Abstract
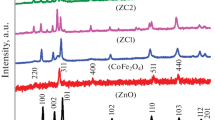
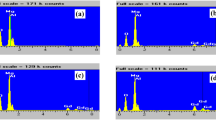
A comprehensive EPR and optical studies of pure MgFe2O4 and ZnO nanoparticles and MgFe2O4–ZnO nanocomposite have been done in order to explore its future possibilities of applications. Pure MgFe2O4 and ZnO nanoparticles have been synthesized using Sol–Gel method. MgFe2O4–ZnO nanocomposite has been prepared using water dispersed pure MgFe2O4 nano seeds (previously synthesized) by ultrasonication. Effect of introducing zinc oxide in pure MgFe2O4 nanomatrix on structural properties was investigated using X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy techniques. They confirm the cubic spinel structure of both pure and ZnO imbedded MgFe2O4 samples. UV–Visible and photoluminescence spectra show that the band gap of composite is tuned and more useful for photocatalytic applications. FTIR spectra indicate the presence of absorption bands in the range 390–561 cm−1, which is a common feature of spinel ferrite. The energy dispersive spectroscopy analysis confirms the composition of specimen. Further, the investigation of electronic and magnetic properties of the powdered samples is done using electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Change in g value, peak-to-peak line width (Hpp), resonance field (Hr) and spin–spin relaxation time (T2) give useful information.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Barrera, P. Tiberto, P. Allia, B. Bonelli, S. Esposito, A. Marocco, M. Pansini, Y. Leterrier, Review: magnetic properties of nanocomposites. Appl. Sci. 9, 212 (2019)
M. Rostami, M.H.M. Ara, The dielectric, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Cu-substituted Mg-Ni spinel ferrite-MWCNT nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.056
A.K. Zak, A.M. Hashim, M. Darroudi, Optical properties of ZnO/BaCO3 nanocomposites in UV and visible regions nanoscale. Res. Lett. 9, 399 (2014)
A.M. Mohammad, S.M.A. Ridha, T.H. Mubarak, Dielectric properties of Cr-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesis by citrate-gel auto combustion method. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 13(8), 6026–6035 (2018)
L. Zheng, K. Fang, M. Zhang, Z. Nan, L. Zhao, D. Zhou, M. Zhub, W. Li, Tuning of spinel magnesium ferrite nanoparticles with enhanced magnetic properties. RSC Adv. 8, 39177–39181 (2018)
M. Amiri, M.S. Niasari, A. Akbari, Magnetic nanocarriers: evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 265, 29–44 (2019)
P. Tiwari, R. Verma, S.N. Kane, T. Tatarchuk, F. Mazaleyrat, Effect of Zn addition on structural, magnetic properties and anti-structural modeling of magnesium-nickel nano ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 229, 78–86 (2019)
D.K. Mahato, Ac conductivity analysis of nanocrystallite MgFe2O4 ferrite. Mater. Today 5(3), 9191–9195 (2018)
N. Sivakumar, A. Narayanasamya, J.-M. Greneche, R. Murugaraj, Y.S. Lee, Electrical and magnetic behaviour of nanostructured MgFe2O4 spinel ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 504, 395–402 (2010)
R.P. Singha, C. Venkataraju, Effect of calcinations on the structural and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol gel method. Chin. J. Phys. 56, 2218–2225 (2018)
J. Balavijayalakshmi, Greeshma, Synthesis and characterization of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles by co-precipitation method. J. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2(2), 53–55 (2013)
S.I. Hussein, A.S. Elkady, M.M. Rashad, A.G. Mostafa, R.M. Megahid, Structural and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles prepared via EDTA-based sol–gel reaction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 379, 9–15 (2015)
N.R. Su, P. Lv, M. Li, X. Zhang, M. Li, J. Niu, Fabrication of MgFe2O4–ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts for application of organic pollutants. Mater. Lett. 122, 201–204 (2014)
S. Maensiri, M. Sangmanee, A. Wiengmoon, Magnesium ferrite (MgFe2O4) nanostructures fabricated by electrospinning nanoscale. Res. Lett. 4, 221–228 (2009)
S.S. Kumar, P. Venkateswarlu, V.R. Rao, G.N. Rao, Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett. 3, 30 (2013)
J. Jiang, J. Pi, J. Cai, Review: the advancing of zinc oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1062562
J.N. Hasnidawani, H.N. Azlina, H. Norita, N.N. Bonnia, S. Ratim, E.S. Ali, Synthesis of ZnO nanostructures using sol-gel method. Procedia Chem. 19, 211–216 (2016)
A. Janotti, Walle C.G. Vde, Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 126501 (2009)
M. Arakha, J. Roy, P.S. Nayak, B. Mallick, S. Jha, Free radical biology and medicine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 110, 42–53 (2017)
M.K. Debanath, S. Karmakar, Study of blueshift of optical band gap in zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles prepared by low-temperature wet chemical method. Mater. Lett. 111, 116–119 (2013)
M.D. Tyona, R.U. Osuji, P.U. Asogwa, S.B. Jambure, F.I. Ezema, Structural modification and band gap tailoring of zinc oxide thin films using copper impurities. J. Solid State Electrochem. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3533-3
N. Hana, Y. Tiana, X. Wua, Y. Chen, Improving humidity selectivity in formaldehyde gas sensing by a two-sensor array made of Ga-doped ZnO. Sens. Actuators B 138, 228–235 (2009)
A. Al-Kahlout, ZnO nanoparticles and porous coatings for dye-sensitized solar cell application: photoelectrochemical characterization. Thin Solid Films 520, 1814–1820 (2012)
H.H. Yun, J.S. Kim, E.H. Kim, S.K. Lee, J.W. Kim, H.J. Lim, S.M. Koo, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2@mercaptofunctionalized silica toward colored organic dyes. J. Mater. Sci. 50, 2577–2586 (2015)
G. Nabiyouni, D. Ghanbari, J. Ghasemi, A. Yousofnejad, Microwave-assisted synthesis of MgFe2O4-ZnO nanocomposite and its photocatalyst investigation in methyl orange degradation. J. Nano Struct. 5(3), 289–295 (2015)
A. Loganathan, K. Kumar, Effects on structural, optical, and magnetic properties of pure and Sr-substituted MgFe2O4 nanoparticles at different calcinations temperatures. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 629–639 (2016)
S. Mallesh, D. Prabu, V. Srinivas, Thermal stability and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4@ZnO nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 7, 056103 (2017)
A.I. Ahmed, A.M.A. Siddig, A.A. Mirghni, M.I. Omer, a Abdelrahman, A.A. Elbadawi, Structural and optical properties of Mg1-xZnxFe2O4 nano-ferrites synthesized using co-precipitation method. Adv. Nanopart. 4, 45–52 (2015)
F.A. Ahmed, L.N. Singh, Effect of Ni substitution on structural and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Surf. Eng. 6(4), 825–830 (2018)
S.K. Sharma, R. Kumar, V.V.S. Kumar, S.N. Dolia, Size dependent magnetic behaviour of nanocrystalline spinel ferrite Mg0.95Mn0.05Fe2O4. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 45, 16–20 (2007)
B. Issa, I.M. Obaidat, B.A. Albiss, Y. Haik, Magnetic nanoparticles: surface effects and properties related to biomedicine application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 21266–21305 (2013)
A.-M. AlTurki, Superparamagnetic MnFe2O4 and MnFe2O4 NPs/ABS nanocomposite: preparation, thermal stability and exchange bias effect. Indian J. Sci. Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2018/v11i19/122884
A. Franco Jr., H.V.S. Pessoni, F.O. Neto, Enhanced high temperature magnetic properties of ZnO _ CoFe2O4 ceramic composite. J. Alloys Compd. 680, 198–205 (2016)
T.J. Castro, S.W. daSilva, F. Nakagomi, N.S. Moura, A. Franco Jr., P.C. Morais, Structural and magnetic properties of ZnO–CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 389, 27–33 (2015)
A.K. Gupta, R. Kripal, EPR and photoluminescence properties of Mn2+ doped CdS nanoparticles synthesized via co-precipitation method. Spectrochim. Acta A 96, 626–631 (2012)
A.K. Verma, D. Singh, S. Singh, R.R. Yadav, Surfactant-free synthesis and experimental analysis of Mn-doped ZnO–glycerol nanofluids: an ultrasonic and thermal study. Appl. Phys. A 125, 253 (2019)
W.R. Agami, Effect of neodymium substitution on the electric and dielectric properties of Mn-Ni-Zn ferrite. Physica B (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.01.021
D. Guan, J. Li, X. Gao, C. Yuan, Effects of amorphous and crystalline MoO3 coatings on the Li-ion insertion behavior of a TiO2 nanotube anode for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 4, 4055 (2014)
M.A. Johar, R.A. Afzal, A.A. Alazba, U. Manzoor, Review article photocatalysis and bandgap engineering using ZnO nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/934587
B.D. Cardoso et al., Magnetoliposomes containing magnesium ferrite nanoparticles as nanocarriers for the model drug curcumin. R. Soc. Open Sci. 5, 181017 (2018)
Y. Wang, H. Yana, Q. Zhang, Enhanced visible light irradiation photocatalytic performance of MgFe2O4 after growing with ZnO nanoshell and silver nanoparticles. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201700110)
H.M. El-Sayed, W.R. Agami, Controlling of optical energy gap of Co-ferrite quantum dots in poly (methyl methacrylate) matrix. Superlattices Microstruct. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2015.04.013
M.E. Sadat et al., Photoluminescence and photothermal effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for medical imaging and therapy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 091903 (2014)
W.R. Agami, M.A. Ashmawy, A.A. Sattar, Structural, IR, and magnetic studies of annealed Li-ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0754-1
M.G. Naseri, M.H.M. Ara, E.B. Saion, A.H. Shaari, Superparamagnetic magnesium ferrite nanoparticles fabricated by a simple, thermal-treatment method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 350, 141–147 (2014)
S. Pandey, R. Kripal, EPR, optical absorption and superposition model study of Fe3+ doped strontium nitrate single crystals. J. Magn. Reson. 209, 220–226 (2011)
K.K. Bamzai, G. Kour, B. Kaur, M. Arora, R.P. Pant, Infrared spectroscopic and electron paramagnetic resonance studies on Dy substituted magnesium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 345, 255–260 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Head, SAIF, I. I. T. Mumbai, Powai, Mumbai for providing the facility of EPR spectrometer. One of the authors, Garima Vaish is thankful to the Head, Department of Physics, University of Allahabad, Allahabad for providing departmental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaish, G., Kripal, R. & Kumar, L. EPR and optical studies of pure MgFe2O4 and ZnO nanoparticles and MgFe2O4–ZnO nanocomposite. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 16518–16526 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02028-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02028-y