Abstract
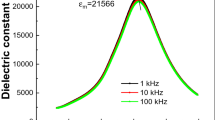
A novel Pb(Sc1/2Nb1/2)O3–Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–PbTiO3 (PSN–PMN–PT) single crystal with large size ϕ25 mm × 40 mm was grown by the Bridgman technique. The crystal was cut along [100] orientation with composition of 6PSN–63PMN–31PT, and then its structure and electric properties were investigated systematically. Raman test demonstrates that the crystal is typical relaxor ferroelectrics with perovskite structure. At room temperature, [100]-oriented 6PSN–63PMN–31PT crystal shows the excellent electric properties, such as the dielectric constant εr = 4793, the piezoelectric constant d33 = 1237 pC/N, and the remanent polarization Pr = 34.41 µC/cm2, respectively. It is more important that the large coercive field Ec = 8.17 kV/cm in [100]-oriented 6PSN–63PMN–31PT crystal is almost four times than that of PMN–PT, even higher than that of Pb(In1/2Nb1/2)O3–Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–PbTiO3 (PIN–PMN–PT) and Pb(Lu1/2Nb1/2)O3–Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–PbTiO3 (PLN–PMN–PT), indicating its potential application for high-power transducers. With elevating temperature, the [100]-oriented 6PSN–63PMN–31PT crystal shows the large pyroelectric coefficient p = 3.49 × 10−2 C/m2/K at phase transition temperature, and the related figures of merit (FOMs) for current responsivity Fi, for voltage responsivity Fv and for detectivity FD increase from 1.968 × 10−10 m/V, 0.00485 m2/C and 0.59 × 10−5 Pa−1/2 to 1.396 × 10−8 m/V, 0.054 m2/C, and 52.94 × 10−5 Pa−1/2, respectively. Furthermore, the thermal strain at heating process was analyzed for unpoled and poled crystal.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Li, X.F. Long, M. Ye, H.R. Wang, H.T. Huang, X.R. Zeng, S.M. Ke, Ceram. Int. 41, 14427 (2015)
K.K. Rajan, M. Shanthi, W.S. Chang, J. Jin, L.C. Lim, Sens. Actuators A 133, 110 (2007)
A. Dąbkowski, H.A. Dąbkowska, J.E. Greedan, W. Ren, B.K. Mukherjee, J. Cryst. Growth 265, 204 (2004)
L.H. Wang, Z. Xu, Z.R. Li, F. Li, Ferroelectrics 402, 187 (2010)
X. Jiang, F. Tang, J.T. Wang, T.P. Chen, Physica C 365, 678 (2001)
Z.Z. Xi, A.M. Han, P.Y. Fang, W. Long, X.J. Li, Q.Q. Bu, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 4223 (2016)
L.H. Luo, W.P. Li, Y.J. Zhu, J. Wang, Solid State Commun. 149, 978 (2009)
Y.L. Wang, E.W. Sun, W. Song, W.C. Li, R. Zhang, W.W. Cao, J. Alloys Compd. 601, 154 (2014)
Z.J. Wang, X.Z. Li, C. He, Y. Liu, S.J. Han, S.L. Pan, X.F. Long, J. Mater. Sci. 50, 3970 (2015)
R.F. Zhu, W.W. Ji, B.J. Fang, D. Wu, Z.H. Chen, J.N. Ding, X.Y. Zhao, H.S. Luo, Ceram. Int. 43, 6417 (2017)
J. Anthoniappen, C.S. Tu, P.Y. Chen, Y.U. Idzerda, S.J. Chiu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 3495 (2015)
X. Liu, F. Li, J.W. Zhai, B. Shen, P. Li, Y. Zhang, B.H. Liu, Mater. Res. Bull. 97, 215 (2018)
S.J. Zhang, P.W. Rehrig, C. Randall, T.R. Shrout, J. Cryst. Growth 234, 415 (2002)
Y.P. Guo, H.Q. Xu, H.S. Luo, G.S. Xu, Z.W. Yin, J. Cryst. Growth 226, 111 (2001)
Y.H. Bing, Z.G. Ye, J. Cryst. Growth 287, 326 (2006)
X.Z. Li, Z.J. Wang, C. He, Y. Liu, X.F. Long, S.J. Han, S.L. Pan, Mater. Lett. 143, 88 (2015)
J.W. Chen, X.B. Li, X.Y. Zhao, H.W. Zhang, H. Deng, C. Chen, X.A. Wang, B. Ren, W.N. Di, H.S. Luo, J. Cryst. Growth 423, 50 (2015)
Y. Li, Y.X. Tang, J.W. Chen, X.Y. Zhao, L.R. Yang, F.F. Wang, Z. Zeng, H.S. Luo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 172901 (2018)
Y.X. Tang, X.Y. Zhao, X.Q. Feng, W.Q. Jin, H.S. Luo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 082901 (2005)
Y.X. Tang, Z.Y. Shen, X.Y. Zhao, F.F. Wang, W.Z. Shi, D.Z. Sun, Z.Y. Zhou, S.J. Zhang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101, 1592 (2018)
M. Schossig, V. Norkus, G. Gerlach, Infrared Phys. Technol. 63, 35 (2014)
P. Yu, Y.X. Tang, H.S. Luo, J. Electroceram. 24, 1 (2010)
H. Wei, Y.J. Chen, Ceram. Int. 41, 6158 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51472197), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Grant No. 2013CB632900), the Shaanxi Key Laboratory Fundament Research Foundation (14JK1333) and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Functional Materials and Devices (Grant No. 2015SZSJ-59-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, A., Xi, Z., Li, X. et al. Structure analysis and systematical electric properties investigation of PSN–PMN–PT single crystal. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 16004–16009 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9686-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9686-8