Abstract
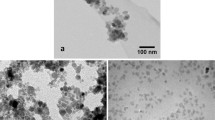
In this work, a successful synthesis of magnetic cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles is presented. The synthesized CoFe2O4 nanoparticles have a spherical shape and highly monodisperse in the selected solvent. The effect of different reaction conditions such as temperature, reaction time and varying capping agents on the phase and morphology is studied. Scanning transmission electron microscopy showed that the size of these nanoparticles can be controlled by varying reaction conditions. Both X-ray diffraction and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy corroborate the formation of CoFe2O4 spinel structure with cubic symmetry. Due to optimized reaction parameters, each nanoparticle was shown to be a single magnetic domain with diameter ranges from 6 to 16 nm. Finally, the magnetic investigations showed that the obtained nanoparticles are superparamagnetic with a small coercivity value of about 315 Oe and a saturation magnetization of 58 emu/g at room temperature. These results make the cobalt ferrite nanoparticles promising for advanced magnetic nanodevices and biomagnetic applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.A. Frey, S. Peng, K. Cheng, S. Sun, Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, functionalization, and applications in bioimaging and magnetic energy storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 2532 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b815548h
A.-H. Lu, E.L. Salabas, F. Schüth, Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 1222–1244 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866
K. Raj, R. Moskowitz, Commercial applications of ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 85, 233–245 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(90)90058-X
H. Anwar, A. Maqsood, Comparison of structural and electrical properties of Co2+ doped Mn–Zn soft nano ferrites prepared via coprecipitation and hydrothermal methods. Mater. Res. Bull. 49, 426–433 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.09.009
X. Huang, Y. Li, Y. Li et al., Synthesis of PtPd bimetal nanocrystals with controllable shape, composition, and their tunable catalytic properties. Nano Lett. 12, 4265–4270 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl301931m
E.V. Rebrov, P. Gao, T.M.W.G.M. Verhoeven et al., Structural and magnetic properties of sol–gel Co2xNi0.5−x Zn0.5−xFe2O4 thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 723–729 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.10.031
Z. Lu, P. Gao, R. Ma et al., Structural, magnetic and thermal properties of one-dimensional CoFe2O4 microtubes. J. Alloys Compd. 665, 428–434 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.262
P.H. Nam, L.T. Lu, P.H. Linh et al., Polymer-coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and toxicity for hyperthermia applications. New J. Chem. 42, 14530–14541 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ01701H
L. Kumar, P. Kumar, M. Kar, Cation distribution by Rietveld technique and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Zn substituted nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 551, 72–81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.10.009
L. Yao, Y. Xi, G. Xi, Y. Feng, Synthesis of cobalt ferrite with enhanced magnetostriction properties by the sol–gel–hydrothermal route using spent Li-ion battery. J. Alloys Compd. 680, 73–79 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.092
Y.C. Wang, J. Ding, J.H. Yin et al., Effects of heat treatment and magnetoannealing on nanocrystalline Co-ferrite powders. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 124306 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2148632
L. Yan, Y. Wang, J. Li et al., Nanogrowth twins and abnormal magnetic behavior in CoFe2O4 epitaxial thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 123910 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3033371
Q. Song, Z.J. Zhang, Shape control and associated magnetic properties of spinel cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 6164–6168 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja049931r
J. Fu, J. Zhang, Y. Peng et al., Unique magnetic properties and magnetization reversal process of CoFe2O4 nanotubes fabricated by electrospinning. Nanoscale 4, 3932 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr30487b
Z. Mahhouti, M. Ben Ali, H. El Moussaoui et al., Structural and magnetic properties of Co0.7Ni0.3Fe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. Appl. Phys. A (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0178-5
I. Galarreta, M. Insausti, I. Gil de Muro et al., Exploring reaction conditions to improve the magnetic response of cobalt-doped ferrite nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 8, 63 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020063
S.M. Asgarian, S. Pourmasoud, Z. Kargar et al., Investigation of positron annihilation lifetime and magnetic properties of Co1−xCuxFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 6, 015023 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aae55d
A. Sobhani-Nasab, M. Behpour, M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi et al., New method for synthesis of BaFe12O19/Sm2Ti2O7 and BaFe12O19/Sm2Ti2O7/Ag nano-hybrid and investigation of optical and photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 5854–5865 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00883-3
C. Yang, H. Yan, A green and facile approach for synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles with tunable sizes and morphologies. Mater. Lett. 73, 129–132 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.01.031
X.-H. Li, C.-L. Xu, X.-H. Han et al., Synthesis and magnetic properties of nearly monodisperse CoFe2O4 nanoparticles through a simple hydrothermal condition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5, 1039–1044 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-010-9599-9
M.L. Aparna, A.N. Grace, P. Sathyanarayanan, N.K. Sahu, A comparative study on the supercapacitive behaviour of solvothermally prepared metal ferrite (MFe2O4, M=Fe Co, Ni, Mn, Cu, Zn) nanoassemblies. J. Alloys Compd. 745, 385–395 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.127
T. Hyeon, S.S. Lee, J. Park et al., Synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse maghemite nanocrystallites without a size-selection process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 12798–12801 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja016812s
L.T. Lu, N.T. Dung, L.D. Tung et al., Synthesis of magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with controlled morphology, monodispersity and composition: the influence of solvent, surfactant, reductant and synthetic conditions. Nanoscale 7, 19596–19610 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR04266F
I.C. Nlebedim, D.C. Jiles, Dependence of the magnetostrictive properties of cobalt ferrite on the initial powder particle size distribution. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 17A928 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4867343
C.P. Gräf, R. Birringer, A. Michels, Synthesis and magnetic properties of cobalt nanocubes. Phys. Rev. B (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.73.212401
Z. Wang, X. Liu, M. Lv et al., Preparation of one-dimensional CoFe2O4 nanostructures and their magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 15171–15175 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp802614v
Z. Zhang, A.J. Rondinone, J.X. Ma et al., Morphologically templated growth of aligned spinel CoFe2O4 nanorods. Adv. Mater. 17, 1415–1419 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200500009
H. El Moussaoui, T. Mahfoud, M. Ben Ali et al., Experimental studies of neodymium ferrites doped with three different transition metals. Mater. Lett. 171, 142–145 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.02.072
S. Hara, J. Aisu, M. Kato et al., One-pot synthesis of monodisperse CoFe2O4@Ag core-shell nanoparticles and their characterization. Nanoscale Res. Lett. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2544-z
L. Pérez-Mirabet, E. Solano, F. Martínez-Julián et al., One-pot synthesis of stable colloidal solutions of MFe2O4 nanoparticles using oleylamine as solvent and stabilizer. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 966–972 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.11.086
W. Baaziz, B.P. Pichon, S. Fleutot et al., Magnetic Iron oxide nanoparticles: reproducible tuning of the size and nanosized-dependent composition, defects, and spin canting. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 3795–3810 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp411481p
C.A. Crouse, A.R. Barron, Reagent control over the size, uniformity, and composition of Co–Fe–O nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 4146 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1039/b806686h
C. Moya, M. del Puerto Morales, X. Batlle, A. Labarta, Tuning the magnetic properties of Co-ferrite nanoparticles through the 1,2-hexadecanediol concentration in the reaction mixture. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 13143–13149 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01052G
Acknowledgements
This work has been carried out with the support of the Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research, and Professional Training (Enssup) (Morocco) and the National Center for Scientific and Technological Research (CNRST) through the grant Number: PPR15, and by the European H2020-MC-RISE-ENIGMA action (N°778072) and FEDER.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahhouti, Z., El Moussaoui, H., Mahfoud, T. et al. Chemical synthesis and magnetic properties of monodisperse cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 14913–14922 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01863-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01863-3