Abstract
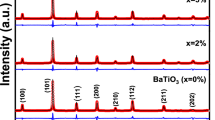
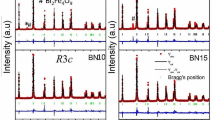
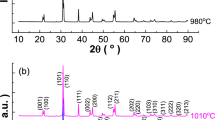
Solid solution 0.75BiFeO3–0.25BaTiO3 (BFO–25 % BT) was prepared by solid state reaction method. Powder X-ray diffraction showed the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) with the coexistence of both rhombohedral and cubic phases due to splitting in the line at 2θ = 39.7°. Scanning electron micrographs indicated that the ceramic has compact and uniform microstructure with average grain size <3 μm. The polarization vs applied electric field analysis showed an unsaturated hysteresis loop with the remnant polarization 12.95 μC/cm2 at 22 kV/cm for 0.75BiFeO3–0.25BaTiO3 ceramic. The calculations of diffuse parameter i.e. slope γ = 1.63 suggested a high degree of diffusion in BFO–BT lattice. The room temperature magnetic measurements confirmed the weak ferromagnetism of magnetization ~0.1 emu/gm at an applied magnetic field of H = 5 kOe for 0.75BiFeO3–0.25BaTiO3 ceramic. The high temperature magnetic and dielectric analysis suggested a coupling between ferroelectric and magnetic parameters near the antiferromagnetic–paramagnetic transition Tc ~ 310 °C, which was responsible for the broad frequency dependent dielectric maxima. The impedance spectroscopy and complex modulus analysis confirmed the conventional relaxor, NTCR (negative temperature coefficient of resistance), giant ferroelectricity and polydispersive non-Debye type dielectric relaxation behaviour for 0.75BiFeO3–0.25BaTiO3 ceramic at 170 °C on 1 kHz with activation energy 2.33 eV. The modulus analysis also confirmed the possibility of hopping mechanism for electrical transport process in material.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Chang, H.M. Jang, S.K. Kim, J Magn 11, 108 (2006)
S.V. Kiselev, R.P. Ozarov, G.S. Zhdanov, Sov Phys Dokl 7, 742 (1962)
P. Fishetr, M. Polomska, S. Sosnowska, M. Szymanski, J Phys C 13, 1931 (1980)
F. Kubel, H. Schmid, Acta Crystallog Sect B 46, 698 (1990)
Y. Yang, V.G.M. Annamdas, C. Wang, Y. Zhou, Sensors 8, 271 (2008)
M. Kumar, S. Shankar, O.M. Parkash, J Alloys Compd 577, 222 (2013)
V.R. Palkar, J. John, Appl Phys Lett 80, 1628 (2002)
J.R. Cheng, N. Li, L.E. Cross, J Appl Phys 94, 5153 (2003)
S.T. Zhang, M.H. Lu, D. Wu, Y.F. Chen, N.B. Ming, Appl Phys Lett 87, 1 (2005)
W. Eerenstein, F.D. Morrrison, J. Dho, M.G. Blamire, J.F. Scott, N.D. Mathur, Science 307, 1203a (2005)
Hunpratub S, Thongbai P (2006) Appl Phys Lett 94: 062904-1-3
Lin YH, Li M, Nan CW, Li J, Wu J, He J (2006) Appl Phys Lett 89: 032907-1-3
S. Chandarak, A. Ngamjarurojana, Ferroelectrics 410, 75 (2011)
M.M. Kumar, A. Srinivas, S.V. Suryanarayana, J Appl Phys 87, 855 (2000)
S. Chandarak, M. Unruan, J Magn 14(3), 120 (2009)
M. Mahesh Kumar, A. Srinivas, S.V. Suryanarayana, J Appl Phys 87, 855 (2000)
Wang TH, Ding Y, Tu CS, Yao, Wu KT, Lin TC, Yu HH, Ku CS, Lee HY (2011) J Appl Phys 109:07D907
G. Catalan, F. Scott, Adv Mater 21, 2463 (2009)
A. Bokov, Z. Ye, J Mat Sci 41, 31 (2006)
T.H. Wang et al., J Appl Phys 109, 044101 (2011)
B. Behera, P. Nayak, R.N.P. Choudhary, J Alloys Compd 436, 226 (2007)
B. Behera, P. Nayak, R.N.P. Choudhary, Mat Res Bull 43, 401 (2008)
A.K. Jonscher, Nature 267, 673 (1977)
C.K. Suman, K. Prasad, R.N.P. Choudhary, J Mater Sci 41, 369 (2007)
S. Sen, R.N.P. Choudhary, P. Pramanik, Phys B 387, 56 (2007)
R.C. Buchanan, Principles of electronic ceramics (Marcel Dekkar, New York, 1991), p. 250
V. Shrivastava, A.K. Jha, R.G. Mendiratta, Phys B 371, 337 (2006)
B. Behera, P. Nayak, R.N.P. Choudhary, J Alloys Compd 436, 226 (2007)
R. Waser, R. Hagenbeck, Acta Mater 48, 797 (2000)
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (M. K.) acknowledges and support from MHRD, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Shankar, S., Parkash, O. et al. Dielectric and multiferroic properties of 0.75BiFeO3–0.25BaTiO3 solid solution. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 888–896 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1661-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1661-9