Abstract
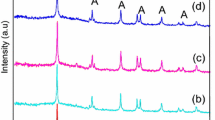
The photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) has been investigated under visible light irradiation with an incandescent light bulb using chromium doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Cr–TiO2 photocatalysts were successfully synthesized by sol–gel method at room temperature and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV–Vis DRS), Raman spectroscopy, Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The band gap energy of the nanoparticles were estimated using UV–Vis DRS technique. With increasing Cr3+ cations content into TiO2 host lattice, the optical absorption band tuned in the visible region. XRD and TEM results reveal uniform and crystalline anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. The photodegradation of MB indicated that the photocatalytic activity of pure TiO2 nanoparticles increased with increasing Cr3+ cations concentration.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.P. Macwan, P.N. Dave, S. Chaturvedi, A review on nano-TiO2 sol–gel type syntheses and its applications. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 3669–3686 (2011)
D.F. Ollis, E. Pelizzetti, N. Serpone, Photocatalyzed destruction of water contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 25, 1522–1529 (1991)
Y. Yalçın, M. Kılıç, Z. Çınar, Fe+3-doped TiO2: a combined experimental and computational approach to the evaluation of visible light activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 99, 469–477 (2010)
J. Virkutyte, R.S. Varma, Visible light activity of Ag-loaded and guanidine nitrate-doped nano-TiO2: degradation of dichlorophenol and antibacterial properties. RSC Adv. 2, 1533–1539 (2012)
S.S. Soni, G.S. Dave, M.J. Henderson, A. Gibaud, Visible light induced cell damage of Gram positive bacteria by N-doped TiO2 mesoporous thin films. Thin Solid Films 531, 559–565 (2013)
S.S. Soni, M.J. Henderson, J.F. Bardeau, A. Gibaud, Visible-light photocatalysis in titania-based mesoporous thin films. Adv. Mater. 20, 1493–1498 (2008)
J.C.S. Wu, C.H. Chen, A visible-light response vanadium-doped titania nanocatalyst by sol–gel method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 163, 509–515 (2004)
J. Choi, H. Park, M.R. Hoffmann, Effects of single metal-ion doping on the visible-light photoreactivity of TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 783–792 (2010)
J. Zhu, Z. Deng, F. Chen, J. Zhang, H. Chen, M. Anpo et al., Hydrothermal doping method for preparation of Cr3+–TiO2 photocatalysts with concentration gradient distribution of Cr3+. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 62, 329–335 (2006)
P. Bouras, E. Stathatos, P. Lianos, Pure versus metal-ion-doped nanocrystalline titania for photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 73, 51–59 (2007)
C.C. Tsai, H. Teng, Chromium-doped titanium dioxide thin-film photoanodes in visible-light-induced water cleavage. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 4912–4918 (2008)
A.T. Vu, Q.T. Nguyen, T.H.L. Bui, M.C. Tran, T.P. Dang, T.K.H. Tran, Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 photocatalyst doped by transition metal ions (Fe3+, Cr3+ and V5+). Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 1, 015009 (2010)
X. Li, Z. Guo, T. He, The doping mechanism of Cr into TiO2 and its influence on the photocatalytic performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 20037–20045 (2013)
S. Zhang, Y. Chen, Y. Yu, H. Wu, S. Wang, B. Zhu et al., Synthesis, characterization of Cr-doped TiO2 nanotubes with high photocatalytic activity. J. Nanoparticle Res. 10, 871–875 (2007)
S. Buddee, S. Wongnawa, U. Sirimahachai, W. Puetpaibool, Recyclable UV and visible light photocatalytically active amorphous TiO2 doped with M(III) ions (M = Cr and Fe). Mater. Chem. Phys. 126, 167–177 (2011)
B. Choudhury, A. Choudhury, Structural, optical and ferromagnetic properties of Cr doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 178, 794–800 (2013)
S. Ould-Chikh, O. Proux, P. Afanasiev, L. Khrouz, M.N. Hedhili, D.H. Anjum et al., Photocatalysis with chromium-doped TiO2: bulk and surface doping. ChemSusChem 7, 1361–1371 (2014)
R. Bechstein, M. Kitta, J. Schütte, H. Onishi, A. Kühnle, The effects of antimony doping on the surface structure of rutile TiO2(110). Nanotechnology 20, 264003 (2009)
Z. Zhang, C. Wang, R. Zakaria, J.Y. Ying, Role of particle size in nanocrystalline TiO2-based photocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. 102, 10871–10878 (1998)
S.D. Delekar, H.M. Yadav, S.N. Achary, S.S. Meena, S.H. Pawar, Structural refinement and photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 263, 536–545 (2012)
H.M. Yadav, S.V. Otari, R.A. Bohara, S.S. Mali, S.H. Pawar, S.D. Delekar, Synthesis and visible light photocatalytic antibacterial activity of nickel-doped TiO2 nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 294, 130–136 (2014)
J.S. Chen, Y.L. Tan, C.M. Li, Y.L. Cheah, D. Luan, S. Madhavi et al., Constructing hierarchical spheres from large ultrathin anatase TiO2 nanosheets with nearly 100 % exposed (001) facets for fast reversible lithium storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 6124–6130 (2010)
K. Bhattacharyya, S. Varma, A.K. Tripathi, S.R. Bharadwaj, A.K. Tyagi, Effect of vanadia doping and its oxidation state on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 for gas-phase oxidation of ethene. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 19102–19112 (2008)
Y. Yu, X. Yin, A. Kvit, X. Wang, Evolution of hollow TiO2 nanostructures via the Kirkendall effect driven by cation exchange with enhanced photoelectrochemical performance. Nano Lett. 14, 2528–2535 (2014)
C.D. Wagner, W.M. Riggs, L.E. Davis, J.F. Moulder, G.E. Muilenberg, Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Perkin-Elmer Corp., Physical Electronics Division, USA, 1979)
J. Zhu, F. Chen, J. Zhang, H. Chen, M. Anpo, Fe3+-TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by combining sol–gel method with hydrothermal treatment and their characterization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 180, 196–204 (2006)
L. Li, C. Liu, Y. Liu, Study on activities of vanadium (IV/V) doped TiO2(R) nanorods induced by UV and visible light. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 551–557 (2009)
J.P. Tardivo, A. Del Giglio, C.S. de Oliveira, D.S. Gabrielli, H.C. Junqueira, D.B. Tada et al., Methylene blue in photodynamic therapy: from basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2, 175–191 (2005)
B.H. Hameed, A.A. Ahmad, Batch adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by garlic peel, an agricultural waste biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 870–875 (2009)
Y. Bulut, H. Aydın, A kinetics and thermodynamics study of methylene blue adsorption on wheat shells. Desalination 194, 259–267 (2006)
T. Zhang, T. Oyama, A. Aoshima, H. Hidaka, J. Zhao, N. Serpone, Photooxidative N-demethylation of methylene blue in aqueous TiO2 dispersions under UV irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 140, 163–172 (2001)
F. Wang, S. Min, Y. Han, L. Feng, Visible-light-induced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue with polyaniline-sensitized composite photocatalysts. Superlattices Microstruct. 48, 170–180 (2010)
T. Mohammad, H. Morrison, Simultaneous photoconjugation of methylene blue and cis-Rh(phen)2Cl2 + to DNA via a synergistic effect†. Photochem. Photobiol. 71, 369–381 (2007)
P. Sangpour, F. Hashemi, A.Z. Moshfegh, Photoenhanced degradation of methylene blue on cosputtered M:TiO2 (M = Au, Ag, Cu) nanocomposite systems: a comparative study. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 13955–13961 (2010)
M.R. Hoffmann, S.T. Martin, W. Choi, D.W. Bahnemannt, Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 95, 69–96 (1995)
M.B. Fisher, D.A. Keane, P. Fernández-Ibáñez, J. Colreavy, S.J. Hinder, K.G. McGuigan et al., Nitrogen and copper doped solar light active TiO2 photocatalysts for water decontamination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 130–131, 8–13 (2013)
M. Pelaez, N.T. Nolan, S.C. Pillai, M.K. Seery, P. Falaras, A.G. Kontos et al., A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 125, 331–349 (2012)
A. Houas, H. Lachheb, M. Ksibi, E. Elaloui, C. Guillard, J.M. Herrmann, Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 31, 145–157 (2001)
B. Ohtani, Y. Ogawa, S. Nishimoto, Photocatalytic activity of amorphous-anatase mixture of titanium(IV) oxide particles suspended in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B. 5647, 3746–3752 (1997)
U.G. Akpan, B.H. Hameed, Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysts: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 170, 520–529 (2009)
S. Liu, J.-H. Yang, J.-H. Choy, Microporous SiO2–TiO2 nanosols pillared montmorillonite for photocatalytic decomposition of methyl orange. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 179, 75–80 (2006)
M.A. Rauf, S.B. Bukallah, A. Hamadi, A. Sulaiman, F. Hammadi, The effect of operational parameters on the photoinduced decoloration of dyes using a hybrid catalyst V2O5/TiO2. Chem. Eng. J. 129, 167–172 (2007)
J.M. Herrmann, Heterogeneous photocatalysis: fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catal. Today 53, 115–129 (1999)
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by a grant (14CTAP-C077607-01) from Infrastructure and transportation technology promotion research program funded by Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korean government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, H.M., Kolekar, T.V., Barge, A.S. et al. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of Cr3+-doped anatase TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 526–534 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3785-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3785-6