Abstract
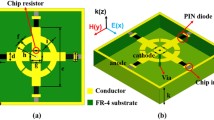
Operation frequencies of traditional metamaterial absorbers are fixed meaning that it is not possible to change that frequency after the fabrication. Therefore, more studies are focused on the design of Tunable metamaterial absorber (TMA) since it is important to expand operation frequency. If the impedance of one or more layers of an absorber can be changed according to the applied electrical optical signal, then it would be possible to realize tunable absorbing designs. However, TMA studies reported previously are mainly focused on absorbing mechanism at microwave frequencies. In this study, TMA with varactor diode is designed and analyzed for absorber and sensor configurations. TMA is constructed by using a simple rectangular-shape geometry having two splits and a varactor diode placed at the right split. Numerical and experimental results show that perfect absorption is achieved when 0–10 V reverse bias voltage is applied. Resonance frequency can be easily tuned by changing the reverse bias voltage. Frequency dependent absorption behavior of TMA is presented with respect to different incident angles for TE and TM polarizations. A sensor application, knowing the absorption resonance frequency can provide the ability to determine the temperature of materials. The novelty of the study is to determine the temperature or the other parameters such as humidity or pressure by using TMA. It is also possible to determine the material type or its density if limited resource such as frequency generator is present.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.P. Scarborough, Z.H. Jiang, D.H. Werner, C. Rivero-Baleine, C. Drake, Experimental demonstration of an isotropic metamaterial super lens with negative unity permeability at 8.5 MHz. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 014101–014104 (2012)
S. Maci, A cloaking metamaterial based on an inhomogeneous linear field transformation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58, 1136–1143 (2010)
C. Sabah, M.D. Thomson, F. Meng, S. Tzanova, H.G. Roskos, Terahertz propagation properties of free-standing woven-steel-mesh metamaterials: pass-bands and signatures of abnormal group velocities. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 064902 (2010)
C. Sabah, F. Dincer, M. Karaaslan, E. Unal, O. Akgol, E. Demirel, Perfect metamaterial absorber with polarization and incident angle independencies based on ring and cross-wire resonators for shielding and a sensor application. Opt. Commun. 322, 137–142 (2014)
F. Bilotti, L. Nucci, L. Vegni, An SRR-based microwave absorber. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 48, 2171–2175 (2006)
N.I. Landy, S. Sajuyigbe, J.J. Mock, D.R. Smith, W.J. Padilla, Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 207402 (2008)
Q. Cheng, T.J. Cui, W.X. Jiang, B.G. Cai, An omnidirectional electromagnetic absorber made of metamaterials. New J. Phys. 12, 063006–063015 (2012)
H.T. Chen, Interference theory of metamaterial perfect absorbers. Opt. Express 20, 7165–7172 (2012)
J. Lee, S. Lim, Bandwidth-enhanced and polarization-insensitive metamaterial absorber using double resonance. Electron. Lett. 47, 8–9 (2012)
J. Sun, L. Liu, G. Dong, J. Zhou, An extremely broad band metamaterial absorber based on destructive interference. Opt. Express 19, 21155–21162 (2011)
L. Li, Y. Yang, C.H. Liang, A wide-angle polarization-insensitive ultra-thin metamaterial absorber with three resonant modes. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 063702–063706 (2011)
J.W. Park, P.V. Tuong, J.Y. Rhee, K.W. Kim, W.H. Jang, E.H. Choi, L.Y. Chen, Y. Lee, Multi-band metamaterial absorber based on the arrangement of donut-type resonators. Opt. Express 21, 9691–9702 (2013)
B. Wang, T. Koschny, C.M. Soukoulis, Wide-angle and polarization-independent chiral metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. B 80, 033108 (2009)
B. Zhu, Z. Wang, C. Huang, Y. Feng, J. Zhao, T. Jiang, Polarization insensitive metamaterial absorber with wide incident angle. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 101, 231–239 (2010)
J. Lee, S. Lim, Bandwidth-enhanced and polarization- insensitive metamaterial absorber using double resonance. Electron. Lett. 47, 8–9 (2011)
O.T. Gunduz, C. Sabah, Polarization angle independent perfect multiband metamaterial absorber and energy harvesting application. J. Comp. Electronics (2015). doi:10.1007/s10825-015-0735-8
D. Schurig, J.J. Mock, B.J. Justice, S.A. Cummer, J.B. Pendry, A.F. Starr, D.R. Smith, Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies. Science 314, 977–980 (2006)
F. Dincer, O. Akgol, M. Karaaslan, E. Unal, C. Sabah, Polarization angle independent perfect metamaterial absorbers for solar cell applications in the microwave, infrared, and visible regime. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 144, 93–101 (2014)
B. Zhu, Y. Feng, J. Zhao, C. Huang, Z. Wang, T. Jiang, Polarization modulation by tunable electromagnetic metamaterial reflector/absorber. Opt. Express 18, 23196–23203 (2010)
I.B. Shadrivov, A.B. Kozyrev, D.W. Weide, Y.S. Kivshar, Tunable transmission and harmonic generation in nonlinear metamaterials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 161903 (2008)
B. Zhu, Y.J. Feng, J.M. Zhao, C. Huang, T.A. Jiang, Switchable metamaterial reflector/absorber for different polarized electromagnetic waves. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 051906 (2010)
Y.J. Yang, J.W. Yong, J.Z. Guang, J.P. Zhong, H.P. Sun, Tunable broadband metamaterial absorber consisting of ferrite slabs and a copper wire. Chin. Phys. B 21, 038501–0358506 (2011)
D. Shrekenhamer, W.C. Chen, W.J. Padilla, Liquid crystal tunable metamaterial absorber (Phys. Rev., Lett, 2013). 77403
B.X. Wang, L.L. Wang, G.Z. Wang, W.Q. Huang, X.F. Li, X. Zhai, Frequency continuous tunable terahertz metamaterial absorber. J. Lightw. Technol. 32, 1183–1189 (2014)
Q.Y. Wen, H.W. Zhang, Q.H. Yang, Z. Chen, Y. Long, Y.L. Jing, Y. Lin, P.X. Zhang, A tunable hybrid metamaterial absorber based on vanadium oxide films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 45, 235106 (2012)
J. Zhao, Q. Cheng, J. Chen, M.Q. Qi, W.X. Jiang, T.J. Cui, A tunable metamaterial absorber using varactor diodes. New J. Phys. 15, 1–11 (2013)
M.L. Yola, N. Atar, Novel voltammetric sensor based on gold nanoparticles involved in p-aminothiophenol functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes: application to the simultaneous determination of quercetin and rutin. Electrochim. Acta 119, 24–31 (2014)
M.L. Yola, T. Eren, N. Atar, A novel and sensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor based on Fe@Au nanoparticles decorated graphene oxide. Electrochim. Acta 125, 38–47 (2014)
M.L. Yola, T. Eren, N. Atar, Molecularly imprinted electrochemical biosensor based on Fe@Au nanoparticles involved in 2-aminoethanethiol functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for sensitive determination of cefexime in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 60, 277–285 (2014)
M.L. Yola, V.K. Gupta, T. Eren, A.E. Şen, N. Atar, A novel electroanalytical nanosensor based on graphene oxide/silver nanoparticles for simultaneous determination of quercetin and morin. Electrochim. Acta 120, 204–211 (2014)
M.L. Yola, N. Atar, Z. Üstündağ, A.O. Solak, A novel voltammetric sensor based on p-aminothiophenol functionalized graphene oxide/gold nanoparticles for determining quercetin in the presence of ascorbic acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 698, 9–16 (2013)
M.L. Yola, T. Eren, N. Atar, A sensitive molecular imprinted electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles decorated graphene oxide: Application to selective determination of tyrosine in milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 210, 149–157 (2015)
N. Atar, T. Eren, M.L. Yola, H.K. Maleh, B. Demirdögen, Magnetic iron oxide and iron oxide@gold nanoparticles anchored nitrogen and sulfur-functionalized reduced graphene oxide electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation. RSC Adv. 5, 26402–26409 (2015)
M.L. Yola, T. Eren, N. Atar, H. Saral, İ. Ermiş, Direct-methanol fuel cell based on functionalized graphene oxide with mono-metallic and bi-metallic nanoparticles: electrochemical performances of nanomaterials for methanol oxidation. Electroanalysis 28–3, 570–579 (2016)
E. Elçin, M.L. Yola, T. Eren, B. Girgin, N. Atar, Highly selective and sensitive voltammetric sensor based on ruthenium nanoparticle anchored calix[4]amidocrown-5 functionalized reduced graphene oxide: simultaneous determination of quercetin, morin and rutin in grape wine. Electroanalysis 28–3, 611–619 (2016)
M.L. Yola, V.K. Gupta, N. Atar, New molecular imprinted voltammetric sensor for determination of ochratoxin A. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 61, 368–375 (2015)
G. Kotan, F. Kardaş, Ö.A. Yokuş, O. Akyıldırım, H. Saral, T. Eren, M.L. Yola, N. Atar, A novel determination of curcumin via Ru@Au nanoparticle decorated nitrogen and sulfur-functionalized reduced graphene oxide nanomaterials. Anal. Methods 8, 401–408 (2016)
N. Atar, M.L. Yola, T. Eren, Sensitive determination of citrinin based on molecular imprinted electrochemical sensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 362, 315–322 (2016)
B. Ertan, T. Eren, İ. Ermiş, H. Saral, N. Atar, M.L. Yola, Sensitive analysis of simazine based on platinum nanoparticles on polyoxometalate/multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 470, 14–21 (2016)
Ö.A. Yokuş, F. Kardaş, O. Akyildirim, M.L. Yola, Sensitive voltammetric sensor based on polyoxometalate/reduced graphene oxide nanomaterial: application to the simultaneous determination of l-tyrosine and l-tryptophan. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 233, 47–54 (2016)
T. Wanghuang, W. Chen, Y. Huang, G. Wen, Analysis of metamaterial absorber in normal and oblique incidence by using interference theory. AIP Adv. 3, 102118 (2013)
B. Badaruzzaman, Application of microwave sensors to potato products (The University of Manchester, Manchester, 2010)
G. Barbillon, Plasmonic nanostructures prepared by soft UV nanoimprint lithography and their application in biological sensing. Micromachines 3, 321–327 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakır, M., Karaaslan, M., Dincer, F. et al. Tunable perfect metamaterial absorber and sensor applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 12091–12099 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5359-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5359-7