Abstract
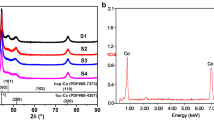
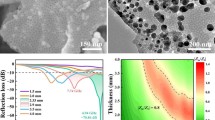
Metal cobalt is one of the most promising candidates for high-performance microwave absorbers due to its compatible dielectric loss and magnetic loss abilities. Rational design on the microstructure of metal cobalt became a popular way to upgrade its microwave absorption performance in the past decade, while much less attention has been paid to the electromagnetic functions derived from its different crystal structures. Herein, we report the microwave absorption of porous cobalt assemblies with varied composition of close-packed hexagonal (hcp) and face-centered cubic (fcc) phases. Electromagnetic analysis reveals that the change of phase composition can significantly impact the complex permittivity and complex permeability of metal cobalt, where hcp-cobalt favors high complex permittivity and fcc-cobalt produces high complex permeability. The optimum phase composition in these porous cobalt assemblies will promise well-matched characteristic impedance and good performance in strong reflection loss (−41.0 dB at 9.4 GHz) and wide response bandwidth (4.0–17.4 GHz over −10.0 dB). The enhanced microwave absorption is superior to many cobalt absorbers ever reported. It is believed that these results will provide a new pathway to the design and preparation of highly effective metal cobalt and cobalt-based composites as novel microwave absorbers in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puntes VF, Krishnan KM, Alivisatos AP (2001) Colloidal nanocrystal shape and size control: the case of cobalt. Science 291:2115–2117
Anagnostopoulou E, Grindi B, Lacroix LM, Ott F, Panagiotopoulos I, Viau G (2016) Dense arrays of cobalt nanorods as rare-earth free permanent magnets. Nanoscale 8:4020–4029
den Breejen JP, Sietsma JR, Friedrich H, Bitter JH, de Jong KP (2010) Design of supported cobalt catalysts with maximum activity for the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J Catal 270:146–152
Kumar VA, Gupta RK, Murty SN, Prasad AD (2016) Hot workability and microstructure control in Co20Cr15W10Ni cobalt-based superalloy. J Alloy Compd 676:527–541
Sachet E, Schubert WD, Mühlbauer G, Yukimura J, Kubo Y (2012) On the formation and in situ observation of thin surface layers of cobalt on sintered cemented carbides. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 31:96–108
Wang ZZ, Bi H, Wang PH, Wang M, Liu ZW, Shen L, Liu XS (2015) Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of self-assemblies composed of core–shell cobalt–cobalt oxide nanocrystals. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:3796–3801
Wen S, Zhao X, Liu Y, Cheng J, Li H (2014) Synthesis of hierarchical sword-like cobalt particles and their microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv 4:40456–40463
Shi XL, Cao MS, Yuan J, Fang XY (2009) Dual nonlinear dielectric resonance and nesting microwave absorption peaks of hollow cobalt nanochains composites with negative permeability. Appl Phys Lett 95:163108
Sun S, Murray CB (1999) Synthesis of monodisperse cobalt nanocrystals and their assembly into magnetic superlattices. J Appl Phys 85:4325–4330
Dinega DP, Bawendi MG (1999) A solution-phase chemical approach to a new crystal structure of cobalt. Angew Chem Int Edit 38:1788–1791
de PR Moreira I, Roldán A, Illas F (2010) Electronic and magnetic structure of bulk cobalt: the α, β, and ε-phases from density functional theory calculations. J Chem Phys 133:024701
Sort J, Surinach S, Munoz JS, Baró MD, Wojcik M, Jedryka E, Nadolski S, Sheludko N, Nogués J (2003) Role of stacking faults in the structural and magnetic properties of ball-milled cobalt. Phys Rev B 68:014421
Wang ZZ, Bi H, Wang M, Wang PH, Liu XS (2015) High microwave permittivity and resonance–antiresonance electromagnetic behaviors of flake-shaped cobalt microcrystals. Mater Chem Phys 159:173–177
Wang XL, Shi GM, Shi FN, Xu G, Qi YY, Li D, Zhang ZD, Zhang YJ, You HP (2016) Synthesis of hierarchical cobalt dendrites based on nanoflake self-assembly and their microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv 6:40844–40853
Wen SL, Liu Y, Zhao XC, Fan ZZ (2015) Synthesis, permeability resonance and microwave absorption of flake-assembled cobalt superstructure. J Magn Magn Mater 385:182–187
Liu T, Zhou PH, Xie JL, Deng LJ (2011) The hierarchical architecture effect on the microwave absorption properties of cobalt composites. J Appl Phys 110:033918
Wen SL, Liu Y, Zhao XC (2015) Facile chemical synthesis, electromagnetic response, and enhanced microwave absorption of cobalt powders with controllable morphologies. J Chem Phys 143:084707
He CZ, Qiu S, Wang XZ, Liu JR, Luan LQ, Liu W, Itoh M, Machida KI (2012) Facile synthesis of hollow porous cobalt spheres and their enhanced electromagnetic properties. J Mater Chem 22:22160–22166
Wang C, Han XJ, Zhang XL, Hu SR, Zhang T, Wang JY, Du YC, Wang XH, Xu P (2010) Controlled synthesis and morphology-dependent electromagnetic properties of hierarchical cobalt assemblies. J Phys Chem C 114:14826–14830
Wen SL, Liu Y, Zhao XC, Cheng JW, Li H (2014) Synthesis, dual-nonlinear magnetic resonance and microwave absorption properties of nanosheet hierarchical cobalt particles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:18333–18340
Ma F, Qin Y, Li YZ (2010) Enhanced microwave performance of cobalt nanoflakes with strong shape anisotropy. Appl Phys Lett 96:202507
Tong GX, Yuan JH, Wu WH, Hu Q, Qian HS, Li LC, Shen JP (2012) Flower-like Co superstructures: morphology and phase evolution mechanism and novel microwave electromagnetic characteristics. CrystEngComm 14:2071–2079
Wen SL, Liu Y, Zhao XC, Cheng JW (2014) Optimal microwave absorption of hierarchical cobalt dendrites enhanced by multiple dielectric and magnetic resonance. J Appl Phys 116:054310
Chen WB, Han MG, Deng LJ (2010) High frequency microwave absorbing properties of cobalt nanowires with transverse magnetocrystalline anisotropy. Physica B 405:1484–1488
Zhao HT, Zhang B, Zhang JS, Zhang LF, Han XJ, Xu P, Zhou Y (2010) Field-assisted synthesis and electromagnetic properties of aligned magnetic nanostructures by γ-irradiation induced reduction. J Phys Chem C 114:21214–21218
Wen SL, Liu Y, Zhao XC (2015) The hierarchical three-dimensional cobalt superstructure: controllable synthesis, electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption. Adv Powder Technol 26:1520–1528
Qiao ZA, Brown SS, Adcock J, Veith GM, Bauer JC, Payzant EA, Unocic RR, Dai S (2012) A topotactic synthetic methodology for highly fluorine-doped mesoporous metal oxides. Angew Chem Int Edit 124:2942–2947
Zhao HT, Du YC, Kang LL, Xu P, Du L, Sun ZH, Han XJ (2013) Precursor-directed synthesis of quasi-spherical barium ferrite particles with good dispersion and magnetic properties. CrystEngComm 15:808–815
Tong GX, Liu Y, Cui TT, Li YN, Zhao YT, Guan JG (2016) Tunable dielectric properties and excellent microwave absorbing properties of elliptical Fe3O4 nanorings. Appl Phys Lett 108:072905
Kong J, Wang F, Wan X, Liu J, Itoh M, Machida KI (2012) Template-free synthesis of Co nanoporous structures and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Mater Lett 78:69–71
Pujol O, Bowen P, Stadelmann PA, Hofmann H (2004) Growth and self-assembly of nanostructured CoC2O4·2H2O particles. J Phys Chem B 108:13128–13136
Zhou JH, He JP, Li GX, Wang T, Sun D, Ding XC, Zhao JQ, Wu SC (2010) Direct incorporation of magnetic constituents within ordered mesoporous carbon-silica nanocomposites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Phys Chem C 114:7611–7617
Du YC, Liu T, Yu B, Gao HB, Xu P, Wang JY, Wang XH, Han XJ (2012) The electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption of mesoporous carbon. Mater Chem Phys 135:884–891
Muñoz-Tabares JA, Bejtka K, Lamberti A, Garino N, Bianco S, Quaglio M, Pirri CF, Chiodoni A (2016) Nanostructural evolution of one-dimensional BaTiO3 structures by hydrothermal conversion of vertically aligned TiO2 nanotubes. Nanoscale 8:6866–6876
Pun GP, Mishin Y (2012) Embedded-atom potential for hcp and fcc cobalt. Phys Rev B 86:134116
Ogo SH, Shimizu T, Nakazawa Y, Mukawa K, Mukai D, Sekine Y (2015) Steam reforming of ethanol over K promoted Co catalyst. Appl Catal A 495:30–38
Kong LT, Zhang RF, Li ZC, Liu BX (2003) Magnetic properties of Co and Co-Ag alloys in equilibrium/nonequilibrium structures studied by ab initio calculations. Phys Rev B 68:134446
Qiang R, Du YC, Chen DT, Ma WJ, Wang Y, Xu P, Ma J, Zhao HT, Han XJ (2016) Electromagnetic functionalized Co/C composites by in situ pyrolysis of metal-organic frameworks (ZIF-67). J Alloy Compd 681:384–393
Leslie-Pelecky DL, Rieke RD (1996) Magnetic properties of nanostructured materials. Chem Mater 8:1770–1783
Du YC, Liu WW, Qiang R, Wang Y, Han XJ, Ma J, Xu P (2014) Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core-shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:12997–13006
Wen B, Cao MS, Hou ZL, Song WL, Zhang L, Lu MM, Jin HB, Fang XY, Wang WZ, Yuan J (2013) Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 65:124–139
Wang Y, Du YC, Qiang R, Tian CH, Xu P, Han XJ (2016) Interfacially engineered sandwich-like rGO/carbon microspheres/rGO composite as an efficient and durable microwave absorber. Adv Mater Interfaces 3:1500684
Tian CH, Du YC, Xu P, Qiang R, Wang Y, Ding D, Xue JL, Ma J, Zhao HT, Han XJ (2015) Constructing uniform core–shell PPy@PANI composites with tunable shell thickness toward enhancement in microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:20090–20099
She W, Bi H, Wen ZW, Liu QH, Zhao XB, Zhang J, Che RC (2016) Tunable microwave absorption frequency by aspect ratio of hollow polydopamine@α-MnO2 microspindles studied by electron holography. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:9782–9789
Liu XG, Li B, Geng DY, Cui WB, Yang F, Xie ZG, Kang DJ, Zhang ZD (2009) (Fe, Ni)/C nanocapsules for electromagnetic-wave-absorber in the whole Ku-band. Carbon 47:470–474
Liu J, Cao WQ, Jin HB, Yuan J, Zhang DQ, Cao MS (2015) Enhanced permittivity and multi-region microwave absorption of nanoneedle-like ZnO in the X-band at elevated temperature. J Mater Chem C 3:4670–4677
Lv HL, Liang XH, Cheng Y, Zhang HQ, Tang DM, Zhang BS, Ji GB, Du YW (2015) Coin-like α-Fe2O3@CoFe2O4 core-shell composites with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:4744–4750
Qiang R, Du YC, Zhao HT, Wang Y, Tian CH, Li ZG, Han XJ, Xu P (2015) Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption. J Mater Chem A 3:13426–13434
Ohlan A, Singh K, Chandra A, Dhawan SK (2010) Microwave absorption behavior of core-shell structured poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxy thiophene)-barium ferrite nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:927–933
Lu B, Dong XL, Huang H, Zhang XF, Zhu XG, Lei JP, Sun JP (2008) Microwave absorption properties of the core/shell-type iron and nickel nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 320:1106–1111
Wu MZ, Zhang YD, Hui S, Xiao TD, Ge SH, Hines WA, Budnick JI, Taylor GW (2002) Microwave magnetic properties of Co50/(SiO2)50 nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 80:4404–4406
Liu QH, Cai Q, Zhao XB, Bi H, Wang C, Wu DS, Che RC (2015) Insights into size-dominant magnetic microwave absorption properties of CoNi microflowers via off-axis electron holography. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:4233–4240
Cui CK, Du YC, Li TH, Zheng XY, Wang XH, Han XJ, Xu P (2012) Synthesis of electromagnetic functionalized Fe3O4 microspheres/polyaniline composites by two-step oxidative polymerization. J Phys Chem B 116:9523–9531
Cao MS, Qin RR, Qiu CJ, Zhu J (2003) Matching design and mismatching analysis towards radar absorbing coatings based on conducting plate. Mater Des 24:391–396
Ma Z, Zhang Y, Cao CT, Yuan J, Liu JB (2011) Attractive microwave absorption and the impedance match effect in zinc oxide and carbonyl iron composite. Physica B 406:4620–4624
Ma Z, Liu QF, Yuan J, Wang ZK, Cao CT, Wang JB (2012) Analyses on multiple resonance behaviors and microwave reflection loss in magnetic Co microflowers. Phys Status Solidi B 249:575–580
Li JG, Huang JJ, Qin Y, Ma F (2007) Magnetic and microwave properties of cobalt nanoplatelets. Mater Sci Eng B 138:199–204
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21371039, 21571043, and 21676065) and Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (B201405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Du, Y., Guo, D. et al. Precursor-directed synthesis of porous cobalt assemblies with tunable close-packed hexagonal and face-centered cubic phases for the effective enhancement in microwave absorption. J Mater Sci 52, 4399–4411 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0687-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0687-9