Abstract
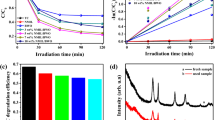
Bismuth oxychloride (BiOCl) with tunable structures and morphologies were successfully synthesized through a facile solvothermal method in water–methanol solution. Size and shape of BiOCl could be effectively tuned by adjusting the volume fraction of water in water–methanol solution. With the increasing water content, BiOCl grows along the c-axis [001] orientation, and the exposure of {001} facets also increases. In the case of 10 % water, dispersed BiOCl nanoplates with the size of 200 nm and the thickness of 40 nm were obtained instead of microspheres as obtained in pure methanol. These BiOCl nanoplates showed higher photocatalytic activity toward methyl orange (MO) than BiOCl microspheres and higher degradation activity for rhodamine B (RhB) than P25. The excellent photocatalytic activity of BiOCl nanoplates could be mainly attributed to its effective separation of electron–hole pairs, increased exposure of {001} facets, and reductions in size and thickness. And BiOCl nanoplates prepared with 15 % water exhibit promising oxygen reduction reaction performance in alkaline electrolyte (KOH) due to the increased exposure of {001} facets.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radisavljevic B, Radenovic A, Brivio J, Giacometti V, Kis A (2011) Single-layer MoS2 transistors. Nature Nanotech 6:147–150
Zhu YW, Murali ST, Stoller MD et al (2011) Carbon-based supercapacitors produced by activation of graphene. Science 332:1537
Feng J, Sun X, Wu CZ et al (2011) Metallic few-layered VS2 ultrathin nanosheets: high two-dimensional conductivity for in-plane supercapacitors. J Am Chem Soc 133:17832–17838
Sun YF, Sun ZH, Gao S et al (2012) Fabrication of flexible and freestanding zinc chalcogenide single layers. Nat Commun 3:1057
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Wang CH, Shao CL, Liu YC, Zhang LN (2008) Photocatalytic properties BiOCl and Bi2O3 nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Scr Mater 59:332–335
Zhang X, Ai ZH, Jia FL, Zhang LZ (2008) Generalized one-pot synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity of hierarchical BiOX (X = Cl, Br, I) nanoplate microspheres. J Phys Chem C 112:747–753
Charkin DO, Berdonosov PS, Dolgikh VA, Lightfoot P (2003) A reinvestigation of quaternary layered bismuth oxyhalides of the Sillén X1 type. J Solid State Chem 175:316–321
Ding LY, Wei RY, Chen H, Hu JC, Li JL (2015) Controllable synthesis of highly active BiOCl hierarchical microsphere self-assembled by nanosheets with tunable thickness. Appl Catal B 172–173:91–99
Cui ZK, Mi LW, Zeng DW (2013) Oriented attachment growth of BiOCl nanosheets with exposed 110 facets and photocatalytic activity of the hierarchical nanostructures. J Alloy Compd 549:70–76
Zhang KL, Liu CM, Huang FQ, Zheng C, Wang WD (2006) Study of the electronic structure and photocatalytic activity of the BiOCl photocatalyst. Appl Catal B 68:125–129
Xiong JY, Cheng G, Li GF, Qin F, Chen R (2011) Well-crystallized square-like 2D BiOCl nanoplates: mannitol-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and improved visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv 1:1542–1553
Bhawna Sarwan B, Pare AD Acharya (2014) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of nile blue dye in aqueous BiOCl suspensions. Appl Surf Sci 301:99–106
Wang WD, Huang FQ, Lin XP (2007) xBiOI−(1−x)BiOCl as efficientvisible-light-driven photocatalysts. Scr Mater 56:669–672
Xiao X, Zhang WD (2011) Hierarchical Bi7O9I3 micro/nano-architecture: facile synthesis, growth mechanism and high visible light photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv 1:1099–1105
Wei PY, Yang QL, Guo L (2009) Bismuth oxyhalide compounds as photocatalysts. Prog Chem 21:1734–1741
Yuan JL, Wang J, She YY et al (2014) BiOCl micro-assembles consisting of ultrafine nanoplates: a high performance electro-catalyst for air electrode of Al–air batteries. J Power Sources 263:37–45
Xiong JY, Cheng G, Qin F et al (2013) Tunable BiOCl hierarchical nanostructures for high-efficient photocatalysis under visible light irradiation. Chem Eng J 220:228–236
Cheng G, Xiong JY, Stadler FJ (2013) Facile template-free and fast refluxing synthesis of 3D desertrose-like BiOCl nanoarchitectures with superior photocatalytic activity. New J Chem 37:3207
Liu QC, Ma DK, Hu YY, Zeng YW, Huang SM (2013) Various bismuth oxyiodide hierarchical architectures: alcohothermal-controlled synthesis, photocatalytic activities, and adsorption capabilities for phosphate in water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:11927–11934
Zhang X, Wang XB, Wang LW et al (2014) Synthesis of a highly efficient BiOCl single-crystal nanodisk photocatalyst with exposing 001 facets. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:7766–7772
Hu JL, Fan WJ, Ye WQ, Huang CJ, Qiu XQ (2014) Insights into the photosensitivity activity of BiOCl under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B 158–159:182–189
Guan ML, Xiao C, Zhang J et al (2013) Vacancy associates promoting solar-driven photocatalytic activity of ultrathin bismuth oxychloride nanosheets. J Am Chem Soc 135:10411–10417
Jiang J, Zhao K, Xiao XY, Zhang LZ (2012) Synthesis and facet-dependent photoreactivity of BiOCl single-crystalline nanosheets. J Am Chem Soc 134:4473–4476
Sun DF, Wang TY, Xu YH, Li RX, Sato T (2015) Hierarchical bismuth oxychlorides constructed by porous nanosheets: preparation, growth mechanism, and application in photocatalysis. Mater Sci Semicond Process 3:666–677
Cui Y, Lieber CM (2001) Functional nanoscale electronic devices assembled using silicon nanowire building blocks. Science 29:851–853
Sun SH, Murray CB, Weller Dieter, Folks Liesl, Moser Andreas (2000) Monodisperse FePt nanoparticles and ferromagnetic FePt nanocrystal superlattices. Science 287:1989–1992
Hatzor A, Weiss PS (2001) Molecular rulers for scaling down nanostructures. Science 291:1019–1020
El-Sayed MA (2001) Some interesting properties of metals confined in time and nanometer space of different shapes. Acc Chem Res 34:257–264
Han JT, Huang YH, Wu XJ et al (2006) Tunable synthesis of bismuth ferrites with various morphologies. Adv Mater 18:2145–2148
Ye LQ, Zan L, Tian LH, Peng TY, Zhang JJ (2011) The 001 facets-dependent high photoactivity of BiOCl nanosheets. Chem Commun 47:6951–6953
Lei YQ, Wang GH, Song SY, Fan WQ, Zhang HJ (2009) Synthesis, characterization and assembly of BiOCl nanostructure and their photocatalytic properties. CrystEngComm 11:1857–1862
Zheng Y, Duan F, Chen MQ, Xie Yi (2010) Synthetic Bi2O2CO3 nanostructures: novel photocatalyst with controlled special surface exposed. J Mol Catal A 317:34–40
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51372113), the Specially Appointed Professors by Universities in Jiangsu Province (SPUJP-2012, China), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0733, China), the scientific research foundation for the Returned Overseas Students, and Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Hu, X., Zhu, H. et al. Insights into BiOCl with tunable nanostructures and their photocatalytic and electrochemical activities. J Mater Sci 51, 4342–4348 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9745-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9745-6