Abstract
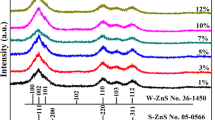
In this paper, the structural and optical properties of ZnS: Mn (0.6 at.%) quantum dots (QDs) synthesized by hydrothermal method at different reaction temperature were reported. X-ray diffraction patterns indicated that the ZnS: Mn QDs had cubic structure, and the average grain size increased from 3.75 to 6.36 nm with rising reaction temperature. Scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscopy images revealed that the small grain size made samples poor dispersion. Also, we provided Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy spectra of the ZnS: Mn QDs to investigate components information. Further, optical properties of ZnS: Mn QDs were found to be affected by quantum confinement effect and specific surface area. The optical energy gap increased from 3.2 to 3.5 eV with the decrease of reaction temperature. Moreover, photoluminescence emissions of all samples showed the blue shift of position and the increase of emissions intensity with decreasing reaction temperature.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Tang, Q. Hu, A. Ren et al., An approach to ZnTe:O intermediate-band photovoltaic materials. Sol. Energy 157, 707–712 (2017)
B. Poornaprakash, R.D. Amaranatha, G. Murali et al., Composition dependent room temperature ferromagnetism and PL intensity of cobalt doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 577, 79–85 (2013)
X.S. Fang, Y. Bando, U.K. Gautam et al., Inorganic semiconductor nanostructures and their field-emission applications. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 509–522 (2008)
W.T. Yao, S.H. Yu, Q.S. Wu, From mesostructured wurtzite ZnS nanowires/amine nanocomposite to ZnS quantum nanowires with quantum size effects: a mild solution approach. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17, 623–631 (2007)
S. Kumar, H.C. Jeon, T.W. Kang et al., Structural and optical properties of silica capped ZnS: Mn quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 3939–3946 (2015)
K.B. Lin, Y.H. Su, Photoluminescence of Cu:ZnS, Ag:ZnS, and Au:ZnS nanoparticles applied in Bio-LED. Appl. Phys. B 113, 351–359 (2013)
W.Q. Peng, G.W. Cong, S.C. Qu, Synthesis and photoluminescence of ZnS: Cu nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 29, 313–317 (2016)
W. Chen, J.O. Malm, V. Zwiller et al., Energy structure and fluorescence of Eu2+ in ZnS:Eu nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 61, 11021 (2000)
S.J. Xu, S.J. Chua, B. Liu et al., Luminescence characteristics of impurities-activated ZnS nanocrystals prepared in microemulsion with hydrothermal treatment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 478 (1998)
B.Y. Geng, L.D. Zhang, G.Z. Wang et al., Synthesis and photoluminescence properties of ZnMnS nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2157–2159 (2004)
P.N. Thanh, D.L. Anh, B.V. Thi et al., Investigations on photoluminescence enhancement of poly (vinyl alcohol)-encapsulated Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots. J. Lumin. 192, 166–172 (2017)
X. Qi, C. Xiao, Synthesis and photoluminescence of water-soluble Mn2+-doped ZnS quantum dots. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 6432–6435 (2008)
C.Y. Zhou, J.H. Song, L. Zhou et al., Greener synthesis and optimization of highly photoluminescence Mn2+-doped ZnS quantum dots. J. Lumin. 158, 176–180 (2015)
A.I. Cadis, L.E. Muresan, I. Perhaita et al., Synthesis and influence of ultrasonic treatment on luminescence of Mn incorporated ZnS nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 72, 533–539 (2017)
Y. Hu, Z.R. Wei, B. Wu et al., Photoluminescence of ZnS: Mn quantum dot by hydrothermal method. AIP Adv. 8, 015014 (2018)
M.F. Bulanyi, B.A. Polezhaev, T.A. Prokof’Ev et al., Excitation spectra and structure of luminescence centers of manganese ions in single crystals of zinc sulfide. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 67, 282–286 (2000)
J. Li, D. Yang, X. Zhu, Effects of aging time and annealing temperature on structural and optical properties of sol-gel ZnO thin films. AIP Adv. 7, 065213 (2017)
J. Li, X. Zhu, D. Yang, Investigations on structural, optical and X-radiation responsive properties of a-Se thin films fabricated by thermal evaporation method at low vacuum degree. Materials 11, 368 (2018)
H.Y. Lu, S.Y. Chu, S.S. Tan, The characteristics of low-temperature-synthesized ZnS and ZnO nanoparticles. J. Cryst. Growth 269, 385–391 (2004)
X.Z. Liu, J.H. Cui, L.P. Zhang et al., A solvothermal route to semiconductor ZnS micrometer hollow spheres with strong photoluminescence properties. Mater. Lett. 60, 2465–2469 (2006)
Y.Y. Bacherikov, N.P. Baran, I.P. Vorona et al., Structural and optical properties of ZnS:Mn micro-powders, synthesized from the charge with a different Zn/S ratio. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 8569–8578 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51671216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YH and JL conceived the study, completed the experiments, and wrote the paper; BH completed the literature search and helped the study design; BW and ZW characterized the data and collected the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Hu, B., Wu, B. et al. Hydrothermal preparation of ZnS: Mn quantum dots and the effects of reaction temperature on its structural and optical properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 16715–16720 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9764-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9764-y