Abstract
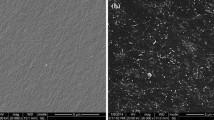
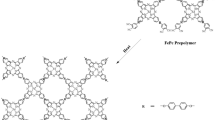
An aromatic, diether-linked phthalocyanine resin (Pc) was prepared from 4,4′-bis (3,4-dicyanophenoxy) biphenyl (BPh) and investigated for morphology, microstructure, dielectric, conductivity and microwave absorption properties at different annealing temperatures from 300 to 800 °C. The results showed that the annealing temperature could significantly change the morphology and microstructure of the Pc polymer, leading to the generation of carbon-Pc polymer composites, and enhance the microwave absorbing and electrical properties of the Pc polymer. The dramatic electrical and dielectric transition happened when the annealing condition was 550 °C 24 h. The conductivity of the samples exhibited a transition of electrical behavior from an insulator to semiconductor of approximately 10+2 S/cm. Pc polymer exhibited excellent microwave absorption properties in the frequency range of 0.5–18.0 GHz after sintering process. The microwave absorption of the annealing Pc polymer can be mainly attributed to the dielectric loss rather than magnetic loss. The sample annealed at 500 °C 24 h had two strong microwave absorbing peaks and achieved a maximum absorbing value of −44 dB around 10.7 and 17.5 GHz when the thickness was 3.0 mm. The novel carbon-Pc polymer composites were believed to have potential applications in the microwave absorbing area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.B. Sastri, T.M. Keller, J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 36, 1885 (1998)
T.M. Keller, D.D. Dominguez, Polymer 46, 4614 (2005)
X.L. Yang, X.B. Liu, Chin. Chem. Lett. 21, 743 (2010)
T.M. Keller, Polymer 34, 952 (1993)
S.B. Sastri, J.P. Armistead, T.M. Keller, Polym. Compos. 17, 816 (1996)
S.B. Sastri, J.P. Armistead, T.M. Keller, U. Sorathia, Polym. Compos. 18, 48 (1997)
S.B. Sastri, T.M. Keller, J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 37, 2105 (1999)
G.P. Cao, W.J. Chen, X.B. Liu, Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 93, 739 (2008)
W.T. Li, F. Zuo, K. Jia, X.B. Liu, Chin. Chem. Lett. 20, 348 (2009)
F.B. Meng, R. Zhao, Y.Q. Zhan, Y.J. Lei, J.C. Zhong, X.B. Liu, Mater. Lett. 65, 264 (2011)
K. Jia, R. Zhao, J.C. Zhong, X.B. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. 21, 708 (2010)
Y.J. Lei, G.H. Hu, R. Zhao, H. Guo, X. Zhao, X.B. Liu, J. Phys. Chem. Soli. 73, 1335 (2012)
Z.C. Wang, X.L. Yang, J.J. Wei, M.Z. Xu, L.F. Tong, R. Zhao, X.B. Liu, J. Polym. Res. 19, 9969 (2012)
T.M. Keller, Polym. Commun. 31, 229 (1990)
S.D. Bruck, Polymer 6, 319 (1965)
T.M. Keller, J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 26, 3199 (1988)
M. Laskoski, T.M. Keller, S.B. Qadri, Polymer 48, 7484 (2007)
Y.J. Lei, R. Zhao, Y.Q. Zhan, F.B. Meng, J.C. Zhong, X.L. Yang, X.B. Liu, Chem. Phys. Lett. 496, 139 (2010)
T.M. Keller, Poly. Chem. 25, 2569 (1987)
K.H. Wu, T.H. Ting, G.P. Wang, W.D. Ho, C.C. Shih, Polym. Degra. Stabl. 93, 483 (2008)
X.L. Yang, Y.J. Lei, J.C. Zhong, R. Zhao, X.B. Liu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 119, 882 (2011)
M.L. Rodríguez-Méndez, J. Souto, J.A. De Saja, J. Raman Spect. 26, 693 (1995)
S.D. Bruck, Polymer 6, 319 (1965)
C.J. Norrell, H.A. Pohl, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Eidt. 12, 913 (1974)
X.L. Dong, X.F. Zhang, H. Huang, F. Zuo, Appl. Phy. Lett. 92, 013127 (2008)
M. Han, L. Deng, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 011108 (2007)
L. Deng, M. Han, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 023119 (2007)
Y.J. Lei, R. Zhao, G.H. Hu, X.L. Yang, X.B. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. 47, 4473 (2012)
X.L. Shi, M.S. Cao, J. Yuan, Q.L. Zhao, Y.Q. Kang, X.Y. Fang, Y.J. Chen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 183118 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank for financial support of this work from the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 51173021) and “863” National Major Program of High Technology (2012AA03A212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yang, X., Xu, M. et al. Effect of elevated annealing temperature on the morphology, microstructure, conductivity and microwave absorption properties of phthalocyanine polymer. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24, 2610–2618 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1140-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1140-3