Abstract
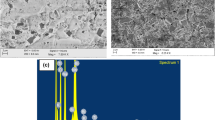
This paper highlights the dielectric and pyroelectric properties of two new complex tungsten bonze ceramics (K2Pb2Eu2W2Ti4Nb4O30 and K2Pb2Nd2W2Ti4Nb4O30) which were prepared by a high temperature mixed oxide method. Room temperature X-ray structural analysis confirms the formation of single phase compounds. The SEM micrographs show uniform distribution of densely packed rod like grains. Variation of dielectric parameters with temperature (27–500 °C) and frequency (1–5 MHz) shows the phase transition at 315 and 299 °C for the above mentioned respective samples. The temperature dependence of hysteresis loops confirms the existence of ferroelectricity in the materials below transition temperature. The current variation with voltage at different temperatures shows the semiconducting behaviour of the materials. The nature of temperature dependent dc conductivity follows the Arrhenius equation, and reveals the negative temperature coefficient of resistance behaviour of the materials. The current (for a fixed voltage) variation with temperature shows that the materials have high pyroelectric co-efficient and figure of merit, thus making them useful for pyroelectric sensors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.K. Singh, R.N.P. Choudhary, Ferroelectrics 325, 7–14 (2005)
M.S. Kim, J.H. Lee, J.J. Kim, H.Y. Lee, S.H. Cho, J. Solid State Elecchem. 10(1), 18–23 (2006)
L. Fang, H. Zhang, T.H. Huang, R.Z. Yuan, H.X. Liu, J. Mat. Sci. 40(2), 533–535 (2005)
B. Behera, P. Nayak, R.N.P. Choudhury, Mat. Lett. 59(27), 3489–3493 (2005)
V. Hornebecq, C. Elissalde, J.M. Reau, J. Ravez, Ferroelectrics 238(1), 57–63 (2000)
L.-X. Pang, H. Wang, D. Zhou, W.H. Liu, Mat. Chem. Phys. 123(2–3), 727–730 (2010)
C.K. Suman, K. Prasad, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Mat. Sci. 41, 5369–5375 (2006)
P.R. Das, R.N.P. Choudhary, B.K. Samantray, Mat. Chem. Phys. 101(1), 228–233 (2007)
P.R. Das, R.N.P. Choudhary, B.K. Samantray, J. Alloys Comp. 448, 32–37 (2008)
P.R. Das, L. Biswal, B. Behera, R.N.P. Choudhary, Mat. Res. Bull. 44, 1214–1218 (2009)
D.K. Pradhan, B. Behera, P.R. Das, J. Mat. Sci. Mater. Electron 23(3), 779–785 (2012)
P. Ganguly, A.K. Jha, Int. Ferroelectr. 115, 149–156 (2010)
P. Ganguly, S. Devi, A.K. Jha, Ferroelectrics 381, 152–159 (2009)
P. Ganguly, A.K. Jha, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94(6), 1725–1730 (2011)
M. Bouziane, M. Taibi, A. Boukhari, Mat. Chem. Phys. 129, 673–677 (2011)
R. Padhee, P.R. Das, B.N. Parida, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Mat. Sci. Mater. Electron. doi:10.1007/s10854-012-0647-3
B.N. Parida, P.R. Das, R. Padhee, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Phy, Chem. Solids 73, 713–719 (2012)
K. Chandramouli, R. Koduri, J. Mater. Sci. 44, 1793–1799 (2009)
H.P. Klug, L.E. Alexander, X-Ray diffraction (Wiley Chester, England), 1974), pp. 966–969
Powd E.W., An interactive powder diffraction data interpretation and indexing program, ver 2.1, School of Physical Science, Finders University of South Australia, Bedford Park
F. Liang, Z. Hui, W. Bolin, R.Y. Zhang, Progs. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 40(1–4), 161–165 (2000)
S.M. Pilgrim, A.E. Sutherland, S.R. Winzer, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 3122 (1990)
L.E. Cross, Ferroelectrics 76, 241–267 (1987)
G.G. Roberts, B. Holcroft, Thin Solid Films 180, 211–216 (1989)
R. Colbrook, G.G. Roberts, Ferroelectrics 118, 199–207 (1991)
R. Çapan, BAÜ FBE Dergisi Cilt:12, Sayı:1, Temmuz, 75–90 (2010)
P. Ganguly, S. Devi, A.K. Jha, Ferroelectrics 381, 111–119 (2009)
M. Petty, J. Tsibouklis, F. Davis, P. Hodge, M.C. Petty, W.J. Feast, J. Phy. D Appl. Phy. 25(6), 1032 (1992). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/25/6/023
J.R. Macdonald, Solid State Ionics 13(2), 147–149 (1984)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padhee, R., Das, P.R., Parida, B.N. et al. Dielectric and pyroelectric properties of niobium based complex tungsten bronze ferroelectrics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24, 799–806 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0812-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0812-8