Abstract
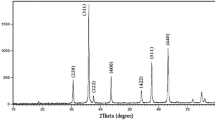
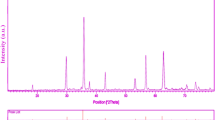
In the present study, for the first time NiFe2−xDyxO4 nanoparticles were prepared through a novel sol–gel route with the aid of nickel (II) nitrate, iron (III) nitrate, dysprosium (III) nitrate and lactose without adding external surfactant. lactose played role as caping agent and reducing agent to produce NiFe2−xDyxO4 nanoparticles. The formation of pure crystallized NiFe2−xDyxO4 nanoparticles occurred when the precursor was heat-treated at 800 °C in air for 2 h. The structural, morphological and optical properties of as-obtained products were characterized by techniques such as XRD, EDS, SEM, and UV–visible. The magnetic properties of as-prepared NiFe2−xDyxO4 nanoparticles were also investigated with vibrating sample magnetometer. To evaluate the photocatalyst properties of nanocrystalline ZnFe2−xLaxO4, the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange under ultraviolet light irradiation was carried out.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Khademolhoseini, M. Zakeri, S. Rahnamaeiyan, M. Nasiri, R. Talebi, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 7303 (2015)
A. Ghasemi, A.M. Davarpanah, M. Ghadiri, Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 207 (2012)
F.S. Ghoreishi, V. Ahmadi, M. Samadpourc, J. NanoStruct. 3, 453 (2013)
M. Panahi-Kalamuei, M. Mousavi-Kamazani, M. Salavati-Niasari, J. NanoStruct. 4, 459 (2014)
Z. Khayat Sarkar, F. Khayat Sarkar, Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 7, 197 (2011)
N. Mir, M. Salavati-Niasari, Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 1660 (2013)
Y.Z. Zheng, X. Tao, L.X. Wang, H. Xu, Q. Hou, W.L. Zhou, J.F. Chen, Chem. Mater. 22, 928 (2009)
G. Nabiyouni, D. Ghanbari, S. Karimzadeh, B. Samani Ghalehtaki, J. NanoStruct. 4, 467 (2014)
J. Safari, Z. Zarnegar, J. NanoStruct. 3, 191 (2013)
S. Hojaghani, M. Hosseyni Sadr, A. Morsali, J. NanoStruct. 3, 109 (2013)
L. Hashemi, A. Tahmasian, A. Morsali, J. Abedini, J. NanoStruct. 2, 163 (2012)
M.U. Rana, T. Abbas, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 246, 110 (2002)
A. Znidarsic, M. Limpel, M. Drofenik, IEEE Trans. Magn. 18, 1544 (1982)
U. Konig, Appl. Phys. 4, 237 (1974)
Y. Zhang, D. Wen, Mater. Sci. Eng. B172, 331 (2010)
M. Ishaque, M.U. Islam, M.A. Khan, I.Z. Rahman, A. Genson, S. Hampshire, Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter 405, 1532 (2010)
E. Melagiriyapp, H.S. Jayanna, J. Alloys Compd. 482, 147 (2009)
E. Rezlescu, L. Sachelarie, P.D. Popa, N. Rezlescu, Trans. Magn. 36, 3962 (2000)
R.I. Coble, T.K. Gupta (Eds.), Sintering and Related Phenomena (Gordon & Breach, New York, 1996), pp. 751–769
E.E. Sileo, E. Silvia, E. Jacobo, Phys. B 354, 241 (2004)
M. Rahimi-Nasarabadi, J. NanoStruct. 4, 211 (2014)
E. Khosravifard, M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Dadkhah, G. Sodeifian, J. NanoStruct. 2, 191 (2010)
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to council of University of Central Tehran for providing financial support to undertake this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goudarzi, M., Talebi, R. A low-cost and eco-friendly viable approach for green synthesis of NiFe2−xDyxO4 nanoparticles using lactose. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 4470–4474 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4319-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4319-6