, L. Yang, B. Zhang, L.P. Wang, G. Ji, Z.J. Xu, Biomass-derived porous carbon-based nanostructures for microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 11(1), 24 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-019-0255-3
W. Liu, S. Tan, Z. Yang, G. Ji, Enhanced low-frequency electromagnetic properties of MOF-derived cobalt through interface design. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10(37), 31610–31622 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b10685
Y. Zhang, X. Wang, M. Cao, Confinedly implanted NiFe2O4-rGO: cluster tailoring and highly tunable electromagnetic properties for selective-frequency microwave absorption. Nano Res. 11(3), 1426–1436 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1758-1
Y. Ding, Z. Zhang, B. Luo, Q. Liao, S. Liu, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, Investigation on the broadband electromagnetic wave absorption properties and mechanism of Co3O4-nanosheets/reduced-graphene-oxide composite. Nano Res. 10(3), 980–990 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1357-6
X. Li, X. Yin, M. Han, C. Song, H. Xu, Z. Hou, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Ti3C2 MXenes modified with in situ grown carbon nanotubes for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 5(16), 4068–4074 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC05226F
Z. Zhang, J. Tan, W. Gu, H. Zhao, J. Zheng, B. Zhang, G. Ji, Cellulose-chitosan framework/polyailine hybrid aerogel toward thermal insulation and microwave absorbing application. Chem. Eng. J. 395, 125190 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125190
X. Liang, Z. Man, B. Quan, J. Zheng, W. Gu, Z. Zhang, G. Ji, Environment-stable CoxNiy encapsulation in stacked porous carbon nanosheets for enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 12(1), 102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00432-2
W.-L. Song, M.-S. Cao, Z.-L. Hou, X.-Y. Fang, X.-L. Shi, J. Yuan, High dielectric loss and its monotonic dependence of conducting-dominated multiwalled carbon nanotubes/silica nanocomposite on temperature ranging from 373 to 873 K in X-band. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94(23), 233110 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3152764
Y.-H. Chen, Z.-H. Huang, M.-M. Lu, W.-Q. Cao, J. Yuan, D.-Q. Zhang, M.-S. Cao, 3D Fe3O4 nanocrystals decorating carbon nanotubes to tune electromagnetic properties and enhance microwave absorption capacity. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(24), 12621–12625 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA02782A
M.-S. Cao, W.-L. Song, Z.-L. Hou, B. Wen, J. Yuan, The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 48(3), 788–796 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.10.028
X. Cui, X. Liang, J. Chen, W. Gu, G. Ji, Y. Du, Customized unique core-shell Fe2N@N-doped carbon with tunable void space for microwave response. Carbon 156, 49–57 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.09.041
B. Quan, W. Shi, S.J.H. Ong, X. Lu, P.L. Wang, G. Ji, Y. Guo, L. Zheng, Z.J. Xu, Defect engineering in two common types of dielectric materials for electromagnetic absorption applications. Adv. Func. Mater. 29(28), 1901236 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201901236
X. Liu, H. Guo, Q. Xie, Q. Luo, L.-S. Wang, D.-L. Peng, Enhanced microwave absorption properties in GHz range of Fe3O4/C composite materials. J. Alloy. Compd. 649, 537–543 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.084
Y. Cheng, H. Zhao, H. Lv, T. Shi, G. Ji, Y. Hou, Lightweight and flexible cotton aerogel composites for electromagnetic absorption and shielding applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 6(1), 1900796 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.201900796
J. Yuan, Q. Liu, S. Li, Y. Lu, S. Jin, K. Li, H. Chen, H. Zhang, Metal organic framework (MOF)-derived carbonaceous Co3O4/Co microframes anchored on RGO with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances. Synth. Met. 228, 32–40 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2017.03.020
R. Qiang, Y. Du, H. Zhao, Y. Wang, C. Tian, Z. Li, X. Han, P. Xu, Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(25), 13426–13434 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA01457C
Q. Wu, J. Wang, H. Jin, T. Yan, G. Yi, X. Su, W. Dai, X. Wang, MOF-derived rambutan-like nanoporous carbon/nanotubes/Co composites with efficient microwave absorption property. Mater. Lett. 244, 138–141 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.02.023
D. Liu, R. Qiang, Y. Du, Y. Wang, C. Tian, X. Han, Prussian blue analogues derived magnetic FeCo alloy/carbon composites with tunable chemical composition and enhanced microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 514, 10–20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.12.013
X. Liang, B. Quan, Z. Man, B. Cao, N. Li, C. Wang, G. Ji, T. Yu, Self-assembly three-dimensional porous carbon networks for efficient dielectric attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(33), 30228–30233 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b08365
X. Cui, X. Liang, W. Liu, W. Gu, G. Ji, Y. Du, Stable microwave absorber derived from 1D customized heterogeneous structures of Fe3N@C. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122589 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122589
Y. Sun, N. Wang, H. Yu, X. Jiang, Metal–organic framework-based Fe/C@Co3O4 core–shell nanocomposites with outstanding microwave absorption properties in low frequencies. J. Mater. Sci. 55(17), 7304–7320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04521-w
Y. Lü, Y. Wang, H. Li, Y. Lin, Z. Jiang, Z. Xie, Q. Kuang, L. Zheng, MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7(24), 13604–13611 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03177
K. Wang, Y. Chen, R. Tian, H. Li, Y. Zhou, H. Duan, H. Liu, Porous Co–C core–shell nanocomposites derived from Co-MOF-74 with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10(13), 11333–11342 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b00965
T. Wu, Y. Liu, X. Zeng, T. Cui, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, G. Tong, Facile hydrothermal synthesis of Fe3O4/C core–shell nanorings for efficient low-frequency microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(11), 7370–7380 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b00264
L. Huang, J. Li, Y. Li, X. He, Y. Yuan, Fibrous composites with double-continuous conductive network for strong low-frequency microwave absorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 58(27), 11927–11938 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b01277
R. Qiang, Y. Du, D. Chen, W. Ma, Y. Wang, P. Xu, J. Ma, H. Zhao, X. Han, Electromagnetic functionalized Co/C composites by in situ pyrolysis of metal-organic frameworks (ZIF-67). J. Alloy. Compd. 681, 384–393 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.225
H.T. Zhu, J. Luo, J.K. Liang, G.H. Rao, J.B. Li, J.Y. Zhang, Z.M. Du, Synthesis and magnetic properties of antiferromagnetic Co3O4 nanoparticles. Phys. B 403(18), 3141–3145 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2008.03.024
M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Khansari, Synthesis and characterization of Co3O4 nanoparticles by a simple method. C. R. Chim. 17(4), 352–358 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2013.01.023
X. Wang, J. Zhou, H. Fu, W. Li, X. Fan, G. Xin, J. Zheng, X. Li, MOF derived catalysts for electrochemical oxygen reduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(34), 14064–14070 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA01506A
Y. Du, W. Liu, R. Qiang, Y. Wang, X. Han, J. Ma, P. Xu, Shell Thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core–shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6(15), 12997–13006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am502910d
Z. Fang, C. Li, J. Sun, H. Zhang, J. Zhang, The electromagnetic characteristics of carbon foams. Carbon 45(15), 2873–2879 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.10.013
Q. Liu, D. Zhang, T. Fan, Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous carbon/Co nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93(1), 013110 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2957035
P.C.P. Watts, W.-K. Hsu, A. Barnes, B. Chambers, High permittivity from defective multiwalled carbon nanotubes in the X-band. Adv. Mater. 15(7–8), 600–603 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200304485
B. Wen, M. Cao, M. Lu, W. Cao, H. Shi, J. Liu, X. Wang, H. Jin, X. Fang, W. Wang, J. Yuan, Reduced graphene oxides: light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater. 26(21), 3484–3489 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201400108
J.-C. Shu, M.-S. Cao, M. Zhang, X.-X. Wang, W.-Q. Cao, X.-Y. Fang, M.-Q. Cao, Molecular patching engineering to drive energy conversion as efficient and environment-friendly cell toward wireless power transmission. Adv. Func. Mater. 30(10), 1908299 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201908299
M. Cao, X. Wang, W. Cao, X. Fang, B. Wen, J. Yuan, Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small 14(29), 1800987 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201800987
L. Huang, C. Chen, X. Huang, S. Ruan, Y.-J. Zeng, Enhanced electromagnetic absorbing performance of MOF-derived Ni/NiO/Cu@C composites. Compos. B Eng. 164, 583–589 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.081
T.S. Bird, Definition and misuse of return loss. IEEE Antenn Propag M 51(2), 166–167 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/Map.2009.5162049
Y. Liu, K. Zhao, M.G.B. Drew, Y. Liu, A theoretical and practical clarification on the calculation of reflection loss for microwave absorbing materials. AIP Adv. 8(1), 015223–015238 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Jia, H., Liu, J. et al. Metal–organic framework-derived C/Co/Co3O4 nanocomposites with excellent microwave absorption properties in low frequencies. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 11700–11713 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03721-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03721-z