Abstract
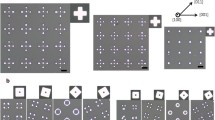
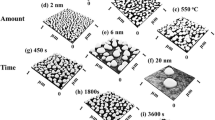
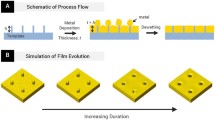
In this work we report on the formation of self-organized and multimodal sized patterned arrays of Au and Ag nanoparticles on SiO2 surface exploiting the thickness-dependent solid-state dewetting properties of template-confined deposited nanoscale films. In this approach, the Au and Ag surface pattern order, on the SiO2 substrate, is established by the template confined deposition on a micrometric scale, while the solid-state dewetting phenomenon is induced by thermal processes (below the Au and Ag melting temperature). The deposited films have not an uniform thickness. They, instead, present a controlled thickness due to shadowing mask effects during depositions. Such an inhomogeneity can be further controlled by changing the deposition angle. After the dewetting process, scanning electron microscopy analyses allowed us to correlate the mean diameter 〈D〉 and spacing 〈s〉 of the formed nanoparticles by the thickness h of the deposited films. Despite the dewetting process of the Au and Ag films occurs in the solid state, relations describing the evolution of 〈D〉 and 〈s〉 with 〈h〉 typical of the linear hydrodynamic spinodal dewetting process of liquid films, 〈D〉 ∝ h 5/3 and 〈s〉 ∝ h 2, were verified within a 20 % experimental error. As a consequence we call this process “pseudo-spinodal dewetting”.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Somorjai GA (2010) Nanoscale advances in catalysis and energy applications. Nano Lett 10:2289–2295
Mahmoud MA, Saira F, El-Sayed MA (2010) Experimental evidence for the nanocage effect in catalysis with hollow nanoparticles. Nano Lett 10:3764–3769
Zeng J, Zhang Q, Chen J, Xia Y (2010) A comparison study of the catalytic properties of Au-based nanocages, nanoboxes, and nanoparticles. Nano Lett 10:30–35
Hashmi ASK (2010) Homogeneous gold catalysis beyond assumptions and proposals—characterized intermediates. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:5232–5241
Ko H, Singamaneni S, Tsukruk VV (2008) Nanostructured surfaces and assemblies as SERS media. Small 4:1576–1599
Tripp RA, Dluhy RA, Zhao Y (2008) Novel nanostructures for SERS biosensing. Nano Today 3:31–37
Smith WE (2008) Practical understanding and use of surface enhanced Raman scattering/surface enhanced resonance Raman scattering in chemical and biological analysis. Chem Soc Rev 37:955–964
Stewart ME, Anderton CR, Thompson LB, Maria J, Gray SK, Rogers JA, Nuzzo RG (2008) Nanostructured plasmonic sensors. Chem Rev 108:494–521
Hong AJ, Liu CC, Wang Y, Kim J, Xiu FX, Ji SX, Zou J, Nealey PF, Wang KL (2010) Metal nanodot memory by self-assembled block copolymer lift-off. Nano Lett 10:224–229
Conoci S, Petralia S, Samori P, Raymo FM, Bella SD, Sortino S (2006) Optically transparent, ultrathin Pt films as versatile metal substrates for molecular optoelectronics. Adv Funct Mater 16:1425–1432
Giljohann DA, Seferos DS, Daniel WL, Massich MD, Patel PC, Mirkin CA (2010) Gold nanoparticles for biology and medicine. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:3280–3294
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer, New York
Akimov YA, Koh WS (2010) Resonant and nonresonant plasmonic nanoparticle enhancement for thin-film silicon solar cells. Nanotechnology 21:235201
Qu D, Liu F, Yu J, Xie W, Xu Q, Li X, Huang Y (2011) Plasmonic core-shell gold nanoparticle enhanced optical absorption in photovoltaic devices. Appl Phys Lett 98:113119
Yu DP, Xing YJ, Hang QL, Yan HF, Xu J, Xi ZH, Feng SQ (2001) Controlled growth of oriented amorphous silicon nanowires via a solid-liquid-solid (SLS) mechanism. Phys E 9:305–309
Chowalla M, Teo KBK, Ducati C, Rupesinghe NL, Amaratunga GAJ, Ferrari AC, Roy D, Robertson J, Milne WI (2001) Growth process conditions of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes using plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. J Appl Phys 90:5308–5317
Yoon YJ, Bae JC, Baik HK, Cho SJ, Lee SJ, Song KM, Myung NS (2002) Nucleation and growth control of carbon nanotubes in CVD process. Phys B 323:318–320
Kwon JY, Yoon TS, Kim KB, Min SH (2003) Comparison of the agglomeration behavior of Au and Cu films sputter deposited on silicon dioxide. J Appl Phys 93:3270–3278
Liu H, Cheng G, Zheng R, Zhao Y, Liang C (2008) Effects of the restructuring of Fe catalyst films on chemical vapor deposition of carbon nanotubes. Surf Coat Technol 202:3157–3163
Ruffino F, Torrisi V, Marletta G, Grimaldi MG (2011) Atomic force microscopy investigation of the kinetic growth mechanisms of sputtered nanostructured Au film on mica: towards a nanoscale morphology control. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:112
Ohring M (1992) The materials science of thin films. Academic Press, New York
Thompson CV (2012) Solid-state dewetting of thin films. Annu Rev Mater Res 42:399–434
Tesler AB, Maoz BM, Feldman Y, Vaskevich A, Rubinstein I (2013) Solid-state thermal dewetting of just-percolated gold films evaporated on glass: development of the morphology and optical properties. J Phys Chem C 117:11337–11346
Luber EJ, Olsen BC, Ophus C, Mitlin D (2010) Solid-state dewetting mechanisms of ultrathin Ni films revealed by combining in situ time resolved differential reflectometry monitoring and atomic force microscopy. Phys Rev B 82:85407
Müller CM, Spolenak R (2013) Dewetting of Au and AuPt alloy films: a dewetting zone model. J Appl Phys 113:094301
Giermann AL, Thompson CV (2005) Solid-state dewetting for ordered arrays of crystallographically oriented metal particles. Appl Phys Lett 86:121903
Oh YJ, Ross CA, Jung YS, Wang Y, Thompson CV (2009) Cobalt nanoparticle arrays made by templated solid-state dewetting. Small 5:860–865
Kim D, Giermann AL, Thompson CV (2009) Solid-state dewetting of patterned thin films. Appl Phys Lett 95:251903
Ye J, Thompson CV (2010) Regular pattern formation through the retraction and pinch-off of edges during solid-state dewetting of patterned single crystal films. Phys Rev B 82:193408
Ye J, Thompson CV (2011) Templated solid-state dewetting to controllably produce complex patterns. Adv Mater 23:1567–1571
Jiran E, Thompson CV (1990) Capillary instabilities in thin films. J Electr Mater 19:1153–1160
Jiran E, Thompson CV (1992) Capillary instabilities in thin, continuous films. Thin Solid Films 208:23–28
Wang D, Ji R, Schaaf P (2011) Formation of precise 2D Au particle arrays via thermally induced dewetting on pre-patterned substrates. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 2:318–326
Wang D, Schaaf P (2012) Thermal dewetting of thin Au films deposited onto line-patterned substrates. J Mater Sci 47:1605–1608
Ruffino F, Grimaldi MG (2013) Template-confined dewetting of Au and Ag nanoscale films on mica substrate. Appl Surf Sci 270:697–706
Ruffino F, Grimaldi MG (2013) Formation of patterned arrays of Au nanoparticles on SiC surface by template confined dewetting of normal and oblique deposited nanoscale films. Thin Solid Films 536:99–110
de Gennes PG (1985) Wetting: statics and dynamics. Rev Mod Phys 57:827–863
Geoghegan M, Krausch G (2003) Wetting at polymer surfaces and interfaces. Prog Polym Sci 28:261–302
Müller-Buschbaum P (2003) Dewetting and pattern formation in thin polymer films as investigated in real and reciprocal space. J Phys Condens Matter 15:R1549–R1582
Le F, Brandl DW, Urzhumov YA, Wang H, Kundu J, Halas NJ, Aizpurua J, Nordlander P (2008) Metallic nanoparticle arrays: a common substrate for both surface-enhanced raman scattering and surface-enhanced infrared absorption. ACS Nano 2:707–718
Lukyanchuk B, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9:707–715
Choe SY, Krauss PR, Renstrom PJ (1996) Imprint lithography with 25-nanometer resolution. Science 272:85–87
Joo J, Chow BY, Jacobson JM (2006) Nanoscale patterning on insulating substrates by critical energy electron beam lithography. Nano Lett 6:2021–2025
Salaita K, Wang Y, Fragala J, Vega RA, Liu C, Mirkin CA (2006) Massively parallel dip-pen nanolithography with 55000-pen two-dimensional arrays. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:7220–7223
Choi Y, Hong S, Lee LP (2009) Shadow overlap ion-beam lithography for nanoarchitectures. Nano Lett 9:3726–3731
Pazos-Perez N, Ni W, Schweikart A, Alvarez-Puebla RA, Fery A, Liz-Marzan LM (2010) Highly uniform SERS substrates formed by wrinkle-confined drying of gold colloids. Chem Sci 1:174–178
Trice J, Thomas D, Favazza C, Sureshkumar R, Kalyanaraman R (2007) Pulsed-laser-induced dewetting in nanoscopic metal films: theory and experiments. Phys Rev B 75:235439
Burger GJ, Smulders EJT, Berenschot JW, Lammerink TSJ, Fluitman JHJ, Imai S (1996) High-resolution shadow-mask patterning in deep holes and its application to an electrical wafer feed-through. Sens Actuators 54:669–673
Egger S, Ilie A, Fu Y, Chongsathien J, Kang DY, Welland ME (2005) Dynamic shadow mask technique: a universal tool for nanoscience. Nano Lett 5:15–20
Robbie K, Sit JC, Brett MJ (1998) Advanced techniques for glancing angle deposition. J Vac Sci Technol B 16:1115–1122
Robbie K, Beydaghyan G, Brown T, Dean C, Adams J, Buzea C (2004) Ultrahigh vacuum glancing angle deposition system for thin films with controlled three-dimensional nanoscale structure. Rev Sci Instr 75:1089–1097
Ruffino F, Canino A, Grimaldi MG, Giannazzo F, Bongiorno C, Roccaforte F, Raineri V (2007) Self-organization of gold nanoclusters on hexagonal SiC and SiO2 surfaces. J Appl Phys 101:064306
Wenzel T, Bosbach J, Stietz F, Träger F (1999) In situ determination of the shape of supported silver clusters during growth. Surf Sci 432:257–264
Ye J (2011) Solid state dewetting of continuous and patterned single crystal Ni thin films. http://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/69671.
Mullins WW (1959) Flattening of a nearly plane solid surface due to capillarity. J Appl Phys 30:77–83
Bollinne C, Cuenot S, Nysten B, Jonas AM (2003) Spinodal-like dewetting of thermodynamically-stable thin polymer films. Eur Phys J E 12:389–396
Wensink KD, Jérôme B (2002) Dewetting induced by density fluctuations. Langmuir 18:413–416
Sharma A, Mittal J, Verma R (2002) Instability and dewetting of thin films induced by density variations. Langmuir 18:10213–10220
Wasa K, Kitabatake M, Adachi H (2004) Thin film materials technology-sputtering of compound materials. William Andrew Publishing, Norwich
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Italian projects PON01_01725 “Nuove Tecnologie Fotovoltaiche per Sistemi Intelligenti Integrati in Edifici”, PON02_00355_3391233 “ENERGETIC”, and by the EU project Grant agreement 316082 “WATER”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruffino, F., Grimaldi, M.G. Self-organized patterned arrays of Au and Ag nanoparticles by thickness-dependent dewetting of template-confined films. J Mater Sci 49, 5714–5729 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8290-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8290-4