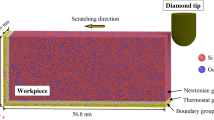
Abstract
Anisotropic deformation behavior of single crystalline material under scratching has a significant effect on machining precision in nano-mechanical machining. In the present work, a crystal plasticity finite element model simulating the scratching process is developed, and the established model is validated by comparison with experimental results. (001)-, (101)- and (111)-oriented coppers are selected to investigate the deformation behavior including scratching depth, surface topography and subsurface deformation affected by scratching path. Further, the deformation mechanisms of (001)-, (101)- and (111)-oriented coppers are analyzed to be caused by deformation of slip systems.

















Similar content being viewed by others

References
Daiguji H, Yang PD, Szeri AJ, Majumdar A (2004) Electrochemomechanical energy conversion in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 4:2315. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0489945
Malekian M, Park SS, Strathearn D, Mostofa MG, Jun MBG (2010) Atomic force microscope probe-based nanometric scribing. J Micromech Microeng. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/20/11/115016
Kassavetis S, Mitsakakis K, Logothetidis S (2007) Nanoscale patterning and deformation of soft matter by scanning probe microscopy. Mater Sci Eng C 27:1456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2006.08.004
Kawasegi N, Takano N, Oka D et al (2006) Nanomachining of silicon surface using atomic force microscope with diamond tip. J Manuf Sci Eng-Trans ASME 128:723–729
Zambaldi C, Raabe D (2010) Plastic anisotropy of gamma-TiAl revealed by axisymmetric indentation. Acta Mater 58:3516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.02.025
Wang Y, Raabe D, Kluber C, Roters F (2004) Orientation dependence of nanoindentation pile-up patterns and of nanoindentation microtextures in copper single crystals. Acta Mater 52:2229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2004.01.016
Liu M, Lu C, Tieu KA, Peng CT, Kong C (2015) A combined experimental-numerical approach for determining mechanical properties of aluminum subjects to nanoindentation. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15072
Zhu J, Xiong C, Ma L et al (2020) Coupled effect of scratching direction and speed on nano-scratching behavior of single crystalline copper. Tribol Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106385
Chavoshi SZ, Xu S (2018) A review on micro- and nanoscratching/tribology at high temperatures: instrumentation and experimentation. J Mater Eng Perform 27:3844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3493-5
Brinckmann S, Dehm G (2015) Nanotribology in austenite: plastic plowing and crack formation. Wear 338:436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2015.05.001
Xu N, Han W, Wang Y, Li J, Shan Z (2017) Nanoscratching of copper surface by CeO2. Acta Mater 124:343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.11.008
Hodge AM, Nieh TG (2004) Evaluating abrasive wear of amorphous alloys using nanoscratch technique. Intermetallics 12:741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2004.02.014
Vencl A, Manic N, Popovic V, Mrdak M (2010) Possibility of the abrasive wear resistance determination with scratch tester. Tribol Lett 37:591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9556-x
Charitidis CA (2010) Nanomechanical and nanotribological properties of carbon-based thin films: a review. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 28:51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2009.08.003
Ha S, Jang J-H, Kim K (2017) Finite element implementation of dislocation-density-based crystal plasticity model and its application to pure aluminum crystalline materials. Int J Mech Sci 120:249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2016.11.011
Choi SH, Kim EY, Woo W, Han SH, Kwak JH (2013) The effect of crystallographic orientation on the micromechanical deformation and failure behaviors of DP980 steel during uniaxial tension. Int J Plast 45:85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2012.11.013
Choi SH, Kim DW, Seong BS, Rollett AD (2011) 3-D simulation of spatial stress distribution in an AZ31 Mg alloy sheet under in-plane compression. Int J Plast 27:1702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2011.05.014
Wei P, Lu C, Tieu K, Su L, Deng G, Huang W (2017) A study on the texture evolution mechanism of nickel single crystal deformed by high pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 684:239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.11.098
Wang Z, Zhang J, Xu Z et al (2019) Crystal plasticity finite element modeling and simulation of diamond cutting of polycrystalline copper. J Manuf Process 38:187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.01.007
Wang Z, Zhang H, Li Z et al (2019) Crystal plasticity finite element simulation and experiment investigation of nanoscratching of single crystalline copper. Wear 430:100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2019.04.024
Becker R, Butler JF, Hu H, Lalli LA (1991) Analysis of an aluminum single-crystal with unstable initial orientation (001) 110 in channel die compression. Metall Trans A 22:45. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03350948
Zhao Z, Ramesh M, Raabe D, Cuitino AM, Radovitzky R (2008) Investigation of three-dimensional aspects of grain-scale plastic surface deformation of an aluminum oligocrystal. Int J Plast 24:2278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2008.01.002
Zhao Z, Kuchnicki S, Radovitzky R, Cultino A (2007) Influence of in-grain mesh resolution on the prediction of deformation textures in fcc polycrystals by crystal plasticity FEM. Acta Mater 55:2361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.11.035
Eisenlohr P, Roters F (2008) Selecting a set of discrete orientations for accurate texture reconstruction. Comput Mater Sci 42:670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2007.09.015
Raabe D, Roters F (2004) Using texture components in crystal plasticity finite element simulations. Int J Plast 20:339. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0749-6419(03)00092-5
Roters F, Eisenlohr P, Hantcherli L, Tjahjanto DD, Bieler TR, Raabe D (2010) Overview of constitutive laws, kinematics, homogenization and multiscale methods in crystal plasticity finite-element modeling: theory, experiments, applications. Acta Mater 58:1152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.10.058
Roters F, Diehl M, Shanthraj P et al (2019) DAMASK–The dusseldorf advanced material simulation kit for modeling multi-physics crystal plasticity, thermal, and damage phenomena from the single crystal up to the component scale. Comput Mater Sci 158:420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2018.04.030
Wang ZF, Zhang JJ, ul Hassan H et al (2018) Coupled effect of crystallographic orientation and indenter geometry on nanoindentation of single crystalline copper. Int J Mech Sci 148:531–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.09.007
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51875373), the Science and Technology Foundation of Sichuan (2019YJ0093) and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (No. 0060204153006). Q.Z. would also like to acknowledge the supports from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 2018M643469, 2019T120836).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: N. Ravishankar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Zhou, Q., Huang, Y. et al. Surface deformation of single crystalline copper on different nano-scratching paths. J Mater Sci 56, 10640–10652 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-05948-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-05948-5