Abstract
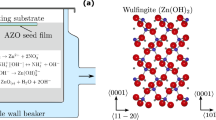
Hexagonal ZnO nanowires were synthesized on pre-seeded silicon (100) substrates by a simple hydrothermal method at a relatively low temperature of 95 °C without any catalyst or template. The pre-seeded layer was produced using the sol–gel spin coating technique with 1 M zinc acetate in ethanol and ethanolamine. The structural properties of the nanowires were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The XRD pattern indicated that the as-grown ZnO nanowires had the single-phase wurtzite structure, formed along the c-axis. SEM revealed that the nanostructure thin film had wire textures and the synthesis processes importantly influence the final size and shape of the ZnO nanowires. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) provided further insight into the structure of ZnO nanostructures. The obtained HRTEM image was of the tip of an individual nanowire. The ZnO nanowires highly preferentially grew in the (002) crystal plane. The lattice spacing between adjacent (002) lattice planes was calculated to be 0.52 nm. The optical characteristics of the nanowires were determined from cathodoluminescence (CL) spectra. The CL revealed a fairly high surface state density of ZnO nanowires that grew at reaction concentrations of 0.01–0.25 M.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.H. Huang, S. Mao, H. Feick, H.Q. Yan, Y.Y. Wu, H. Kind, E. Weber, R. Russo, P.D. Yang, Science 292, 1897–1899 (2001)
X.D. Wang, C.J. Summers, Z.L. Wang, Nano. Lett. 4, 423–426 (2004)
J.B. Baxter, A.M. Walker, K.V. Ommering, E.S. Aydil, Nanotechnology 17, S304–S312 (2006)
D.I. Suh, S.Y. Lee, T.H. Kim, J.M. Chun, E.K. Suh, O.B. Yang, S.K. Lee, Chem. Phys. Lett. 442, 348–353 (2007)
C.J. Lee, T.J. Lee, S.C. Lyu, Y. Zhang, H. Ruh, H.J. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 3648–3650 (2002)
J. Zhang, J. Liu, J.L. Huang, P. Kim, C.M. Lieber, Science 274, 757–760 (1996)
P.D. Yang, H.Q. Yan, S. Mao, R. Russo, J. Johnson, R. Saykally, N. Morris, J. Pham, R.R. He, H.J. Choi, Adv. Funct. Mater. 12, 323–331 (2002)
C.X. Xu, X.W. Sun, B.J. Chen, P. Shum, S. Li, X. Hu, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 661–666 (2004)
B.D. Yao, Y.F. Chan, N. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 757–759 (2002)
D. Banerjee, J.Y. Lao, D.Z. Wang, J.Y. Huang, Z.F. Ren, D. Steeves, B. Kimball, M. Sennett, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2061–2063 (2003)
S. Kar, B.N. Pal, S. Chaudhuri, D. Chakravorty, J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 4605–4611 (2006)
Y. Sun, N.G.N. Angwafor, D.J. Riley, M.N.R. Ashfold, Chem. Phys. Lett. 431, 352–357 (2006)
Y. Sun, G.M. Fuge, M.N.R. Ashfold, Chem. Phys. Lett. 396, 21–26 (2004)
J. W. P. Hsu, D. R. Tallant, R. L. Simpson, N. A. Missert, R. G. Copeland, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 252103-1–252103-3 (2006)
F. Xu, Z.Y. Yuan, G.H. Du, T.Z. Ren, C. Bouvy, M. Halasa, B.L. Su, Nanotechnology 17, 588–594 (2006)
S.N. Bai, H.H. Tsai, T.Y. Tseng, Thin Solid Films 516, 155–158 (2007)
S.N. Bai, Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun 4, 654–656 (2010)
C.J. Pan, B.J. Pong, B.W. Chou, G.C. Chi, C.W. Tu, Phys. Stat. Sol (c) 3, 611–613 (2006)
M.S. Mo, J.C. Yu, L.Z. Zhang, S.K. Li, Adv. Mater. 17, 756–760 (2005)
Z. Fang, K.B. Tang, G.Z. Shen, D. Chen, R. Kong, S.J. Lei, Mater. Lett. 60, 2530–2533 (2006)
S.N. Bai, T.Y. Tseng, J Mater Sci. Mater Electron 20, 604–608 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the National Nano Device Laboratories for equipment that was used in this research, under Contract No. NDL98-C05SP-051. Mr. K. L. Juan is appreciated for his assistance with the experiments. Ted Knoy is appreciated for his editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, SN. Growth and properties of ZnO nanowires synthesized by a simple hydrothermal method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23, 398–402 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0440-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0440-8