Abstract
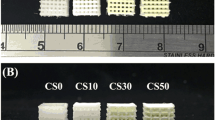
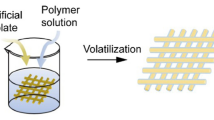
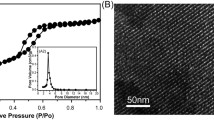
In the study, we developed hierarchical composite scaffolds by 3D printing technique with mesoporous CaSiO3 containing controlled amounts of Ce substitution in Ca–Si system. The scaffolds were porous with 3D interconnected large pores (size ~400 μm) and an overall porosity above 70 %, combined with a relative high compressive strength (~7 MPa). These properties are essential for enhancing bone ingrowth in tissue engineering. The in vitro biological properties of apatite formation, cell proliferation, and differentiation were characterized on CeO2-MCS scaffolds and MCS scaffolds. Results indicated that CeO2-MCS scaffolds induced similar apatite deposition and cell attachment of human bone marrow stromal cells. In addition, CeO2-MCS scaffolds enhanced expression of alkaline phosphatase, osteogenesis genes (bone morphogenetic protein-2, collagen type I), and angiogenesis gene markers (fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor), compared to that for MCS scaffolds. Therefore, the 3D-printed CeO2-MCS scaffolds showed the potential of enhanced osteogenic activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu CT, Chang J (2012) Mesoporous bioactive glasses: structure characteristics, drug/growth factor delivery and bone regeneration application. Interface Focus 2:292. doi:10.1098/rsfs.2011.0121
Vallet-Regi M, Ruiz-Hernandez E (2011) Bioceramics: from bone regeneration to cancer nanomedicine. Adv Mater 23:5177. doi:10.1002/adma.201101586
Xia W, Chang J (2008) Preparation and the phase transformation behavior of amorphous mesoporous calcium silicate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 108:345. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.04.013
Li X, Shi JL, Zhu YF et al (2007) A template route to the preparation of mesoporous amorphous calcium silicate with high in vitro bone-forming bioactivity. J Biomed Mater Res B 83B:431. doi:10.1002/Jbm.B.30813
Fan Y, Huang SS, Jiang JH et al (2011) Luminescent, mesoporous, and bioactive europium-doped calcium silicate (MCS: Eu3 +) as a drug carrier. J Colloid Interface Sci 357:280. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.01.109
Lu BQ, Zhu YJ, Ao HY, Qi C, Chen F (2012) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic iron oxide/calcium silicate mesoporous nanocomposites as a promising vehicle for drug delivery. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 4:6968. doi:10.1021/Am3021284
Wu CT, Chang J, Fan W (2012) Bioactive mesoporous calcium-silicate nanoparticles with excellent mineralization ability, osteostimulation, drug-delivery and antibacterial properties for filling apex roots of teeth. J Mater Chem 22:16801. doi:10.1039/C2jm33387b
Zhu HL, Wu BW, Feng XX, Chen JY (2011) Preparation and characterization of bioactive mesoporous calcium silicate-silk fibroin composite films. J Biomed Mater Res B 98B:330. doi:10.1002/Jbm.B.31856
Wei J, Chen FP, Shin JW et al (2009) Preparation and characterization of bioactive mesoporous wollastonite–Polycaprolactone composite scaffold. Biomaterials 30:1080. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.10.046
Iimori Y, Kameshima Y, Okada K, Hayashi S (2005) Comparative study of apatite formation on CaSiO3 ceramics in simulated body fluids with different carbonate concentrations. J Mater Sci 16:73. doi:10.1007/s10856-005-6449-x
Zreiqat H, Ramaswamy Y, Wu CT et al (2010) The incorporation of strontium and zinc into a calcium-silicon ceramic for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 31:3175. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.024
Zhu YF, Zhu M, He X, Zhang JH, Tao CL (2013) Substitutions of strontium in mesoporous calcium silicate and their physicochemical and biological properties. Acta Biomater 9:6723. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2013.01.021
Wu CT, Ramaswamy Y, Kwik D, Zreiqat H (2007) The effect of strontium incorporation into CaSiO3 ceramics on their physical and biological properties. Biomaterials 28:3171. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.04.002
Chen XC, Ou J, Wei Y, Huang ZB, Kang YQ, Yin GF (2010) Effect of MgO contents on the mechanical properties and biological performances of bioceramics in the MgO-CaO-SiO2 system. J Mater Sci 21:1463. doi:10.1007/s10856-010-4025-5
Zhang JC, Liu CL, Li YP et al (2010) Effect of cerium ion on the proliferation, differentiation and mineralization function of primary mouse osteoblasts in vitro. J Rare Earth 28:138. doi:10.1016/S1002-0721(09)60067-3
Leonelli C, Lusvardi G, Malavasi G, Menabue L, Tonelli M (2003) Synthesis and characterization of cerium-doped glasses and in vitro evaluation of bioactivity. J Non-Cryst Solids 316:198. doi:10.1016/S0022-3093(02)01628-9
Salinas AJ, Shruti S, Malavasi G, Menabue L, Vallet-Regi M (2011) Substitutions of cerium, gallium and zinc in ordered mesoporous bioactive glasses. Acta Biomater 7:3452. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2011.05.033
Shruti S, Salinas AJ, Malavasi G et al (2012) Structural and in vitro study of cerium, gallium and zinc containing sol-gel bioactive glasses. J Mater Chem 22:13698. doi:10.1039/C2jm31767b
Shruti S, Salinas AJ, Lusvardi G, Malavasi G, Menabue L, Vallet-Regi M (2013) Mesoporous bioactive scaffolds prepared with cerium-, gallium- and zinc-containing glasses. Acta Biomater 9:4836. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2012.09.024
Zhang JH, Zhu YF (2014) Synthesis and characterization of CeO2-incorporated mesoporous calcium-silicate materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 197:244. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.06.018
Hollister SJ (2005) Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Nat Mater 4:518. doi:10.1038/Nmat1421
Yoo D (2013) New paradigms in hierarchical porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Mat Sci Eng C 33:1759. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2012.12.092
Vallet-Regi M (2010) Evolution of bioceramics within the field of biomaterials. C R Chim 13:174. doi:10.1016/j.crci.2009.03.004
Gerhardt LC, Boccaccini AR (2010) Bioactive glass and glass-ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Materials 3:3867. doi:10.3390/Ma3073867
Mourino V, Boccaccini AR (2010) Bone tissue engineering therapeutics: controlled drug delivery in three-dimensional scaffolds. J R Soc Interface 7:209. doi:10.1098/rsif.2009.0379
Manzano M, Vallet-Regi M (2010) New developments in ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. J Mater Chem 20:5593. doi:10.1039/B922651f
Zhang JH, Zhao SC, Zhu YF et al (2014) Three-dimensional printing of strontium-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater 10:2269. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2014.01.001
Rutz AL, Hyland KE, Jakus AE, Burghardt WR, Shah RN (2015) A multimaterial bioink method for 3D printing tunable, cell-compatible hydrogels. Adv Mater 27:1607. doi:10.1002/adma.201405076
Nichol JW, Koshy ST, Bae H, Hwang CM, Yamanlar S, Khademhosseini A (2010) Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 31:5536. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.064
Zhao SC, Zhu M, Zhang JH et al (2014) Three dimensionally printed mesoporous bioactive glass and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B 2:6106. doi:10.1039/C4tb00838c
Zhang JH, Zhao SC, Zhu M et al (2014) 3D-printed magnetic Fe3O4/MBG/PCL composite scaffolds with multifunctionality of bone regeneration, local anticancer drug delivery and hyperthermia. J Mater Chem B 2:7583. doi:10.1039/C4tb01063a
Nair LS, Laurencin CT (2007) Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog Polym Sci 32:762. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.05.017
Matsubara T, Suardita K, Ishii M et al (2005) alveolar bone marrow as a cell source for regenerative medicine: differences between alveolar and iliac bone marrow stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res 20:399. doi:10.1359/Jbmr.041117
Yun HS, Kim SE, Hyeon YT (2007) Design and preparation of bioactive glasses with hierarchical pore networks. Chem Commun 21:2139–2141. doi:10.1039/B702103h
Wang K (1997) The analogy in chemical and biological behavior between non-essential ions compared with essential ions. South Afr J Chem 50:232
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 51302170), the Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (14YZ085), the Program for Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning, the Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (14YZ085), and the Hujiang Foundation of China (B14006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Min Zhu and Jianhua Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Zhang, J., Zhao, S. et al. Three-dimensional printing of cerium-incorporated mesoporous calcium-silicate scaffolds for bone repair. J Mater Sci 51, 836–844 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9406-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9406-1