Abstract
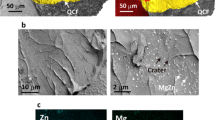
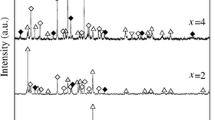
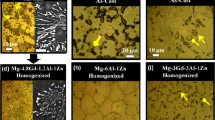
In this paper, the effect of local hydrogen concentration and distribution in magnesium (Mg) alloys is studied in regard to hydrogen embrittlement. Quantitative studies of hydrogen trapping sites and release behavior in AZ91 and AZ31 magnesium alloys are being studied by thermal desorption analysis (TDS). The trapping energy levels are used to discuss the embrittlement mechanisms due to their control on hydrogen availability. The embrittlement process is caused by hydrogen in combination with residual or applied stress and can lead to the mechanical degradation of a material. The susceptibility of Mg alloys is directly related to the role of the second phases controlling the hydrogen trapping mechanisms. In this work, we examine the effect of Mg’s microstructure on the magnesium hydride (MgH2) reaction, referred to as hydriding, and its decomposition, referred to as dehydriding. The MgH2 compound was investigated in regard to two aspects: first, as the main source for controlling the hydrogen dehydriding process; second, as a hydrogen trapping site for preventing hydrogen embrittlement process. The TDS analysis was used to study the hydrogen trapping mechanisms by studying the traps’ density and distribution and relating them to potential lattice defects. The TDS analysis revealed a certain hydrogen concentration evolving near β-Mg17Al12 phase, accompanied by H2 desorption at a temperature range between ~200 and 300 °C. It is proposed that β-phase plays a fundamental role in the dehydriding process, and this response is a crucial step in effecting the embrittlement behavior.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eliezer D, Alves H (2002) Corrosion and oxidation of magnesium alloys. Handb Mater Sel 267–289
For S, Distributors E (2000) Magnesium alloys development toward the 21st century. Mater Sci Forum 350–351:19–30. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.350
Soenke S, Horst EF (2006) Automotive applications in Europe. Magnes Technol 499–569
Kappes M, Iannuzzi M, Carranza RM (2013) Hydrogen embrittlement of magnesium and magnesium alloys: a review. J Electrochem Soc 160:168–178. doi:10.1149/2.023304jes
Yuasa M, Nishihara D, Mabuchi M, Chino Yasumasa (2012) Hydrogen embrittlement in a magnesium grain boundary: a first-principles study. J Phys Condens 24:1–9. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/24/8/085701
Song RG, Dietzel W, Zhang BJ et al (2004) Stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Acta Mater 52:4727–4743. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2004.06.023
Robertson IM, Sofronis P, Nagao A et al (2015) Hydrogen Embrittlement Understood. Metall Mater Trans B 46:1085–1103
Minkovitz E, Talianker M, Eliezer D (1981) TEM investigation of hydrogen induced ε-hcp-martensite in 316L-type stainless steel. J Mater Sci 16:3506–3508. doi:10.1007/BF00586316
Scully, JR, Young, GA, Smith, SW (2012) Hydrogen embrittlement of aluminum and aluminum-based alloys. Gaseoues Hydrog embrittlement Mater Energy Technol 707
Silverstein R, Eliezer D (2016) Hydrogen trapping energy levels and hydrogen diffusion at high and low strain rates (~ 10 5 s−1 and 10−7 s−1) in lean duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A 674:419–427. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2016.08.019
Silverstein R, Eliezer D, Glam B et al (2015) Evaluation of hydrogen trapping mechanisms during performance of different hydrogen fugacity in a lean duplex stainless steel. J Alloys Compd 648:601–608. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.029
Sofronis P, Dadfarnia M, Novak P, et al (2009) A combined applied mechanics/materials science approach toward quantifying the role of hydrogen on material degradation. In: Proc. 12th int. conf. fract. Ottawa, Canada, pp 1–10
Tal-Gutelmacher E, Eliezer D (2005) High fugacity hydrogen effects at room temperature in titanium based alloys. J Alloys Compd 404–406:613–616. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.12.172
Choo WY, Lee JY (1982) Hydrogen trapping phenomena in carbon steel. J Mater Sci 17:1930–1938. doi:10.1007/BF00540409
Abramov E, Eliezer D (1988) Trapping of hydrogen in helium-implanted metals. J Mater Sci Lett 7:108–110. doi:10.1007/BF01730586
Shang CX, Bououdina M, Song Y, Guo ZX (2004) Mechanical alloying and electronic simulations of (MgH2 + M) systems (M = Al, Ti, Fe, Ni, Cu and Nb) for hydrogen storage. Int J Hydrogen Energy 29:73–80. doi:10.1016/S0360-3199(03)00045-4
Bouaricha S, Dodelet JP, Guay D et al (2000) Hydriding behavior of Mg-Al and leached Mg-Al compounds prepared by high-energy ball-milling. J Alloys Compd 297:282–293. doi:10.1016/S0925-8388(99)00612-X
Renner J, Grabke HJ (1979) Determination of diffusion coefficients in the hydriding of alloys. Chem Informationsd. doi:10.1002/chin.197903007
Ben-Haroush M, Ben-Hamu G, Eliezer D, Wagner L (2008) The relation between microstructure and corrosion behavior of AZ80 Mg alloy following different extrusion temperatures. Corros Sci 50:1766–1778. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2008.03.003
Ben-Hamu G, Eliezer D, Kaya A et al (2006) Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg-Zn-Ag alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 435–436:579–587. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.07.109
Nunes R, Adams JH, Ammons M, Al E (2001) Properties and selection: nonferrous alloys ans special- purpose materials. ASM Handb 2:127–425
Silverstein R, Eliezer D, Glam B et al (2014) Influence of hydrogen on microstructure and dynamic strength of lean duplex stainless steel. J Mater Sci 49:4025–4031. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8075-9
Crank J (1975) The mathematics of diffusion, 2nd edn. Clarendon, Oxford
Atrens A, Winzer N, Song G et al (2006) Stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen diffusion in magnesium. Adv Eng Mater 8:749–751. doi:10.1002/adem.200600050
Silverstein R, Eliezer D (2015) Hydrogen trapping mechanism of different duplex stainless steels alloys. J Alloys Compd 644:280–286. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.04.176
Silverstein R, Sobol O, Boellinghaus T et al (2016) Hydrogen behavior in SAF 2205 duplex stainless steel. J Alloys Compd 659:2689–2695. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.184
Lee S, Lee J (1986) The trapping and transport phenomena of hydrogen in nickel. Metall Trans A 17:181–187
Turnbull A, Hutchings RB, Ferriss DH (1997) Modelling of thermal desorption of hydrogen from metals. Mater Sci Eng 238:317–328
Stampfer JF, Holley CE, Suttle JF (1960) The magnesium-hydrogen system. J Am Chem Soc 82:3504–3508. doi:10.1021/ja01499a006
Chen J, Ai M, Wang J et al (2009) Formation of hydrogen blister on AZ91 magnesium alloy during cathodic charging. Corros Sci 51:1197–1200. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2009.02.020
Chen J, Wang J, Han E et al (2008) States and transport of hydrogen in the corrosion process of an AZ91 magnesium alloy in aqueous solution. Corros Sci 50:1292–1305. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2008.01.028
Schober T (1981) The magnesium-hydrogen system: transmission electron-microscopy. Metall Trans A 12A:951–957. doi:10.1007/bf02643475
Ghali E (2011) Magnesium and magnesium alloys. In: Winston R (ed) Uhlig’s corrosion handbook, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 809–836
Smith WF, Hashemi J (2009) Foundation of materials science and engineering, Chap 8, 4th edn. pp 318–321
Turnbull A, Hutchings RB (1994) Analysis of hydrogen atom transport in a two-phase alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 177:161–171. doi:10.1016/0921-5093(94)90488-X
Eliezer D, Tal-Gutelmacher E, Cross CE, Boellinghaus T (2006) Hydrogen trapping in β-21S titanium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 421:200–207. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.01.067
Tal-Gutelmacher E, Eliezer D, Abramov E (2007) Thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS)—Application in quantitative study of hydrogen evolution and trapping in crystalline and non-crystalline materials. Mater Sci Eng A 445–446:625–631. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.09.089
Laine ESU (1978) A high-speed determination of the volume fraction of ferrite in austenitic stainless steel by EDXRD. J Phys F Met Phys 8:1343–1348. doi:10.1088/0305-4608/8/7/007
Chino Y, Nishihara D, Ueda T, Mabuchi M (2011) Effects of hydrogen on the mechanical properties of pure magnesium. Mater Trans 52:1123–1126. doi:10.2320/matertrans.MC201009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamilyan, M., Silverstein, R. & Eliezer, D. Hydrogen trapping and hydrogen embrittlement of Mg alloys. J Mater Sci 52, 11091–11100 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1268-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1268-2