Abstract
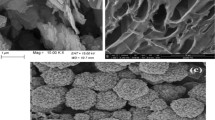
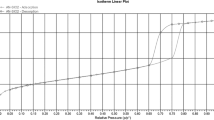
Mineral-coated silsesquioxane particles of approximately 600 nm diameter were synthesized from the hydrolytic co-condensation of N-[3-trimethoxysilyl]-propyl]ethylenediamine (DAS) and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS). The hybrid particles involve nanocomposites with a mineral core (montmorillonite—MMT—or goethite—Gt—nanoparticles) and coated with a silsesquioxane shell containing hydroxyl and amine groups. These particles were specially designed (exposing amino groups) to be highly efficient for the removal of As(V) and to enhance the adsorption properties of the minerals employed in this work. They were characterized by infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, zeta potential, dynamic light scattering and thermogravimetric techniques such as dynamic scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis. The characteristics found in the composite particles compared with pure organosilane DAS/TEOS or with the unmodified minerals proved the effectiveness of the silanization process. As result, hybrid nanocomposite materials were obtained, denoting versatility in their adsorption properties of different types of pollutants. Moreover, all synthesized particles showed a high arsenic retention capacity; experimental results demonstrated that superficial modification of the minerals is the preponderant factor that determines their adsorbent properties, favoring the versatility of these materials making them suitable for the removal of pollutants of diverse charge and nature.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Sracek O, Bhattacharya P, Jacks G, Gustafsson JP, von Brömssen M (2004) Behavior of arsenic and geochemical modeling of arsenic enrichment in aqueous environments. Appl Geochem 19:169–180
Bundschuh J, Litter MI, Parvez F, Román-Ross G, Nicolli HB, Jean JS, Liu CW, López D, Armienta MA, Guilherme LR, Cuevas AG, Cornejo L, Cumbal L, Toujaguez R (2012) One century of arsenic exposure in Latin America: a review of history and occurrence from 14 countries. Sci Total Environ 429:2–35
Atkinson RJ, Posner AM, Quirk JP (1967) Adsorption of potential-determining ions at the ferric oxide-aqueous electrolyte interface. J Phys Chem 71:550–558
Ilari R, Etcheverry M, Zenobi C, Zanini G (2014) Effect of the surfactant benzalkonium chloride in the sorption of paraquat and cadmium on montmorillonite. Int J Environ Health 7:70–82
Ungureanu G, Santos S, Boaventura R, Botelho C (2015) Arsenic and antimony in water and wastewater: overview of removal techniques with special reference to latest advances in adsorption. J Environ Manag 151:326–342
Martinez-Vargas S, Martínez AI, Elias E, Hernández-Beteta EE, Mijangos-Ricardez OJ, Vázquez-Hipólito V, Patiño-Carachure C, Hernandez-Flores H, López-Luna J (2017) Arsenic adsorption on cobalt and manganese ferrite nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 52:6205–6215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0852-9
Delorme F, Seron A, Gautier A, Crouzet C (2007) Comparison of the fluoride, arsenate and nitrate anions water depollution potential of a calcined quintinite, a layered double hydroxide compound. J Mater Sci 42:5799–5804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0752-x
Musso TB, Parolo ME, Pettinari G, Francisca FM (2014) Cu(II) and Zn(II) adsorption capacity of three different clay liner materials. J Environ Manag 146:50–58
Chakraborty U, Singha T, Chianelli RR, Hansda C, Paul PK (2017) Organic-inorganic hybrid layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembled film of cationic dye methylene blue and a clay mineral: spectroscopic and atomic force microscopic investigations. J Lumin 187:322–332
Waiman CV, Arroyave JM, Chen H, Tan W, Avena MJ, Zanini GP (2016) The simultaneous presence of glyphosate and phosphate at the goethite surface as seen by XPS, ATR-FTIR and competitive adsorption isotherms. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 498:121–127
Wu H, Xie H, He G, Guan Y, Zhang Y (2016) Effects of the pH and anions on the adsorption of tetracycline on iron-montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci 119:161–169
Ogden SG, Lewis D, Shapter JG (2008) Silane functionalization of iron oxide nanoparticles. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.810679
Gatti MN, Fernández LG, Sánchez MP, Parolo ME (2016) Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane- and aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-silver-modified montmorillonite for the removal of nitrate ions. Environ Technol 37:2658–2668
Liu F, Niu F, Peng N, Su Y, Yang Y (2015) Synthesis, characterization, and application of Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 5:18128–18136
Safaei-Ghomi J, Nazemzadeh SH, Shahbazi-Alavi H (2016) Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2/APTPOSS core–shell composite nanomagnetics as a novel family of reusable catalysts and their application in the one-pot synthesis of 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives. Appl Organomet Chem 30:911–916
Kang JK, Park JA, Kim JH, Lee CG, Kim SB (2016) Surface functionalization of mesoporous silica MCM-41 with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane for dye removal: kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Desalin Water Treat 57:7066–7078
Mahmoud ME, Saad EA, Soliman MA, Abdelwahab MS (2016) Synthesis and surface protection of nano zero valent iron (NZVI) with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane for water remediation of cobalt and zinc and their radioactive isotopes. RSC Adv 6:66242–66251
Yin JX, Wang XZ, Qi LH, Hao Y, Chen ZJ (2013) Preparation of amination magnetic nanoparticles and their application in Pb2+ adsorption property. Gongneng Cailiao/J Funct Mater 44:2511–2515
Lin Y, Chen H, Lin K, Chen B, Chiou C (2011) Application of magnetic particles modified with amino groups to adsorb copper ions in aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 23:44–50
Wu Z, Wu J, Xiang H, Chun MS, Lee K (2006) Organosilane-functionalized Fe3O4 composite particles as effective magnetic assisted adsorbents. Colloid Surf A 279:167–174
Nodeh HR, Sereshti H, Gaikani H, Kamboh MA, Afsharsaveh Z (2017) Magnetic graphene coated inorganic-organic hybrid nanocomposite for enhanced reconcentration of selected pesticides in tomato and grape. J Chromatogr A 1509:26–34
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Meier LP, Kahr G (1999) Determination of the cation exchange capacity (cec) of clay minerals using the complexes of copper(II) ion with Triethylenetetramine and tetraethylenepentamine. Clays Clay Miner 47:380–388
Sabnis RW (2010) Handbook of biological dyes and stains: synthesis and industrial applications. Wiley, Hoboken
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Lenoble V, Deluchat V, Serpaud B, Bollinger JC (2003) Arsenite oxidation and arsenate determination by the molybdene blue method. Talanta 61:267–276
Mori H, Lanzendörfer MG, Müller AHE (2004) Silsesquioxane-based nanoparticles formed via hydrolytic condensation of organotriethoxysilane containing hydroxy groups. Macromolecules 37:5228–5238
Rubio F, Rubio J, Oteo JL (1998) A FT-IR study of the hydrolysis of tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS). Spectrosc Lett 31:199–219
Wang R, Baran G, Wunder SL (2000) Packing and thermal stability of polyoctadecylsiloxane compared with octadecylsilane monolayers. Langmuir 16:6298–6305
Tejedor-Tejedor MI, Anderson MA (1986) “In Situ” attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared studies of the goethite (α-FeOOH)-aqueous solution interface. Langmuir 2:203–210
Launer PJ (1987) Infrared analysis of organosilicon compounds: spectra-structure correlations. In: Arkles B et al (eds) Reprinted from silicon compounds register and review. Petrarch Systems, Bristol, pp 211–214
McCarthy SA, Davies GL, Gun’ko YK (2012) Preparation of multifunctional nanoparticles and their assemblies. Nat Protoc 9:1677–1693
Zhai SR, Zhang L, Zhai B, An QD (2012) Facile sol–gel synthesis of thiol-functionalized materials from TEOS-MPTMS-PMHS system. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 61:23–33
Gómez ML, Fasce DP, Williams RJJ, Previtali CM, Montejano HA (2010) Transparent polysilsesquioxane films obtained from bridged ureasil precursors: tunable photoluminescence emission in the visible region and filtering of UV-radiation. Macromol Mater Eng 295:1042–1048
Gómez ML, Hoppe CE, Williams RJJ (2011) In situ generation of silver microstructures by thermal decomposition of silver n dodecanethiolate dispersed in an organic-inorganic hybrid coating. Mater Chem Phys 130:519–523
Waiman CV, dell’Erba IE, Chesta CA, Gómez ML (2016) Hybrid films based on a bridged silsesquioxane doped with goethite and montmorillonite nanoparticles as sorbents of wastewater contaminants. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6286247
Grewer T (1991) The influence of chemical structure on exothermic decomposition. Thermochim Acta 187:133–149
Gualtieri AF, Venturelli P (1999) In situ study of the goethite-hematite phase transformation by real time synchrotron powder diffraction. Am Mineral 84:895–904
Luengo C, Puccia V, Avena M (2011) Arsenate adsorption and desorption kinetics on a Fe(III)-modified montmorillonite. J Hazard Mater 186:1713–1719
Song K, Sandi G (2001) Characterization of montmorillonite surfaces after modification by organosilane. Clays Clay Miner 49:119–125
Fina A, Tabuani D, Carniato F, Frache A, Boccaleri E, Camino G (2006) Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) thermal degradation. Thermochim Acta 440:36–42
Chen C, Huang S, Chen M, Lu Q (2012) Synthesis and characterization of three kinds of bifunctionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes with the same cage structure. High Perform Polym 24:119–124
Li J, Zhou H, Qian K, Xie X, Xue X, Yang Y, Wang Y (2017) Fluoride and iodine enrichment in groundwater of North China Plain: evidences from speciation analysis and geochemical modeling. Sci Total Environ 598:239–248
Luengo C, Brigante M, Avena M (2007) Adsorption kinetics of phosphate and arsenate on goethite. A comparative study. J Colloid Interface Sci 311:354–360
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M, Sarzanini C, Mentasti E (2003) Adsorption of heavy metals on Na-montmorillonite. Effect of pH and organic substances. Water Res 37:1619–1627
Essington ME, Leeand J, Seo Y (2010) Adsorption of antibiotics by montmorillonite and kaolinite. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74:1577–1588
Yu S, Wang X, Chen Z, Tan X, Wang H, Hu J, Alsaedi A, Alharbi NS, Guo W, Wang X (2016) Interaction mechanism of radionickel on Na-montmorillonite: influences of pH, electrolyte cations, humic acid and temperature. Chem Eng J 302:77–85
Torres JJ, Montejano HA, Chesta CA (2012) Characterization of imprinted microbeads synthesized via minisuspension polymerization. Macromol Mater Eng 297:342–352
Kumar E, Bhatnagar A, Hogland W, Marques M, Sillanpää M (2014) Interaction of anionic pollutants with Al-based adsorbents in aqueous media—a review. Chem Eng J 241:443–456
Gong Y, Tang J, Zhao D (2016) Application of iron sulfide particles for groundwater and soil remediation: a review. Water Res 89:309–320
Asta MP, Cama J, Martínez M, Giménez J (2009) Arsenic removal by goethite and jarosite in acidic conditions and its environmental implications. J Hazard Mater 171:965–972
Puccia V, Luengo C, Avena M (2009) Phosphate desorption kinetics from goethite as induced by arsenate. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 348:221–227
Deng S, Yu G, Xie S, Yu Q, Huang J, Kuwaki Y, Iseki M (2008) Enhanced adsorption of arsenate on the aminated fibers: sorption behaviour and uptake mechanism. Langmuir 24:10961–10967
Acknowledgements
All authors are members of Consejo Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (CONICET). C. V. Waiman thanks CONICET for postdoctoral fellowship. The financial support of Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Universidad Nacional del Sur (PGI 24/Q051), Consejo Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (PIP 11220100100284) and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT 0115/2016 and PICT 1439/2013) from Argentina is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waiman, C.V., dell’Erba, I.E., Chesta, C.A. et al. Hybrid mineral@silsesquioxane particles for water remediation: synthesis, characterization and application as adsorbent of As(V) and other water pollutants. J Mater Sci 53, 12781–12794 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2529-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2529-4