Abstract
The temperature resistance of a magnetic powder core is determined by the organic resin in it, while the conventionally used phenolic resin and epoxy resin are sensitive to temperature. Herein, iron-based amorphous powder cores with heat-resisting polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) insulating layers were fabricated by processes of ball-milling mixing, cold pressing, simultaneously sintering, and annealing, and the effect of different PTFE contents on magnetic properties was analyzed. The PTFE played the roles of lubricant, insulating layer, and binder in the fabrication of magnetic powder cores. The high lubricity and deformability of PTFE well protected the amorphous powder from ball-milling or cold-pressing damage, making it feasible for mixing amorphous powder with PTFE. In the sintering process, melting PTFE could fill the air gaps among powders and endow the powder cores with available strength. The analysis of microstructure showed that the amorphous powders could be well coated by PTFE, and the tests of magnetic properties showed that the PTFE content had a fluctuating influence on the total core losses of the powder cores. Owing to the better microstructure homogeneity and more proper compositions, the powder cores with 2.4% and 3.6% mass fractions of PTFE show relatively high effective permeabilities above 25 under 100 kHz, and relatively low total core losses of 1448 and 1402 kW/m3 respectively under 100 kHz, 100 mT. Moreover, all the prepared magnetic powder cores exhibit superior DC-bias properties, the percentages of incremental permeability are as high as 83–90% under a direct magnetic field of 100 Oe.
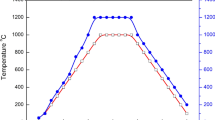
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan T-Y, Lin S-T (1999) Injection molding of Fe–Ni–P composite powders prepared by electroless nickel plating and the magnetic properties of the sintered alloys. J Mater Process Tech 89:165–170
Hamler A, Goričan V, Šuštaršič B, Sirc A (2006) The use of soft magnetic composite materials in synchronous electric motor. J Magn Magn Mater 304:e816–e819
Liu Y, He S (2010) Development of high DC-bias Mn–Zn ferrite working at frequency higher than 3 MHz. J Alloy Compd 489:523–529
Zhou B, Dong Y, Liu L et al (2019) The core-shell structured Fe-based amorphous magnetic powder cores with excellent magnetic properties. Adv Powder Tech 30:1504–1512
Neamţu BV, Opriş A, Pszola P et al (2020) Preparation and characterisation of soft magnetic composites based on Fe fibres. J Mater Sci 55:1414–1424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04088-1
Raybould D, Tan K (1985) Factors affecting the magnetic properties of consolidated amorphous powder cores. J Mater Sci 20:2776–2786. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00553039
Li Z, Dong Y, Pauly S et al (2017) Enhanced soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous powder cores by longitude magnetic field annealing. J Alloy Compd 706:1–6
Saito T, Tsuruta H, Watanabe A, Ishimine T, Ueno T (2018) Pure-iron/iron-based-alloy hybrid soft magnetic powder cores compacted at ultra-high pressure. AIP Adv 8:047708
Liu M, Huang K, Liu L et al (2018) Fabrication and magnetic properties of novel Fe-based amorphous powder and corresponding powder cores. J Mater Sci-Mater El 29:6092–6097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8584-4
Ma R, Yu P (2021) The influences of matrix materials on the magnetic and mechanical properties of Fe78Si9B13 soft magnetic composites fabricated by injection molding. Mater Res Bull 139:111256
Schoppa A, Delarbre P (2014) Soft magnetic powder composites and potential applications in modern electric machines and devices. IEEE T Magn 50:1–4
Luan J, Sharma P, Yodoshi N, Zhang Y, Makino A (2016) Mechanically strong nanocrystalline Fe–Si–BP–Cu soft magnetic powder cores utilizing magnetic metallic glass as a binder. AIP Adv 6:055934
Jiang C, Li X, Ghosh SS, Zhao H, Shen Y, Long T (2020) Nanocrystalline powder cores for high-power high-frequency power electronics applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 35:10821–10830
Shen B, Akiba M, Inoue A (2006) Excellent soft-ferromagnetic bulk glassy alloys with high saturation magnetization. Appl Phys Lett 88:131907
McHenry ME, Willard MA, Laughlin DE (1999) Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials for applications as soft magnets. Prog Mater Sci 44:291–433
Shi L, Qin X, Yao K (2020) Tailoring soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous alloys through C addition. Prog Nat Sci 30:208–212
Nakahara S, Périgo E, Pittini-Yamada Y, De Hazan Y, Graule T (2010) Electric insulation of a FeSiBC soft magnetic amorphous powder by a wet chemical method: identification of the oxide layer and its thickness control. Acta Mater 58:5695–5703
Wang X, Lu C, Guo F, Lu Z, Li D, Zhou S (2012) New Fe-based amorphous compound powder cores with superior DC-bias properties and low loss characteristics. J Magn Magn Mater 324:2727–2730
Guo J, Dong Y, Man Q et al (2016) Fabrication of FeSiBPNb amorphous powder cores with high DC-bias and excellent soft magnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater 401:432–435
Zhou B, Dong Y, Liu L, Chang L, Bi F, Wang X (2019) Enhanced soft magnetic properties of the Fe-based amorphous powder cores with novel TiO2 insulation coating layer. J Magn Magn Mater 474:1–8
Zhang Y, Dong Y, Zhou B et al (2020) Poly-para-xylylene enhanced Fe-based amorphous powder cores with improved soft magnetic properties via chemical vapor deposition. Mater Des 191:108650
Li B, Zheng Z, Yu H, Zeng D (2017) Improved permeability of Fe based amorphous magnetic powder cores by adding Permalloy. J Magn Magn Mater 438:138–143
Chang C, Dong Y, Liu M, Guo H, Xiao Q, Zhang Y (2018) Low core loss combined with high permeability for Fe-based amorphous powder cores produced by gas atomization powders. J Alloy Compd 766:959–963
Sun H, Wang C, Wang J, Yu M, Guo Z (2020) Fe-based amorphous powder cores with low core loss and high permeability fabricated using the core-shell structured magnetic flaky powders. J Magn Magn Mater 502:166548
Asim M, Saba N, Jawaid M, Nasir M, Pervaiz M, Alothman OY (2018) A review on phenolic resin and its composites. Curr Anal Chem 14(3):185–197
Matykiewicz D, Barczewski M, Michałowski S (2019) Basalt powder as an eco-friendly filler for epoxy composites: thermal and thermo-mechanical properties assessment. Compos Part B-Eng 164:272–279
Pan C, Kou K, Wu G, Zhang Y, Wang Y (2016) Fabrication and characterization of AlN/PTFE composites with low dielectric constant and high thermal stability for electronic packaging. J Mater Sci-Mater El 27(1):286–292
Rajesh S, Murali K, Priyadarsini V, Potty S, Ratheesh R (2009) Rutile filled PTFE composites for flexible microwave substrate applications. Mater Sci Eng: B 163(1):1–7
Makowiec ME, Blanchet TA (2017) Improved wear resistance of nanotube-and other carbon-filled PTFE composites. Wear 374:77–85
Shao W, Liu D, Cao T, Cheng H, Kuang J, Deng Y, Xie W (2021) Study on favorable comprehensive properties of superhydrophobic coating fabricated by polytetrafluoroethylene doped with graphene. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4(3):521–533
Sperati CA, Starkweather HW (1961) Fluorine-containing polymers. II. Polytetrafluoroethylene. Fortschritte Der Hochpolymeren-Forschung. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 465–495
Dhanumalayan E, Joshi GM (2018) Performance properties and applications of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)—a review. Adv Compos and Hybrid Ma 1:247–268
Puts GJ, Crouse P, Ameduri BM (2019) Polytetrafluoroethylene: synthesis and characterization of the original extreme polymer. Chem Rev 119:1763–1805
Zhao T, Chen C, Wu X, Zhang C, Volinsky AA, Hao J (2021) FeSiBCrC amorphous magnetic powder fabricated by gas-water combined atomization. J Alloy Compd 857:157991
Gamboni OC, Riul C, Billardon R, Bose Filho WW, Schmitt N, Canto RB (2016) On the formation of defects induced by air trapping during cold pressing of PTFE powder. Polymer 82:75–86
Chang C, Shen B, Inoue A (2006) FeNi-based bulk glassy alloys with superhigh mechanical strength and excellent soft-magnetic properties. Appl Phys Lett 89:051912
Xu K, Ling H, Li Q, Li J, Yao K, Guo S (2014) Effects of Co substitution for Fe on the glass forming ability and properties of Fe80P13C7 bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 51:53–58
Si J, Wu Y, Wang T, Liu Y, Hui X (2018) Composition-controlled active-passive transition and corrosion behavior of Fe–Cr(Mo)–Zr–B bulk amorphous steels. Appl Surf Sci 445:496–504
Si J, Du C, Wang T, Wu Y, Wang R, Hui X (2018) Glass formation and soft magnetic properties of novel Fe-rich Fe–B–Ti–Zr bulk metallic glasses. J Alloy Compd 741:542–548
Wang A, Zhao C, Men H et al (2015) Fe-based amorphous alloys for wide ribbon production with high Bs and outstanding amorphous forming ability. J Alloy Compd 630:209–213
Luborsky F, Walter J (1978) Stress relaxation in amorphous alloys. Mater Sci Eng 35:255–261
Neǐman M, Kovarskaya B, Golubenkova L, Strizhkova A, Levantovskaya I, Akutin M (1962) The thermal degradation of some epoxy resins. J Polym Sci 56(164):383–389
Snelling EC (1969) Soft ferrites: properties and applications. Butterworths
McLyman CWT (2004) Transformer and inductor design handbook. CRC Press
Zaspalis V, Tsakaloudi V, Kolenbrander M (2007) The effect of dopants on the incremental permeability of MnZn-ferrites. J Magn Magn Mater 313:29–36
Chang C, Guo J, Li Q, Zhou S, Liu M, Dong Y (2019) Improvement of soft magnetic properties of FeSiBPNb amorphous powder cores by addition of FeSi powder. J Alloy Compd 788:1177–1181
Wang C, Guo Z, Wang J, Sun H, Chen D, Chen W, Liu X (2020) Industry-oriented Fe-based amorphous soft magnetic composites with SiO2-coated layer by one-pot high-efficient synthesis method. J Magn Magn Mater 509:166924
Guo J, Dong Y, Man Q, Li Q, Chang C, Wang XM, Li RW (2016) Fabrication of FeSiBPNb amorphous powder cores with high DC-bias and excellent soft magnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater 401:432–435
Huang K, Dong Y, Liu M, Ren J, Lu S, Zhao Z, Chang C, Wang X (2018) Controllable SiO2 coating layer of FeSiBPNb amorphous powder cores with excellent soft magnetic properties. J Iron Steel Res Int 25(6):624–629
Wang J, Guo Z, Zeng Q, Hang G, Xue Z, Chen D, Liang Z, Sun H (2020) Magnetic properties regulation and loss contribution analysis for Fe-based amorphous powder cores doped with micron-sized FeSi powders. J Magn Magn Mater 510:166931
Li Z, Dong Y, Pauly S, Chang C, Wei R, Li F, Wang XM (2017) Enhanced soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous powder cores by longitude magnetic field annealing. J Alloy Compd 706:1–6
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the financial supports from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51801111 and 51871129) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (22CX06022A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Catalin Croitoru.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Si, J., Ma, R., Wu, Y. et al. Microstructure and magnetic properties of novel powder cores composed of iron-based amorphous alloy and PTFE. J Mater Sci 57, 8154–8166 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07199-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07199-4