Abstract
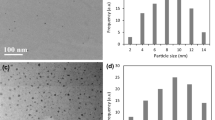
Bacterial biofilm infection is perplexing people’s life. Systemic administration of antibiotics usually causes adverse effects and bacterial resistance. How to make antibacterial agents quickly penetrate and eradicate the biofilm without adverse effects is an urgent problem. Here, polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots (CQDs), abbreviated as CQD600, CQD1w and CQD2.5w, are synthesized by a simple hydrothermal treatment of citric acid and branched polyethyleneimine (bPEI) with different molecular weight (MW). It is found that the antibacterial activity is promoted with high MW of bPEI, which is due to the protonated amines on the surface of the CQDs. Moreover, in terms of eradicating mature Staphylococcus aureus biofilm, CQD2.5w possesses significantly higher activity than CQD600 and CQD1w because of stronger electrostatic interactions and longer surface coronas. Additionally, the cytotoxicity test exhibits the L929 cells can keep at high survival rates even treated with 500 µg mL−1 CQDs for 3 days. In this study, the surface chemistry related to antibacterial activity and low cytotoxicity give the chance in designing and developing better CQDs for biofilm infection.
Graphic abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Götz F (2002) Staphylococcus and biofilms. Mol Microbiol 43:1367–1378. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02827.x
Hall-Stoodley L, Stoodley P (2009) Evolving concepts in biofilm infections. Cell Microbiol 11:1034–1043. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01323.x
Van de Belt H, Neut D, Schenk W, van Horn JR, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (2001) Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation on different gentamicin-loaded polymethylmethacrylate bone cements. Biomaterials 22:1607–1611. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00313-6
Li X, Wu B, Chen H, Nan K, Jin Y, Sun L, Wang B (2018) Recent developments in smart antibacterial surfaces to inhibit biofilm formation and bacterial infections. J Mater Chem B 6:4274–4292. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tb01245h
Liu Y, Shi L, Su L, van der Mei HC, Jutte PC, Ren Y, Busscher HJ (2019) Nanotechnology-based antimicrobials and delivery systems for biofilm-infection. Control Chem Soc Rev 48:428–446. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00807d
Khalid HF, Tehseen B, Sarwar Y, Hussain SZ, Khan WS, Raza ZA, Bajwa SZ, Kanaras AG, Hussain I, Rehman A (2019) Biosurfactant coated silver and iron oxide nanoparticles with enhanced anti-biofilm and anti-adhesive properties. J Hazard Mater 364:441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.049
Maleki Dizaj S, Mennati A, Jafari S, Khezri K, Adibkia K (2015) Antimicrobial activity of carbon-based nanoparticles. Adv Pharm Bull 5:19–23. https://doi.org/10.5681/apb.2015.003
Wehling J, Dringen R, Zare RN, Maas M, Rezwan K (2014) Bactericidal activity of partially oxidized nanodiamonds. ACS Nano 8:6475–6483. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn502230m
Gunawan P, Guan C, Song X, Zhang Q, Leong SSJ, Tang C, Chen Y, Chan-Park MB, Chang MW, Wang K, Xu R (2011) Hollow fiber membrane decorated with Ag/MWNTs: toward effective water disinfection and biofouling control. ACS Nano 5:10033–10040. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2038725
Zou X, Zhang L, Wang Z, Luo Y (2016) Mechanisms of the antimicrobial activities of graphene materials. J Am Chem Soc 138:2064–2077. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b11411
Liu S, Zeng TH, Hofmann M, Burcombe E, Wei J, Jiang R, Kong J, Chen Y (2011) Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 5:6971–6980. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn202451x
Mi G, Shi D, Wang M, Webster TJ (2018) Reducing bacterial infections and biofilm formation using nanoparticles and nanostructured antibacterial surfaces. Adv Healthc Mater 7:1800103. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201800103
Wang H, Song Z, Gu J, Li S, Wu Y, Han H (2019) Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for preventing biofilm formation and eradicating drug-resistant bacteria infection. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5:4739–4749. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b00583
Ran H, Cheng X, Bao Y, Hua X, Gao G, Zhang X, Jiang Y, Zhu Y, Wu F (2019) Multifunctional quaternized carbon dots with enhanced biofilm penetration and eradication efficiencies. J Mater Chem B 7:5104–5114. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TB00681H
Yang J, Gao G, Zhang X, Ma YH, Chen X, Wu FG (2019) One-step synthesis of carbon dots with bacterial contact-enhanced fluorescence emission: fast gram-type identification and selective gram-positive bacterial inactivation. Carbon 146:827–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.02.040
Yang J, Zhang X, Ma YH, Gao G, Chen X, Jia HR, Li YH, Chen Z, Wu FG (2016) Carbon dot-based platform for simultaneous bacterial distinguishment and antibacterial applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:32170–32181. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b10398
Bing W, Sun H, Yan Z, Ren J, Qu X (2016) Programmed bacteria death induced by carbon dots with different surface charge. Small 12:4713–4718. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201600294
Travlou NA, Giannakoudakis DA, Algarra M, Labella AM, Rodríguez-Castellón E, Bandosz TJ (2018) S-and N-doped carbon quantum dots: surface chemistry dependent antibacterial activity. Carbon 135:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.04.018
Jian HJ, Wu RS, Lin TY, Li YJ, Lin HJ, Harroun SG, Lai JY, Huang CC (2017) Super-cationic carbon quantum dots synthesized from spermidine as an eye drop formulation for topical treatment of bacterial keratitis. ACS Nano 11:6703–6716. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b01023
Li YJ, Harroun SG, Su YC, Huang CF, Unnikrishnan B, Lin HJ, Lin CH, Huang CC (2016) Synthesis of self-assembled spermidine-carbon quantum dots effective against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Adv Healthc Mater 5:2545–2554. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201600297
Anand A, Manavalan G, Mandal RP, Chang HT, Chiou YR, Huang CC (2019) Carbon dots for bacterial detection and antibacterial applications-a minireview. Curr Pharm Des 25:4848–4860. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612825666191216150948
Cao L, Wang X, Meziani MJ, Lu F, Wang H, Luo PG, Lin Y, Harruff BA, Monica Veca L, Murray D, Xie SY, Sun YP (2007) Carbon dots for multiphoton bioimaging. J Am Chem Soc 129:11318–11319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja073527l
Dong Y, Wang R, Li H, Shao J, Chi Y, Lin X, Chen G (2012) Polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots for chemical sensing. Carbon 50:2810–2815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.02.046
Wang R, Li G, Dong Y, Chi Y, Chen G (2013) Carbon quantum dot-functionalized aerogels for NO2 gas sensing. Anal Chem 85:8065–8069. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac401880h
Hou P, Yang T, Liu H, Li YF, Huang CZ (2017) An active structure preservation method for developing functional graphitic carbon dots as an effective antibacterial agent and a sensitive pH and Al(III) nanosensor. Nanoscale 9:17334–17341. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr05539k
Qu D, Zheng M, Du P, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Li D, Tan H, Zhao Z, Xie Z, Sun Z (2013) Highly Luminescent S, N Co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale 5:12272–12277. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr04402e
Li P, Han F, Cao W, Zhang G, Li J, Zhou J, Gong X, Turnbull G, Shu W, Xia L, Fang B, Xing X, Li B (2020) Carbon quantum dots derived from lysine and arginine simultaneously scavenge bacteria and promote tissue repair. Appl Mater Today 19:100601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100601
Cao W, Peng X, Chen X, Wang X, Jin F, Li Q, Chen H, Jiang C, Ye Z, Xing X (2017) Facile synthesis of cationic polymer functionalized nanodiamond with high dispersity and antibacterial activity. J Mater Sci 52:1856–1867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0475-6
Zhang H, Dunphy DR, Jiang X, Meng H, Sun B, Tarn D, Xue M, Wang X, Lin S, Ji Z, Li R, Garcia FL, Yang J, Kirk ML, Xia T, Zink JI, Nel A, Brinker CJ (2012) Processing pathway dependence of amorphous silica nanoparticle toxicity: colloidal vs pyrolytic. J Am Chem Soc 134:15790–15804. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja304907c
Li P, Liu S, Cao W, Zhang G, Yang X, Gong X, Xing X (2020) Low-toxicity carbon quantum dots derived from gentamicin sulfate to combat antibiotic resistance and eradicate mature biofilms. Chem Commun 56:2316–2319. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CC09223D
Li P, Liu S, Yang X, Du S, Tang W, Cao W, Zhou J, Gong X, Xing X (2021) Low-drug resistance carbon quantum dots decorated injectable self-healing hydrogel with potent antibiofilm property and cutaneous wound healing. Chem Eng J 403:126387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126387
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
Li P, Liu S, Zhang G, Yang X, Cao W, Gong X, Xing X (2020) Design of pH-responsive dissociable nanosystem based on carbon dots with enhanced anti-biofilm property and excellent biocompatibility. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3:1105–1115. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.9b01053
Dong Y, Lin J, Chen Y, Fu F, Chi Y, Chen G (2014) Graphene quantum dots, graphene oxide, carbon quantum dots and graphite nanocrystals in coals. Nanoscale 6:7410–7415. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr01482k
Liu Y, Xue JS, Zheng T, Dahn JR (1996) Mechanism of lithium insertion in hard carbons prepared by pyrolysis of epoxy resins. Carbon 34:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(96)00177-7
Yang Z, Xu M, Liu Y, He F, Gao F, Su Y, Wei H, Zhang Y (2014) Nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, highly photoluminescent carbon dots from ammonium citrate. Nanoscale 6:1890–1895. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR05380F
Chin SF, Yazid SNAM, Pang SC, Ng SM (2012) Facile Synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanodots from starch nanoparticles. Mater Lett 85:50–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.06.082
Cao J, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Tian S, Zheng C, Liu C, Zhai Y, An Y, Busscher HJ, Shi L, Liu Y (2019) Phosphorylcholine-based polymer encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles enhance the penetration of antimicrobials in a staphylococcal biofilm. ACS Macro Lett 8:651–657. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.9b00142
Fulaz S, Vitale S, Quinn L, Casey E (2019) Nanoparticle-biofilm interactions: the role of the EPS matrix. Trends Microbiol 27:915–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2019.07.004
Alarcon EI, Udekwu K, Skog M, Pacioni NL, Stamplecoskie KG, González-Béjar M, Polisetti N, Wickham A, Richter-Dahlfors A, Griffith M, Scaiano JC (2012) The biocompatibility and antibacterial properties of collagen-stabilized, photochemically prepared silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 33:4947–4956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.03.033
Hühn D, Kantner K, Geidel C, Brandholt S, De Cock I, Soenen SJH, Rivera_Gil P, Montenegro JM, Braeckmans K, Müllen K, Nienhaus GU, Klapper M, Parak WJ (2013) Polymer-coated nanoparticles interacting with proteins and cells: focusing on the sign of the net charge. ACS Nano 7:3253–3263. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn3059295
Fischer D, Bieber T, Li Y, Elsässer HP, Kissel TA (1999) Novel non-viral vector for DNA delivery based on low molecular weight, branched polyethylenimine: effect of molecular weight on transfection efficiency and cytotoxicity. Pharm Res 16:1273–1279. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014861900478
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81970972) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (30920140112002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PL and XY were involved in investigation, data curation, formal analysis and writing—original draft. XZ, JP, WT, WC, JZ and XG were involved in investigation and formal analysis. XX helped in conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, methodology and writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Annela M. Seddon.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Yang, X., Zhang, X. et al. Surface chemistry-dependent antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots. J Mater Sci 55, 16744–16757 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05262-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05262-6