Abstract
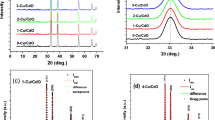
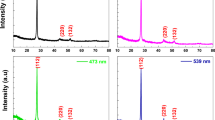
Transparent conducting aluminum (i.e. 2 at.%) doped zinc oxide (AZO) thin films were prepared on glass substrates by sol–gel dip coating technique using different solvents. This inexpensive dip coating method involves dipping of substrate consecutively in zinc solution and tube furnace for required cycles. Prepared films were investigated by XRD, SEM, PL, Raman spectroscopy optical and electrical studies. From the XRD studies, it confirmed the incorporation of aluminum in ZnO lattice. The prepared samples are polycrystalline nature, and these films reveal hexagonal wurtzite arrangement with (002) direction. The structural parameters such as crystallite size, dislocation density, micro strain, texture coefficient and lattice constant were investigated. SEM study showed well defined smooth and uniformed ganglia shaped grains are regularly distributed on to the entire glass substrate without any pinholes and cracks, and the average grain size is 75 nm. From the optical studies, the observed highest transmittance is 93% in the visible range and the band gap (Eg) is 3.26 eV. Room temperature PL spectra exhibited strong UV emission peak located at 386 nm for all the films. The electrical properties of the AZO thin films were studied by Hall-Effect measurements and found as n-type conductivity with high carrier concentrations (n), 2.76 × 1019 cm− 3 and low resistivity (ρ), 7.56 × 10− 3 Ω cm for the film deposed using methanol as solvent.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Janotti, C.G. Van de Walle, Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 1–29 (2009)
Z. Zang, A. Nakamura, J. Temmyo, Optics Express 21(9), 11448–11451 (2013)
Z. Zang, X. Zeng, J. Du, M. Wang, X. Tang, Opt. Lett. 41(15), 3463–3466 (2016)
C. Lia, C. Hana, Y. Zhang, Z. Zanga, M. Wanga, X. Tanga, J. Dua, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 172, 341–346 (2017)
K. Ellmer, A. Klein, ZnO and its applications, in Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide: Basics and Applications in Thin Film Solar Cells, Springer Series in Materials Science, vol 104, ed. by K. Ellmer, A. Klein, B. Rech (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2008), pp. 1–33
J.L. Chen, D. Chen, Z.H. Chen, Optimization of the process for preparing Al-doped ZnO thin films by sol-gel method. Sci. China Ser. E Tech. Sci. 52, 88–94 (2009)
F. Ahmed, N. Arshi, M.S. Anwar, R. Danish, B.H. Koo, Thin Solid Films 547, 168–172 (2013)
Y.K. Tseng, G.J. Gao, S.C. Chien, Synthesis of c-axis preferred orientation ZnO:Al transparent conductive thin films using a novel solvent method. Thin Solid Films 518, 6259–6263 (2010)
Ü. Özgür, I. AlivovYa, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Doğan, V. Avrutin, S.J. Cho, H. Morkoç, A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301:1–041301:103 (2005)
C. Bundesmann, R. Schmidt-Grund, M. Schubert, Optical properties of ZnO and related compounds, in Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide—Basics and Applications in Thin Film Solar Cells (Springer Series in Materials Science), vol 104, ed. by K. Ellmer, A. Klein, B. Rech (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2008), pp. 79–124
H. Von Wenckstern, H. Schmidt, M. Brandt, A. Lajn, R. Pickenhain, M. Lorenz, M. Grundmann, D.M. Hofmann, A. Polity, B.K. Meyer et al., Anionic and cationic substitution in ZnO. Prog. Solid State Chem. 37, 153–172 (2009)
F. Khan, V.S.N. Singh, M. Husain, P.K. Singh, Sol-gel derived hydrogen annealed ZnO:Al films for silicon solar cell application. Sol. Energy. Mater. Sol. Cells 100, 57–60 (2012)
J.I. Nomoto, T. Hirano, T. Miyata, T. Minami, Thin Solid Films 520, 1400–1406 (2011)
A.C. Galca, M. Secu, A. Vlad, J.D. Pedarnig, Thin Solid Films 518, 4603 (2010)
M. Farbod, M. Zargar Shoushtari, S. Parhoodeh, J Physica B 406, 205–210 (2011)
W.H. Kim, W.J. Maeng, M.K. Kim, H. Kim, J. Electro. Chem. Soc. 158, D495 (2011)
K. Mahmood, S.B. Park, Electron. Mater. Lett. 9, 161 (2013)
K. Deva Arun Kumar, S. Valanarasu, A Study of aluminium doped ZnO (AZO) thin film by SILAR method, in Journal of Latest Research in Engineering and Technology (IJLRET), pp. 17–19 (2016)
J. Zhang, W. Que, J. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 94, 2181–2186 (2010)
C. Boukaous, A. Telia, D. Horwat, M.S. Aida, B.B.S. Ghanem, Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 65, 20302 (2014)
C. Boukaous, A. Telia, D. Horwat, S. Ghanem, P. Miska, Effect of solvents on the properties of ZnO thin layers obtained by sol gel dip coating process. J. New Technol. Mater. JNTM 04(01), 94–98 (2014)
P. Mondal, D. Das, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 20450–20458 (2016)
N.S. Sabri, A.K. Yahya, M.K. Talari, AIP Conf. Proc. 1250, 436 (2010)
M. Shkir, I.S. Yahia, S. AlFaify, M.M. Abutalib, S. Muhammad, J. Mol. Struct. 1110, 83–90 (2016)
M. Shkir, I.S. Yahia, V. Ganesh, H. Algarni, S. AlFaify, Mater. Lett. 176, 135–138 (2016)
D. Guo, K. Satob, S. Hibinob, T. Takeuchi, H. Bessho, K. Kato, Low-temperaturepreparation of (002)-oriented ZnO thin films by sol–gel method. Thin Solid Films 550, 250–258 (2014)
R. Mariappan, M. Ragavendar, V. Ponnuswamy, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 7337–7343 (2011)
Z.R. Khan, M.S. Khan, M. Zulfequar, M.S. Khan, Mater. Sci. Appl. 2, 340 (2011)
C. Barret, T.B. Massalski, Structure of Metals, (Pergamon, Oxford, 1980), p. 923
M. Ren, Z. Mal, Y. Lu, The effect of the thermal annealing on ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition, J. Appl. Phys. 88(1), 498–502 (2000). doi:10.1063/1.373685
C. Bundesmann, N. Ashkenov, M. Schubert, D. Spemann, T. Butz, E.M. Kaidashev, M. Lorenz, M. Grundmann, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 1974–1983 (2003)
G. Srinivasan, R.T. Rajendra Kumar, J. Kumar, Influence of Al dopant on microstructure and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel spin coating methodOptical. Materials 30, 314–317 (2007)
N.V. Kaneva, C.D. Dushkin, A.S. Bojinova, ZnO thin films preparation on glass substrates by two different sol-gel methods. Bulgarian Chem. Commun. 44, 63–69 (2012)
V. Senthamilselvi, K. Saravanakumar, N. Jabena Begum, R. Anandhi, A.T. Ravichandran, B. Sakthivel, K. Ravichandran, J.Mater. Sci. 23, 302–308 (2012)
M. Arshad, A. Azam, A.S. Ahmed, S. Mollah, A.H. Naqvi, J. Alloy. Compd. 506, 8378–8381 (2011)
M. Bouloudenine, N. Viart, S. Colis, A. Dinia, Catal. Today 113, 240–244 (2006)
K. Ravichandran, R. Mohan, N. Jabena Begum, S. Snega, K. Swaminathan, C. Ravidhas, B. Sakthivel, S. Varadharajaperumal, Vacuum 107, 68–76 (2014)
J. Tauc, Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors. (Plenum Press, New York, 1974)
M. Shakir, S.K. Kushwaha, K.K. Maurya, G. Bhagavannarayana, M.A. Wahab, Solid State Commun. 149, 2047–2049 (2009)
M. Shkir, H. Abbas, Z.R. Khan, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 73, 1309–1313 (2012)
M. Shkir, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, I.S. Yahia, J. Mater. Sci. 28, 10573–10581 (2017)
M. Shkir, S. Alfaify, S. Muhammad, M. Nasir, N. Vijayan, S.K. Jat, M. Zulfequar, S. Rubio, E. Dieguez, Materials Focus 4, 202–207 (2015)
W.-W. Zhong, F.-M. Liu, L.-G. Cai, P. Ding, C.-C. Zhou, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 3847–3851 (2011)
N. Jabena Begum, R. Mohan, K. Ravichandran, Superlatt. Micro Struct. 53, 89–98 (2013)
L. Ma, S. Ma, H. Chen, X. Ai, X. Huang, Microstructuresand optical properties of Cu-doped ZnO films prepared byradio frequency reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 10036–10041 (2011)
Y.C. Kong, D.P. Yu, B. Zhang, W. Fang, S.Q. Feng, Ultraviolet-emitting ZnO nanowires synthesized by a physical vapor deposition approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 407–409 (2001)
S.C. Lyu, Y. Zhanga, H. Ruh, H.J. Lee, H.W. Shim, E.K. Suh, C.J. Lee, Low temperature growth and photoluminescence of well-aligned zinc oxide nanowires. Chem. Phys. Lett. 363, 134–138 (2002)
N.L. Tarwal, P.R. Jadhav, S.A. Vanalakar, S.S. Kalagi, R.C. Pawar, J.S. Shaikh, S.S. Mali, D.S. Dalavi, P.S. Shinde, P.S. Patil, Photoluminescence of Zinc oxide nanopowder synthesized by a combustion method. Powder Technol. 208, 185–188 (2011)
R. Mariappan, V. Ponnuswamy, P. Suresh, Effect of dopingconcentration on the structural and optical properties of pureand tin doped zinc oxide thin films by nebulizer spray pyrolysistechnique. Superlattices Microstruct. 52, 500–513 (2012)
Q.P. Wang, X.J. Zhang, G.Q. Wang, S.H. Chen, X.H. Wu, H.L. Ma, Influence of excitation light wavelength on the photo-luminescence properties for ZnO films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 5100–5104 (2008)
H.L. Shen, H. Zhang, L.F. Lu, F. Jiang, C. Yang, Progress in natural science. Mater. Int. 20, 44–48 (2010)
G. Haacke, J. Appl. Phys. 47, 4086 (1976)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to deanship of scientific research, King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia for providing the financial support under the Project Number R.G.P. 2/3/38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declares that there is no conflict of interest in the current article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deva Arun Kumar, K., Ganesh, V., Shkir, M. et al. Effect of different solvents on the key structural, optical and electronic properties of sol–gel dip coated AZO nanostructured thin films for optoelectronic applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 887–897 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7985-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7985-0