Abstract
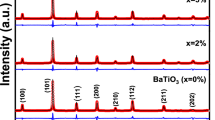
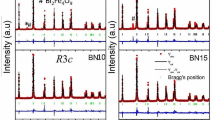
Single phase of pure BiFeO\(_{3}\) (BFO) and \({{{{\text{Bi}}_{0.99}{\text{Y}}_{0.01}{\text{Fe}}}_{1-{x}}\text{Co}_{{x}}\text{O}_{3}}}\) (\(0.01\le x\le 0.03\)) (\(\text {BYFC}\)) multiferroic ceramics were prepared by using a modified solid state reaction method. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) images revealed that the grain size and morphology were dependent on the nature of dopant. X-ray diffraction peaks were found to belong to the pure \(\text {BFO}\) structure with R3c space group of symmetry. It was found that the dielectric constant (\(\varepsilon '\)) values increased \(\sim\)13.5 times with the addition of Co ions; being \(\sim\)170 and \(\sim\)2300, for pure BFO and \(x=0.01\), respectively, at the lower frequencies (100 Hz). The dielectric behavior was described by the modified Cole–Cole model. Ferromagnetic (FM) ordering with saturation magnetization, \(M_{s}\), and coercivity \(H_{c}\) values of \(\sim\)0.75 emu/g and \(\sim\) \(\text {400 Oe}\), was found in the BYFC ceramics at \(\text {x = 0.03}\) at room temperature. A decrease in the band gap was observed due to the amount of doping in the BYFC ceramics. The origin of the enhanced dielectric and magnetic properties was discussed on the basis of the size effect and the nature of the dopants like \(\text {Y}^{3+}\), \({{{\text{Co}}^{2+}}}\) and \({{\text{Co}}^{3+}}\) ions in the lattice structure of the doped ceramics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Dong, J.M. Liu, Recent progress of multiferroic perovskite manganites. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 26(09), 1230004 (2012)
N. Panwara, I. Coondooa, A. Tomar, Nanoscale piezoresponse and magnetic studies of multiferroic Co and Pr co-substituted BFO thin films. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(12), 4240 (2012)
P. Banerjee, A. Franco Jr, Enhanced dielectric and magnetic properties in multiferroic Bi0.99Y0.01Fe0.99Ni0.01O3 ceramic. Mater. Lett. 184, 17–20 (2016)
P. Banerjee, A. Franco Jr., Rare earth and transition metal doped BiFeO\(_{3}\) ceramics: structural, magnetic and dielectric characterization. J. Mater. Sci. 27(6), 6053–6059 (2016)
C. Chen, J. Cheng, S. Yu, L. Che, Z. Meng, Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite bismuth ferrite crystallites. J. Cryst. Growth 291(1), 135–139 (2006)
R.Y. Umetsu, Y. Mitsui, I. Yuito, T. Takeuchi, H. Kawarada, Substitution effects of Cr or Fe on the curie temperature for mn-based layered compounds MnAlGe and MnGaGe with Cu\(_{2}\)Sb -type structure. IEEE Trans. Magn. 50(11), 1–4 (2014)
Z. Yan, K.F. Wang, J.F. Qu, Y. Wang, Processing and properties of Yb-doped BiFeO\(_{3}\) ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 082906 (2007)
T.D. Berman, T.M. Pollock, J.W. Jones, Microstructure and texture through thixomolding and thermomechanical processing and the role of Mg\(_{17}\)Al\(_{12}\) particles. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47(6), 3125–3136 (2016)
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83(1), 121 (1951)
Y.-Q. Mao, Z.-J. Zhou, T. Ling, X.-W. Du, P-type CoO nanowire arrays and their application in quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 3, 1217–1221 (2013)
D.K. Pradhan, R.N.P. Choudhary, B.K. Samantaray, Studies of dielectric relaxation and AC conductivity behavior of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 3, 597–608 (2008)
W. Hu, Y. Liu, R.L. Withers, T.J. Frankcombe, L. Noraon, A. Snashall, M. Kitchin, P. Smith, B. Gong, H. Chen, J. Schiemer, F. Brink, J. Wong-Leung, Electron-pinned defect-dipoles for high-performance colossal permittivity materials. Nat. Mater. 12(9), 821–826 (2013)
Kennieth S. Cole, Robert H. Cole, Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics. J. Chem. Phys. 9, 341 (1941)
Y. Gonzalez Abreu, A. Pelaiz Barranco, E .B. Araujo, A. Franco Jr, Dielectric relaxation and relaxor behavior in bilayered perovskites. Appl. Phy. Lett. 94, 262903 (2009)
C. Kittel, Introduction to solid state physics (Wiley, New York, 1995)
S.S. Naira, M. Mathews, P. Joy, S.D. Kulkarni, M.R. Anantharaman, Effect of cobalt doping on the magnetic properties of superparamagnetic \(\gamma\)-Fe\(_{2}\)O\(_{3}\)-polystyrene nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 283(2–3), 344–352 (2004)
S.K. Pradhan, Effect of barium substitution on ferroelectric and magnetic properties of bismuth ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 3614 (2010)
S.K. Pradhan, B.K. Roul, Electrical behavior of high resistivity Ce-doped BiFeO\(_{3}\) multiferroic. Phys. B 407(13), 2527–2532 (2012)
M. Naeem, S. Qaseem, I.H. Gul, A. Maqsood, Study of active surface defects in Ti doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 107(12), 124303 (2010)
H. Liu, Y. Guo, B. Guo, D. Zhang, Synthesis and visible-light photocatalysis capability of BiFeO\(_{3}\)–(Na\(_{0.5}\)Bi\(_{0.5}\))TiO\(_{3}\) nanopowders by a sol–gel method. Solid State Sci. 19, 69–72 (2013)
H. Kim, C.M. Gilmore, A. Pique, J.S. Horwitz, H. Mattoussi, H. Murata, Z.H. Kafafi, D.B. Chrisey, Electrical, optical, and structural properties of indium-tin-oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. J. Appl. Phys. 86(11), 6451–6461 (1999)
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge the support received from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Goiás (FAPEG) project Grant DCR-14/2013 and by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) postdoctoral fellowship Grant 300810/2015-6. One of us (A. Franco Jr) is a CNPq fellow under Grant No. 308183/2012-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banerjee, P., Franco Jr, A. Influence of Y and Co co-doping in the multiferroic behaviors of BiFeO3 ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 8562–8568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6579-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6579-1