Abstract
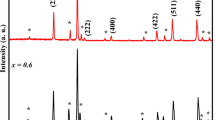
Substituted strontium hexaferrite ceramics SrCr x Al x Fe12−2x O19 (x = 0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0) were prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) study revealed the M-type hexagonal structure of the synthesized nanoferrites with some additional peaks of Fe2O3. The lattice constants (a and c), unit cell volume (V), X-ray density (ρ x ), bulk density (ρ m ), porosity (P) and average crystallite size (t) values changes when Al–Cr ions are co-substituted in SrFe12O19 lattice, resulting in the structural variation. The surface morphology of the grains was examined by scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) confirmed the formation of hexagonal ferrite structure. Ferromagnetic nature confirmed by recording M-H curves exhibited typical hysteresis loop at room temperature using pulse field hysteresis loop tracer technique. The large coercivity (H c ) values indicate the nanocrystalline nature of the present samples. The coercivity (H c ), saturation magnetization (M s ), remanence magnetization (M r ) and magneton number (n B ) decreases with increase in Al–Cr content x. The DC electrical resistivity studies of the prepared samples were carried out in the temperature range of 300–873 K using a standard two-probe technique. Curie temperature (Tc) i.e. ferrimagnetic to paramagnetic transition temperature for all samples was obtained from resistivity data. The Curie temperature decreases linearly as the concentration of Al–Cr content is increased. The activation energy below and above Tc was calculated. The dielectric parameters such as dielectric constant (ɛ′), dielectric loss (ɛ″) and loss tangent (tan δ) were measured in the frequency range 50 Hz–5 MHz at room temperature. All the dielectrical parameters show compositional as a function of frequency dependences. At lower frequencies, it is observed that the dielectric constant (ɛ′), dielectric loss (ɛ″) and loss tangent (tan δ) are high.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Meshram, N.K. Agrawal, B. Sinha, P. Misra, Characterization of M-type barium hexagonal ferrite-based wide band microwave absorber. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 271, 207–214 (2004)
P. Tenaud, A. Morel, F. Kools, J. Le Breton, L. Lechevallier, Recent improvement of hard ferrite permanent magnets based on La–Co substitution. J. Alloy. Compd. 370, 331–334 (2004)
T. Nakamura, E. Hankui, Control of high-frequency permeability in polycrystalline (Ba, Co)-Z-type hexagonal ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 257, 158–164 (2003)
O. Kubo, T. Ido, H. Yokoyama, Properties of Ba ferrite particles for perpendicular magnetic recording media. Magn. IEEE Trans 18, 1122–1124 (1982)
S. Ram, D. Bahadur, D. Chakravorty, Crystallisation of W-type hexagonal ferrites in an oxide glass with As2O3 as nucleation catalyst. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 67, 378–386 (1987)
J. Uher, W.J. Hoefer, Tunable microwave and millimeter-wave band-pass filters. Microw. Theory Tech. IEEE Trans. 39, 643–653 (1991)
R. Tiwary, S. Narayan, O. Pandey, Preparation of strontium hexaferrite magnets from celestite and blue dust by mechanochemical route. J. Min. Metall.Sect. B. 44, 91–100 (2008)
T.-S. Chin, Permanent magnet films for applications in microelectromechanical systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 209, 75–79 (2000)
M.J. Iqbal, M.N. Ashiq, Physical and electrical properties of Zr–Cu substituted strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Chem. Eng. J. 136, 383–389 (2008)
M.J. Iqbal, M.N. Ashiq, P. Hernandez-Gomez, J.M. Munoz, Magnetic, physical and electrical properties of Zr–Ni-substituted co-precipitated strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles. Scripta Mater. 57, 1093–1096 (2007)
M. Hessien, M. Rashad, K. El-Barawy, Controlling the composition and magnetic properties of strontium hexaferrite synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 336–343 (2008)
S. Hussain, A. Maqsood, Influence of sintering time on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Si–Ca added Sr-hexa ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 73–80 (2007)
F. Leccabue, R. Panizzieri, G. Salviati, G. Albanese, J.S. Llamazares, Magnetic and morphological study of BaZn2Fe16O27 hexagonal ferrite prepared by chemical coprecipitation method. J. Appl. Phys. 59, 2114–2118 (1986)
E. Kiani, A.S. Rozatian, M.H. Yousefi, Synthesis and characterization of SrFe12O19 nanoparticles produced by a low-temperature solid-state reaction method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 2485–2492 (2013)
R. Pullar, A. Bhattacharya, Crystallisation of hexagonal M ferrites from a stoichiometric sol–gel precursor, without formation of the α-BaFe 2 O 4 intermediate phase. Mater. Lett. 57, 537–542 (2002)
H.-I. Hsiang, R.-Q. Yao, Hexagonal ferrite powder synthesis using chemical coprecipitation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 104, 1–4 (2007)
A. Xia, C. Zuo, L. Chen, C. Jin, Y. Lv, Hexagonal SrFe 12 O 19 ferrites: hydrothermal synthesis and their sintering properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 332, 186–191 (2013)
P. Xu, X. Han, M. Wang, Synthesis and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 hexaferrite nanoparticles by a reverse microemulsion technique. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 5866–5870 (2007)
Z. Yue, J. Zhou, L. Li, H. Zhang, Z. Gui, Synthesis of nanocrystalline NiCuZn ferrite powders by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 208, 55–60 (2000)
L.L. Hench, J.K. West, The sol-gel process. Chem. Rev. 90, 33–72 (1990)
Y. Li, R. Liu, Z. Zhang, C. Xiong, Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline BaFe 9.6 Co 0.8 Ti 0.8 M 0.8 O 19 particles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 64, 256–259 (2000)
Q. Fang, H. Cheng, K. Huang, J. Wang, R. Li, Y. Jiao, Doping effect on crystal structure and magnetic properties of chromium-substituted strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 294, 281–286 (2005)
P. Röschmann, M. Lemke, W. Tolksdorf, F. Welz, Anisotropy fields and FMR linewidth in single-crystal Al, Ga and Sc substituted hexagonal ferrites with M structure. Mater. Res Bull. 19, 385–392 (1984)
Z. Wang, Z. Zhou, W. Zhang, H. Qian, M. Jin, Preparation and magnetic properties of Nd3+ , Al3+ , Ca2+ substituted M-type strontium hexaferrites. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 26, 3501–3506 (2013)
A. Sharbati, J.M.V. Khani, Effect of Ho3+ substitution on magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Sr (ZnZr) 0.5 Fe12O19 hexagonal ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 3629–3633 (2013)
S. Kanagesan, S. Jesurani, R. Velmurugan, S. Prabu, T. Kalaivani, Magnetic properties of Ni–Co doped barium strontium hexaferrite. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 23, 1575–1579 (2012)
G. Albanese, M. Carbucicchio, A. Deriu, Temperature dependence of the sublattice magnetizations in Al-and Ga-substituted M-type hexagonal ferrites. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 23, 351–358 (1974)
A. Kamzin, L. Ol’khovik, Surface magnetism of Al-substituted Sr-M-type hexagonal ferrites. Phys. Solid State 41, 1658–1664 (1999)
S. Ounnunkad, P. Winotai, Properties of Cr-substituted M-type barium ferrites prepared by nitrate–citrate gel-autocombustion process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 301, 292–300 (2006)
M.N. Ashiq, M. Javed, I. Iqbal, H. Gul, Effect of Al–Cr doping on the structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of strontium hexaferrite nanomaterials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 259–263 (2011)
R. Alange, P.P. Khirade, S.D. Birajdar, A.V. Humbe, K. Jadhav, Structural, magnetic and dielectrical properties of Al–Cr Co-substituted M-type barium hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 1106, 460–467 (2016)
X. Obradors, X. Solans, A. Collomb, D. Samaras, J. Rodriguez, M. Pernet, M. Font-Altaba, Crystal structure of strontium hexaferrite SrFe12O19. J. Solid State Chem. 72, 218–224 (1988)
A. Ataie, S. Heshmati-Manesh, Synthesis of ultra-fine particles of strontium hexaferrite by a modified co-precipitation method. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 1951–1955 (2001)
L. Vegard, Die konstitution der mischkristalle und die raumfüllung der atome. Zeitschrift für Physik A Hadrons Nuclei 5, 17–26 (1921)
C. Fang, F. Kools, R. Metselaar, R. De Groot, Magnetic and electronic properties of strontium hexaferrite SrFe12O19 from first-principles calculations. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15, 6229 (2003)
V.N. Dhage, M. Mane, A. Keche, C. Birajdar, K. Jadhav, Structural and magnetic behaviour of aluminium doped barium hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by solution combustion technique. Phys B 406, 789–793 (2011)
F. Khademi, A. Poorbafrani, P. Kameli, H. Salamati, Structural, magnetic and microwave properties of Eu-doped barium hexaferrite powders. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 25, 525–531 (2012)
A. Thakur, R. Singh, P. Barman, Synthesis and characterizations of Nd 3+ doped SrFe 12 O 19 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 141, 562–569 (2013)
A. Das, A. Roychowdhury, S. Pati, S. Bandyopadhyay, D. Das, Structural, magnetic and hyperfine properties of single-phase SrFe12O19 nanoparticles prepared by a sol–gel route. Phys. Scr. 90, 025802 (2015)
I. Auwal, H. Güngüneş, S. Güner, S.E. Shirsath, M. Sertkol, A. Baykal, Structural, magneto-optical properties and cation distribution of SrBi x La x Y x Fe 12–3x O 19 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.33) hexaferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 80, 263–272 (2016)
R. Turton, The physics of solids (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2000)
M.N. Ashiq, M.F. Ehsan, M.J. Iqbal, M. Najam-ul-Haq, Role of Zr–Co substitution at iron site on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Sr-hexaferrites nanomaterials synthesized by the sol–gel combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 332, 93–97 (2013)
H. Luo, B. Rai, S. Mishra, V. Nguyen, J. Liu, Physical and magnetic properties of highly aluminum doped strontium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by auto-combustion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2602–2608 (2012)
A.A. Nourbakhsh, M. Noorbakhsh, M. Nourbakhsh, M. Shaygan, K.J. Mackenzie, The effect of nano sized SrFe12O19 additions on the magnetic properties of chromium-doped strontium-hexaferrite ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 22, 1297–1302 (2011)
A.V. Raut, D. Kurmude, D. Shengule, K. Jadhav, Effect of gamma irradiation on the structural and magnetic properties of Co–Zn spinel ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 63, 123–128 (2015)
P.P. Khirade, S.D. Birajdar, A.V. Humbe, K. Jadhav, Structural, electrical and dielectrical property investigations of Fe-doped BaZrO3 nanoceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 3227–3235 (2016)
P.P. Khirade, S.D. Birajdar, A. Raut, K.M. Jadhav, Effect of Fe–substitution on phase transformation, optical, electrical and dielectrical properties of BaTiO3 nanoceramics synthesized by sol-gel auto combustion method, J. Electroceram. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10832-016-0044-z
G. Sawatzky, J. Coey, A. Morrish, Mössbauer study of electron hopping in the octahedral sites of Fe3O4. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 1402–1403 (1969)
M.J. Iqbal, M.N. Ashiq, I.H. Gul, Physical, electrical and dielectric properties of Ca-substituted strontium hexaferrite (SrFe 12 O 19) nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 1720–1726 (2010)
Z. Zi, Y. Sun, X. Zhu, C. Hao, X. Luo, Z. Yang, J. Dai, W. Song, Electrical transport and magnetic properties in La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 and SrFe 12 O 19 composite system. J. Alloy. Compd. 477, 414–419 (2009)
V. Vinayak, P.P. Khirade, S.D. Birajdar, R. Alange, K. Jadhav, Electrical and dielectrical properties of low-temperature-synthesized nanocrystalline Mg2+ -substituted cobalt spinel ferrite. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 28, 3351–3356 (2015)
M. Shen, S. Ge, W. Cao, Dielectric enhancement and Maxwell-Wagner effects in polycrystalline ferroelectric multilayered thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 34, 2935 (2001)
C. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121 (1951)
B.H. Bhat, B. Want, Magnetic, dielectric and complex impedance properties of lanthanum and magnesium substituted strontium hexaferrite, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-5389-1
A. Farea, S. Kumar, K.M. Batoo, A. Yousef, C.G. Lee, Structure and electrical properties of Co 0.5 Cd x Fe 2.5 − x O 4 ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 464, 361–369 (2008)
M.J. Iqbal, S. Farooq, Extraordinary role of Ce–Ni elements on the electrical and magnetic properties of Sr–Ba M-type hexaferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 2050–2055 (2009)
N. Singh, A. Agarwal, S. Sanghi, Dielectric relaxation, conductivity behavior and magnetic properties of Mg substituted Zn–Li ferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, 783–789 (2011)
S. Sanghi, A. Agarwal, N. Ahlawat, Structure refinement and dielectric relaxation of M-type Ba, Sr, Ba-Sr, and Ba-Pb hexaferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 014110 (2012)
I. Ali, M. Islam, M. Awan, M. Ahmad, Effects of heat-treatment time on the structural, dielectric, electrical, and magnetic properties of BaM hexaferrite. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 22, 2104–2114 (2013)
A. Shaikh, S. Bellad, B. Chougule, Temperature and frequency-dependent dielectric properties of Zn substituted Li–Mg ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 195, 384–390 (1999)
K. Praveena, M. Bououdina, M.P. Reddy, S. Srinath, R. Sandhya, S. Katlakunta, Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of microwave-sintered Cr3+ -doped Sr hexaferrites. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 524–531 (2015)
Acknowledgments
The authors are very much thankful to Department of Physics, IIT Mumbai for providing X-ray diffraction (XRD), Shrikrushna College, Gunjoti (Osmanabad) for dielectrical measurement and North Maharashtra University, Jalgaon for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) characterization facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alange, R.C., Khirade, P.P., Birajdar, S.D. et al. Influence of Al–Cr co-substitution on physical properties of strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel auto combustion method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 407–417 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5537-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5537-7