Abstract
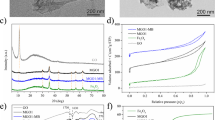
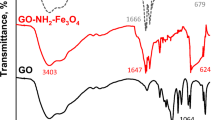
The poly(4-vinylpyridine)–graphene oxide–Fe3O4 magnetic nanohybrid (GO-Fe3O4@P4VP) was prepared and used as a novel nanoadsorbent to efficiently remove methyl blue (MB) from aqueous solution. The GO-Fe3O4@P4VP was characterized with scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, elemental analysis, BET surface area, X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and vibrating sample magnetometer. The GO-Fe3O4@P4VP had high surface area, porous structure and magnetic properties. Adsorption performances of GO-Fe3O4@P4VP for MB were investigated at different pH, initial concentrations of MB, ionic strength, adsorbent dosage, contact time and the temperature. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetic process of MB on GO-Fe3O4@P4VP were well described by the Freundlich isotherm model and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, respectively. Additionally, the characteristics of high adsorption capacity, rapid adsorption rate, good reusability and magnetic separation would make GO-Fe3O4@P4VP become a perfect candidate to remove MB in aqueous solution.













Similar content being viewed by others

References
Zhu G, Xing X, Wang J et al (2017) Effect of acid and hydrothermal treatments on the dye adsorption properties of biomass-derived activated carbon. J Mater Sci 52:7664–7676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1055-0
Ma H, Pu S, Hou Y et al (2018) A highly efficient magnetic chitosan “fluid” adsorbent with a high capacity and fast adsorption kinetics for dyeing wastewater purification. Chem Eng J 345:556–565
Afkhami A, Moosavi R (2010) Adsorptive removal of Congo red, a carcinogenic textile dye, from aqueous solutions by maghemite nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 174(1–3):398–403
Parmar KR, Patel I, Basha S et al (2014) Synthesis of acetone reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4composite through simple and efficient chemical reduction of exfoliated graphene oxide for removal of dye from aqueous solution. J Mater Sci 49(19):6772–6783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8378-x
González JA, Villanueva ME, Piehl LL et al (2015) Development of a chitin/graphene oxide hybrid composite for the removal of pollutant dyes: adsorption and desorption study. Chem Eng J 280:41–48
Ma H, Pu S, Hou Y et al (2018) A highly efficient magnetic chitosan “fluid” adsorbent with a high capacity and fast adsorption kinetics for dyeing wastewater purification. Chem Eng J 345:556–565
Liang GZ, Sun SP, Li FY et al (2014) Treatment of highly concentrated wastewater containing multiple synthetic dyes by a combined process of coagulation/flocculation and nanofiltration. J Membr Sci 469:306–315
Rajeswari A, Vismaiya S, Anitha Pius (2017) Preparation, characterization of nano ZnO-blended cellulose acetate-polyurethane membrane for photocatalytic degradation of dyes from water. Chem Eng J 313:928–937
Villalobos MC, Cid AAP, González AMH (2016) Removal of textile dyes and metallic ions using polyelectrolytes and macroelectrolytes containing sulfonic acid groups. J Environ Manag 117:65–73
Ilyas S, Joseph N, Szymczyk A et al (2016) Weak polyelectrolyte multilayers as tunable membranes for solvent resistant nanofiltration. J Membr Sci 514:322–331
Hu E, Wu X, Shang S et al (2016) Catalytic ozonation of simulated textile dyeing wastewater using mesoporous carbon aerogel supported copper oxide catalyst. J Clean Prod 112(5):4710–4718
Li X, Lu H, Zhang Y et al (2017) Efficient removal of organic pollutants from aqueous media using newly synthesized polypyrrole/CNTs-CoFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 316:893–902
Fan L, Luo C, Li X et al (2012) Fabrication of novel magnetic chitosan grafted with graphene oxide to enhance adsorption properties for methyl blue. J Hazard Mater 215–216:272–279
Rêgo TV, Cadaval TR Jr, Dotto GL et al (2013) Statistical optimization, interaction analysis and desorption studies for the azo dyes adsorption onto chitosan films. J Colloid Interface Sci 411:27–33
Xu R, Mao J, Peng N et al (2018) Chitin/clay microspheres with hierarchical architecture for highly efficient removal of organic dyes. Carbohydr Polym 188:143–150
Singh H, Chauhan G, Jain AK et al (2017) Adsorptive potential of agricultural wastes for removal of dyes from aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 5(1):122–135
Goswami M, Phukan P et al (2017) Enhanced adsorption of cationic dyes using sulfonic acid modified activated carbon. J Environ Chem Eng 5(4):3508–3517
Banerjee SS, Joshi MV, Jayaram RV et al (2006) Effect of quaternary ammonium cations on dye sorption to fly ash from aqueous media. J Colloid Interface Sci 303(2):477–483
Wan S, He F, Wu J et al (2016) Rapid and highly selective removal of lead from water using graphene oxide-hydrated manganese oxide nanocomposites. J Hazard Mater 314:32–40
Shen Y, Chen B et al (2015) Sulfonnated graphene nanosheets as a superb adsorbent for various environmental pollutants in water. Environ Sci Technol 49(12):7364–7372
Shen Y, Fang Q, Chen B et al (2015) Environmental applications of three-dimensional graphene-based macrostructures: adsorption, transformation, and detection. Environ Sci Technol 49(1):67–84
Das TR, Patra S, Madhuri R et al (2018) Bismuth oxide decorated graphene oxide nanocomposites synthesized via sonochemical assisted hydrothermal method for adsorption of cationic organic dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci 509:82–93
Liu M, Wen T, Wu X et al (2013) Synthesis of porous Fe3O4 hollow microspheres/graphene oxide composite for Cr(VI) removal. Dalton Trans 42:14710–14717
Tayyebi A, Outokesh M, Moradi S et al (2015) Synthesis and characterization of ultrasound assisted “graphene oxide–magnetite” hybrid, and investigation of its adsorption properties for Sr(II) and Co(II) ions. Appl Surf Sci 353:350–362
Larraza I, López-Gónzalez M, Corrales T et al (2012) Hybrid materials: magnetite-polyethylenimine-montmorillonite, as magnetic adsorbents for Cr(VI) water treatment. J Colloid Interface Sci 385(1):24–33
Gholampoor M, Movassagh-Alanagh Salimkhani H (2017) Fabrication of nano-Fe3O4, 3D structure on carbon fibers as a microwave absorber and EMI shielding composite by modified EPD method. Solid State Sci 64:51–61
Lee JS, Hong SK, Hur NJ et al (2013) Fabrication of spherical silica aerogel/magnetite nanocomposite particles. Mater Lett 112:153–157
Doustkhah E, Rostamnia S (2016) Covalently bonded sulfonic acid magnetic graphene oxide: Fe3O4@GO-Pr-SO3H as a powerful hybrid catalyst for synthesis of indazolophthalazinetriones. J Colloid Interface Sci 478:280–287
Hatel R, Goumri M, Ratier B et al (2017) Graphene derivatives/Fe3O4/polymer nanocomposite films: optical and electrical properties. Mater Chem Phys 193:156–163
Janakiraman S, Farrell SL, Hsieh CY et al (2015) Kinetic analysis of the initiated chemical vapor deposition of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) and poly(4-vinylpyridine). Thin Solid Films 595:244–250
Ghadimi H, Tehrani RMA, Basirun WJ et al (2016) Electrochemical determination of aspirin and caffeine at MWCNTs-poly-4-vinylpyridine composite modified electrode. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 65:101–109
Li Y, Hong L, Chen Y et al (2017) Poly(4-vinylpyridine)/carbon black composite as a humidity sensor. Sens Actuators B 123(1):554–559
Chetouani A, Medjahed K, Sid-Lakhdar KE et al (2004) Poly(4-vinylpyridine-poly(3-oxide-ethylene) tosyle) as an inhibitor for iron in sulphuric acid at 80°C. Corros Sci 46(10):2421–2430
Tenhaeff WE, McIntosh LD, Gleason KK (2010) Poly(4-vinylpyridine) thin films by initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) for selective nanotrench-based sensing of nitroaromatics. Adv Funct Mater 20:1144–1151
Mehdinia A, Ramezani M, Jabbari A (2017) Preconcentration and determination of lead ions in fish and mollusk tissues by nanocomposite of Fe3O4@graphene oxide@polyimide as a solid phase extraction sorbent. Food Chem 237:1112–1117
Qin S, Qin D, Ford WT et al (2004) Grafting of poly(4-vinylpyridine) to single-walled carbon nanotubes and assembly of multilayer films. Macromolecules 37(26):9963–9967
Wang L, Hu D, Kong X et al (2018) Anionic polypeptide poly(γ-glutamic acid)-functionalized magnetic Fe3O4-GO-(o-MWCNTs) hybrid nanocomposite for high-efficiency removal of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) heavy metal ions. Chem Eng J 346:38–49
Zeng S, Duan S, Tang R et al (2014) Magnetically separable Ni0.6Fe2.4O4 nanoparticles as an effective adsorbent for dye removal: synthesis and study on the kinetic and thermodynamic behaviors for dye adsorption. Chem Eng J 258:218–228
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1368
Fu J, Xin Q, Wu X et al (2016) Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes from aqueous solution on polydopamine microspheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 461:292–304
Ho YS, Kay GM (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Xie G, Xi P, Liu H et al (2011) A facile chemical method to produce superparamagnetic graphene oxide–Fe3O4 hybrid composite and its application in the removal of dyes from aqueous solution. J Mater Chem 22:1033–1039
Sahiner N, Atta AM, Yasar AO et al (2015) Surface activity of amphiphilic cationic pH-responsive poly(4-vinylpyridine) microgel at air/water interface. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 482:647–655
Li J, Qiu JD, Xu JJ et al (2010) The synergistic effect of Prussian blue grafted carbon nanotube/poly(4-vinylpyridine) composites for amperometric sensing. Adv Funct Mater 17:1574–1580
Zeng B, Yang L, Zheng W et al (2018) Analysis of the formation process and performance of magnetic Fe3O4@Poly(4-vinylpyridine) absorbent prepared by in situ synthesis. J Mater Sci Technol 34:999–1007
Sun Z, Yu Y, Mao L et al (2008) Sorption behavior of tetrabromobisphenol A in two soils with different characteristics. J Hazard Mater 160:456–461
Yu Q, Deng S, Yu G (2008) Selective removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate from aqueous solution using chitosan-based molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents. Water Res 42:3089–3097
Su Y, Cui H, Li Q et al (2013) Strong adsorption of phosphate by amorphous zirconium oxide nanoparticles. Water Res 47:5018–5026
Ren X, Shao D, Yang S et al (2011) Comparative study of Pb(II) sorption on XC-72 carbon and multi-walled carbon nanotubes from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 170:170–177
Shao Y, Wang X, Kang Y et al (2014) Application of Mn/MCM-41 as an adsorbent to remove methyl blue from aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 429:25–33
Lv M, Yan L, Liu C et al (2018) Non-covalent functionalized graphene oxide (GO) Adsorbent with an organic gelator for co-adsorption of dye, endocrine-disruptor, pharmaceutical and metal ion. Chem Eng J 349:791–799
Abdi J, Vossoughi M, Mahmoodi NM et al (2017) Synthesis of metal-organic framework hybrid nanocomposites based on GO and CNT with high adsorption capacity for dye removal. Chem Eng J 326:1145–1158
Zhao L, Sun X, Lei Z et al (2015) Thermoelectric behavior of aerogels based on graphene and multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Compos Part B Eng 83:317–322
Jiang Y, Lu M, Ling X et al (2015) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of three-dimensional porous grapheme aerogels/sulfur nanocrystals for lithium-sulfur batteries. J Alloy Compd 645:509–516
Zhou S, Xue A, Zhang Y et al (2015) Novel polyamidoamine dendrimer-functionalized palygorskite adsorbents with high adsorption capacity for Pb2+ and reactive dyes. Appl Clay Sci 107:220–229
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21407071) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. lzujbky-2017-218).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Lu, H., Wang, Y. et al. Efficient removal of methyl blue from aqueous solution by using poly(4-vinylpyridine)–graphene oxide–Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 54, 7603–7616 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03441-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03441-8